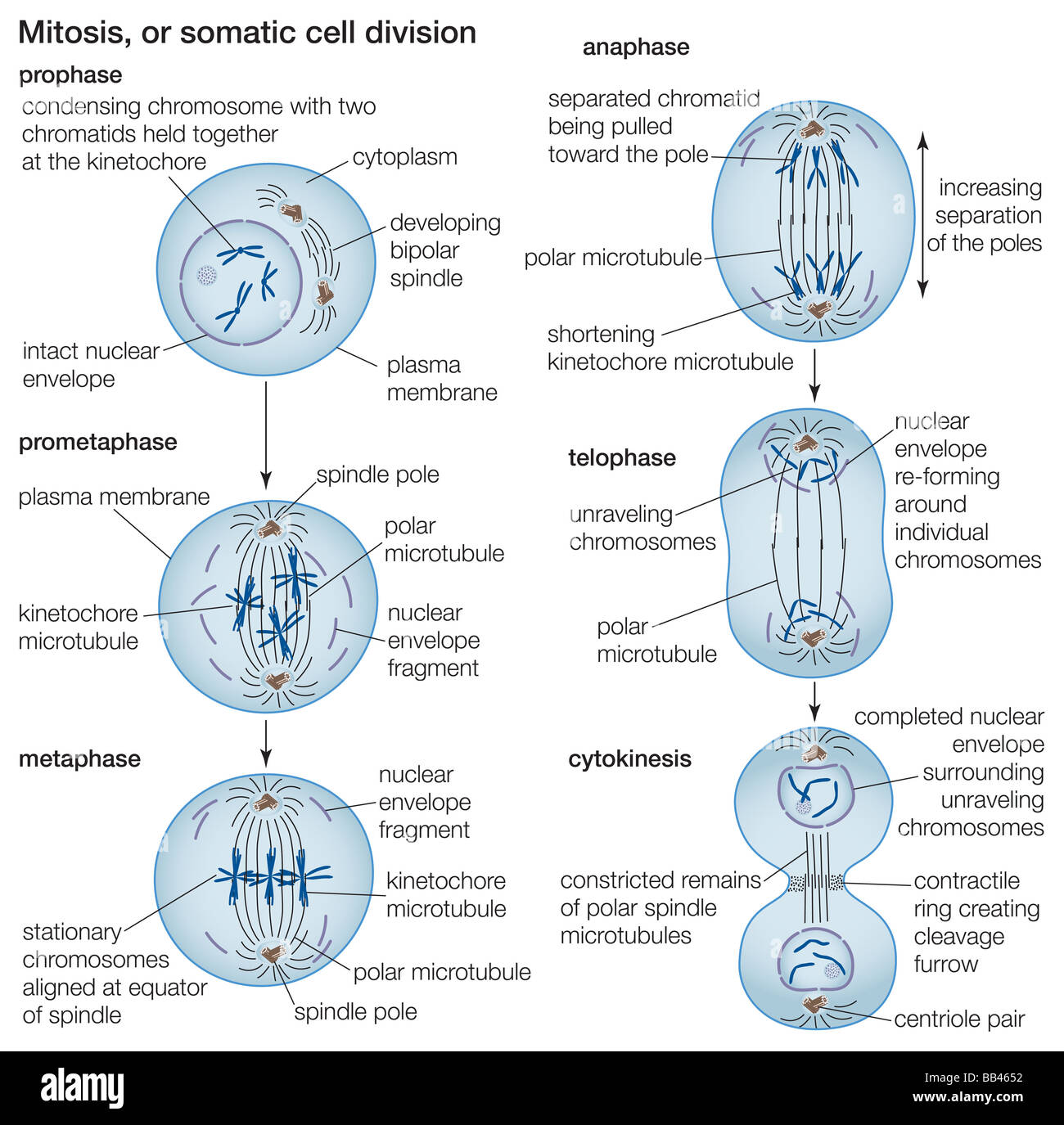
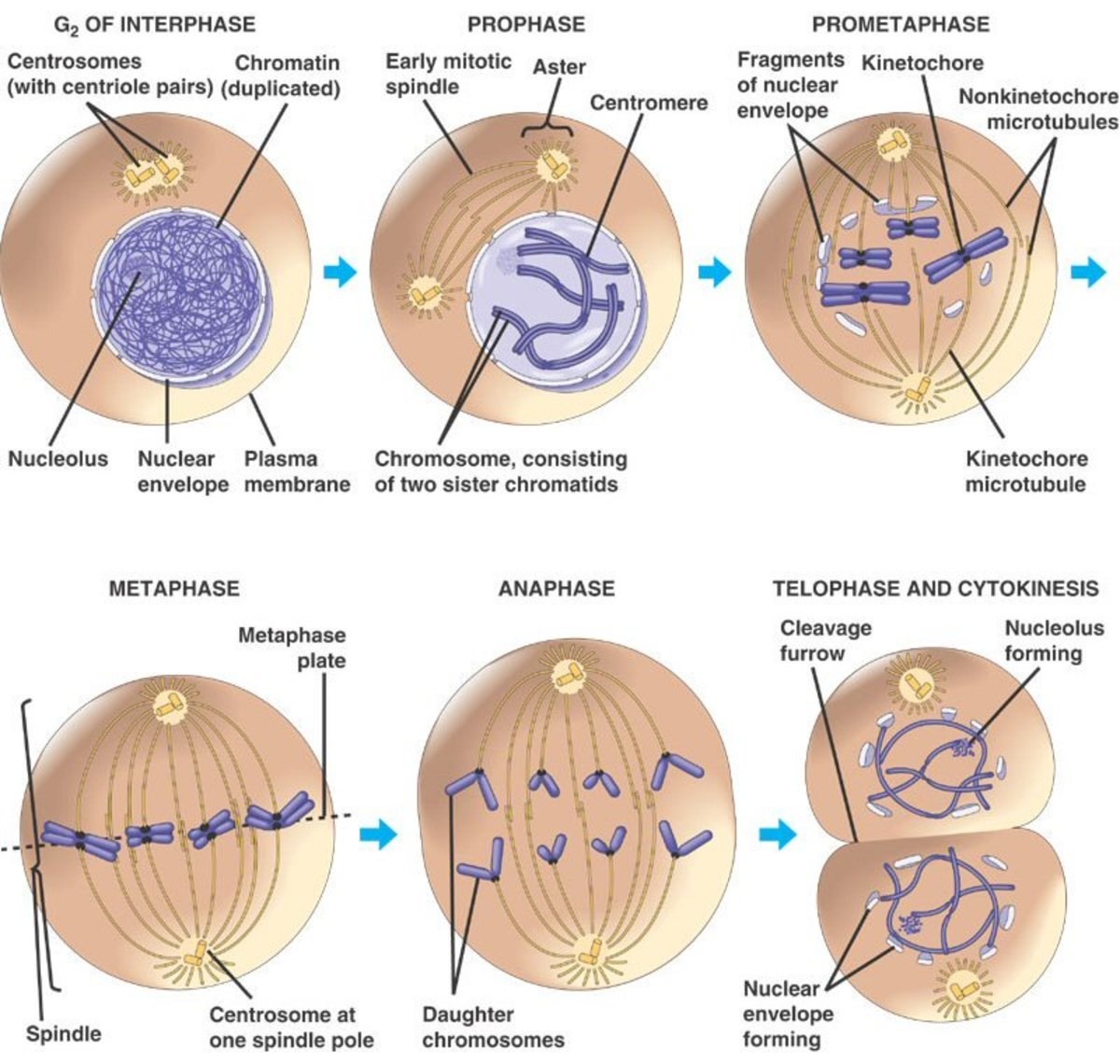
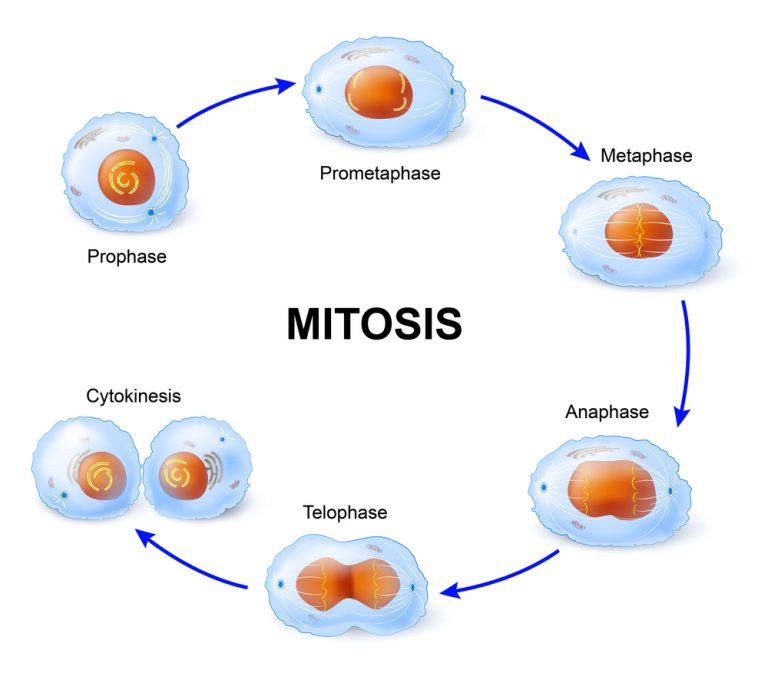
Cell Division Drawing
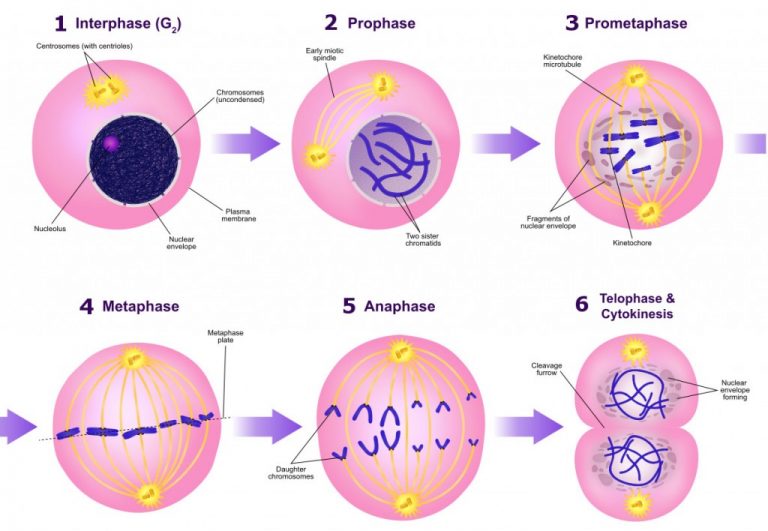
Cell Division Drawing - It will also help you understand the concept of how do cell. Learn more about cell cycle control, cancer cells, and stem cells. It will also help you understand the concept of how do cell multiply and genetic. One of the key differences in mitosis is a single cell divides into two cells that are replicas of each other and have the same number of chromosomes. Mitosis consists of four basic phases:
[do cells always grow before they divide?] s phase. Mitosis consists of four basic phases: The difference is that each species has its own set number of chromosomes. During these activities you will demonstrate your understanding of cell division by identifying and drawing various stages of these events as well as answering questions about each. G1 is the period after cell division, and before the start of dna replication. Web illustration of an uncoiled and coiled snake the basic construction of chromosomes (made of chromatin) and structure (long but scrunched up) is the same in all animals. Set of brochure cover design layouts with abstract geometric.
Cell Division Mitosis and Meiosis Ask A Biologist
The difference is that each species has its own set number of chromosomes. Identify and draw a cell in each of the four stages of mitosis in the onion slide. Mitosis diagram showing the different.
Mitosis Cell Division
Web during mitosis, chromosomes become attached to the structure known as the mitotic spindle. Web mitosis is the process of cell division in which one cell gives rise to two genetically identical daughter cells, resulting.
Cell Division
Web representing the dynamic nature of biological processes is a challenge. Web the chromosomes begin to decondense and return to their “stringy” form. This involved a series of group drawing labs, one. The number of.
Cell Division Types, Stages & Processes Plantlet
Cell division is the driving process of reproduction at the cellular level. Web i am demonstrating the colorful diagram of mitosis / phases of mitosis (cell division) step by step which you can draw very.
Understand the Stages of Mitosis and Cell Division
Web mitosis is the division of a cell into two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. Web mitosis is the process of cell division in which one cell gives rise to.
The process of cell division by mitosis Stock Photo Alamy
During these activities you will demonstrate your understanding of cell division by identifying and drawing various stages of these events as well as answering questions about each. Identify and draw a cell in each of.
Stages of the Cell Cycle Mitosis (Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase
Learn more about cell cycle control, cancer cells, and stem cells. This involved a series of group drawing labs, one. Cell division is the driving process of reproduction at the cellular level. During these activities.
How Does Cell Division Work A Step By Step Process
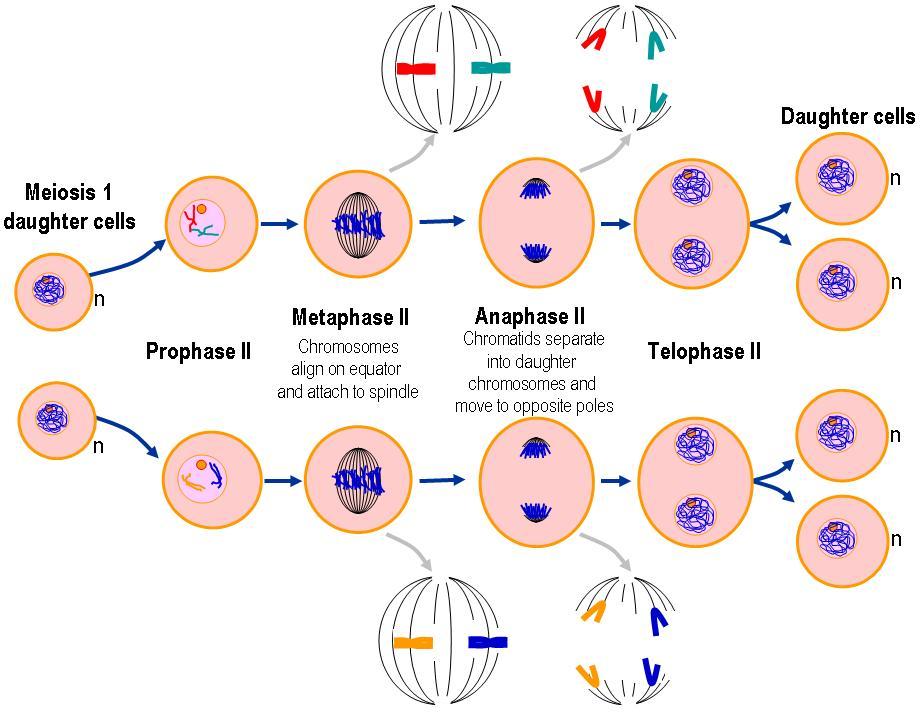
The second one is meiosis, which divides into four haploid daughter cells. It will also help you understand the concept of how do cell. If they're healthy cells, they divide in a carefully controlled way,.
Cell Division CK12 Foundation
Mitosis diagram showing the different stages of mitosis G1 is the period after cell division, and before the start of dna replication. Web i am demonstrating the colorful diagram of meiosis (cell division) step by.
Biology 2e, The Cell, Cell Reproduction, The Cell Cycle OpenEd CUNY
Mitosis diagram showing the different stages of mitosis During g 1 phase, also called the first gap phase, the cell grows physically larger, copies organelles, and makes the molecular building blocks it will need in.
Cell Division Drawing Web the role of mitosis in the cell cycle is to replicate the genetic material in an existing cell—known as the “parent cell”—and distribute that genetic material to two new cells, known as “daughter cells.” in order to pass its genetic material to the two new daughter cells, a parent cell must undergo cell division, or mitosis. Most eukaryotic cells divide in a manner where the ploidy or the number of chromosomes remains the same, except in the case of germ cells where the number of chromosomes is halved. Depending on the type of cell, there are two ways cells divide—mitosis and meiosis. Web the chromosomes begin to decondense and return to their “stringy” form. Web mitosis is the division of a cell into two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell.

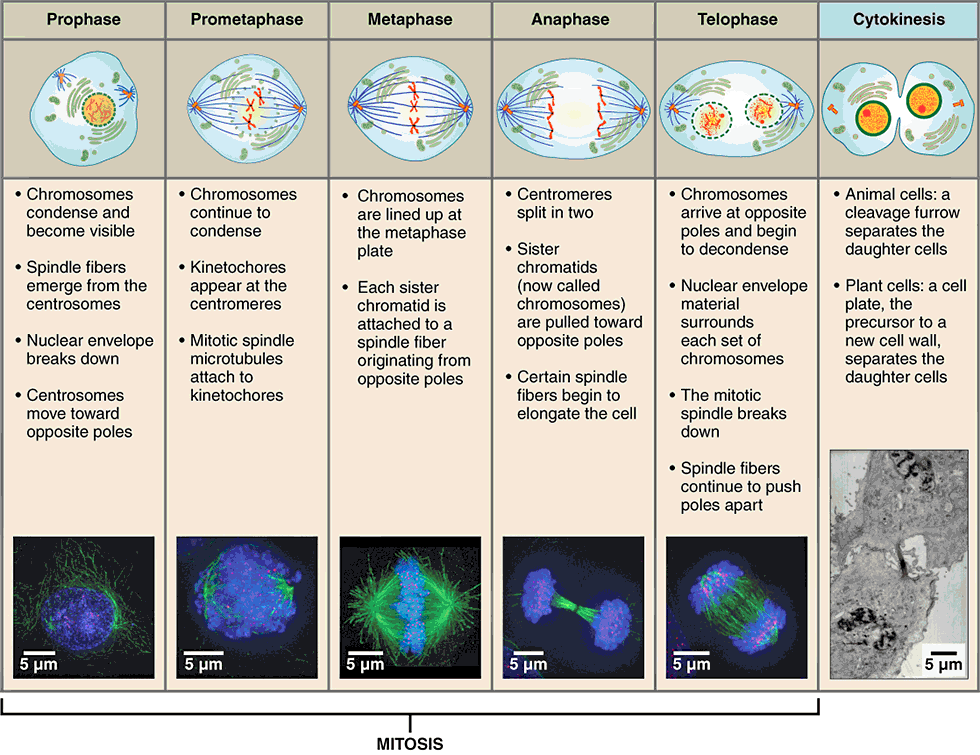

/GettyImages-5304586361-59dfd070845b3400116b5d8b.jpg)