Draw The Hydrological Cycle
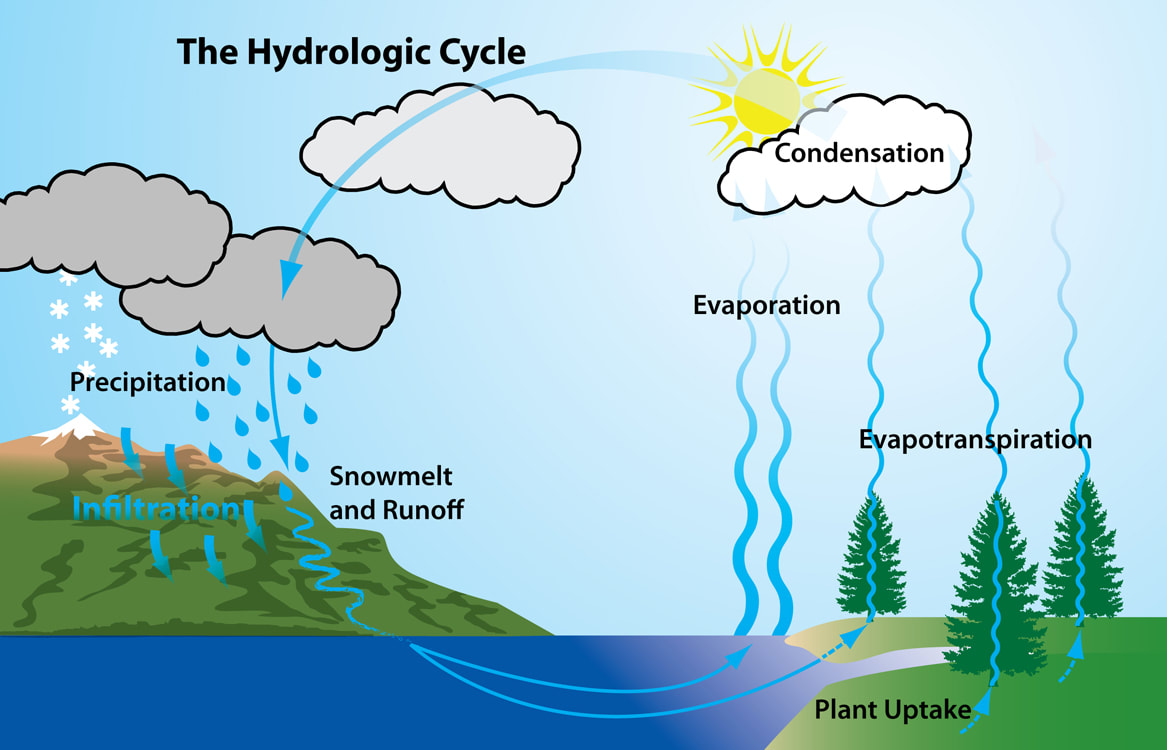
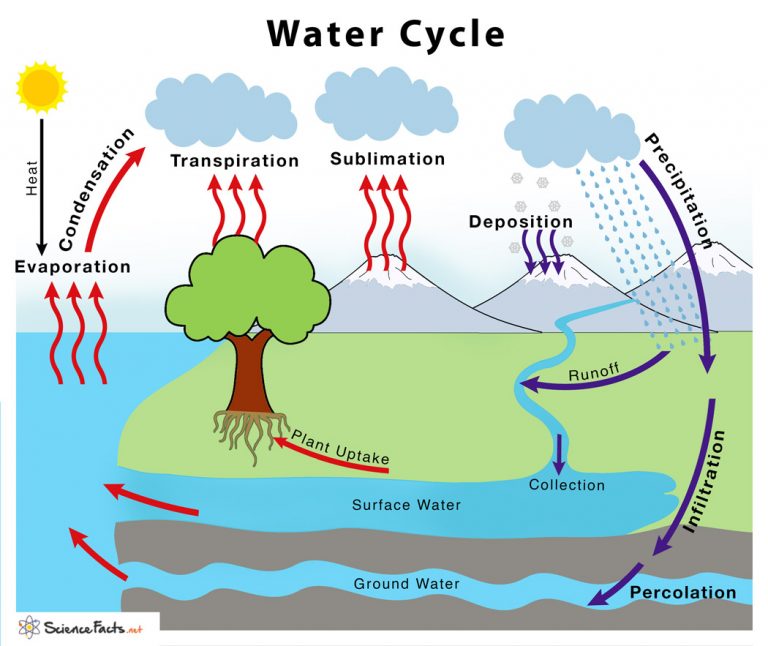
Draw The Hydrological Cycle - Water cycle diagram during this process, water changes its state from one phase to another, but the total number of water particles remains the same. It is moved through the atmosphere by winds and condenses to form clouds of water droplets or ice crystals. 96.5% of the water on earth is saltwater and is held in oceans. Water is always changing states between liquid, vapor, and ice, with these processes happening in the blink of an eye and over millions of years. Web in this article we will discuss about the hydrologic cycle with the help of a suitable diagram.
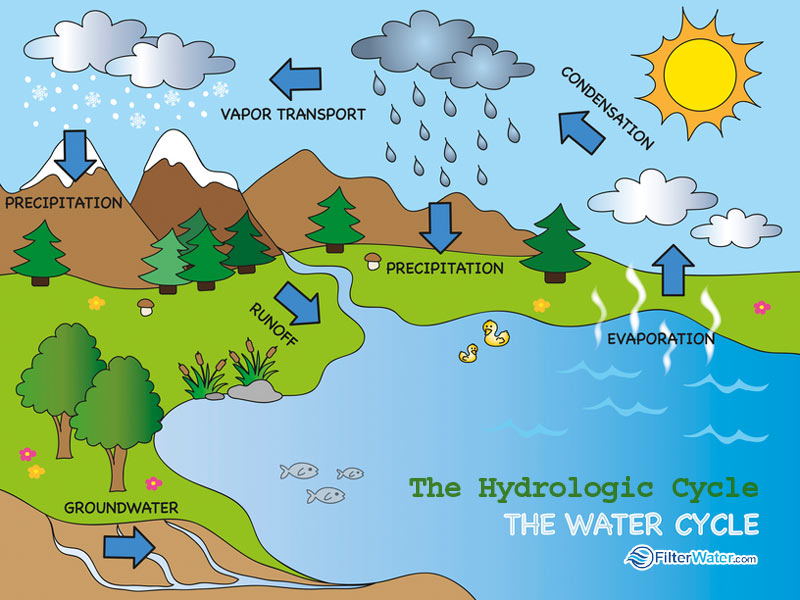
Web the accumulation stage of the water cycle is a holding stage where most of earth's water is collected. Water vapor condenses into millions of tiny droplets that form clouds. Web hydrological cycle can be defined as the continuous process of exchange of water from the earth surface to the atmosphere or vice versa by the influence of solar radiation or solar heat. It is also known as the hydrological cycle or the hydrologic cycle. The hydrologic cycle (also called the water cycle) is the continuous movement of water in the air, on the surface of and below the earth. Get their supplies from rains, while the rain water itself is. Water cycle diagram during this process, water changes its state from one phase to another, but the total number of water particles remains the same.
The hydrological Cycle notesychs
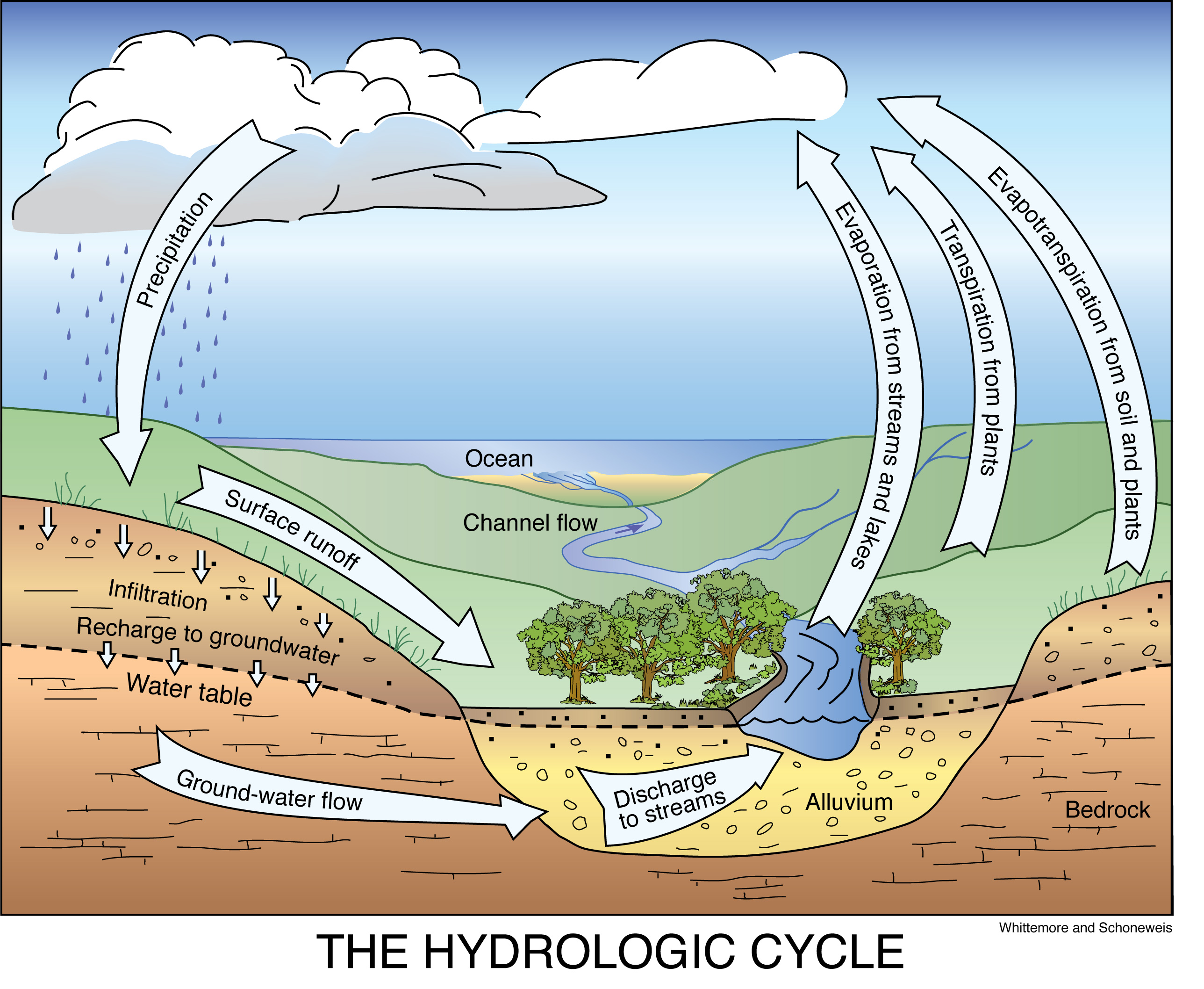
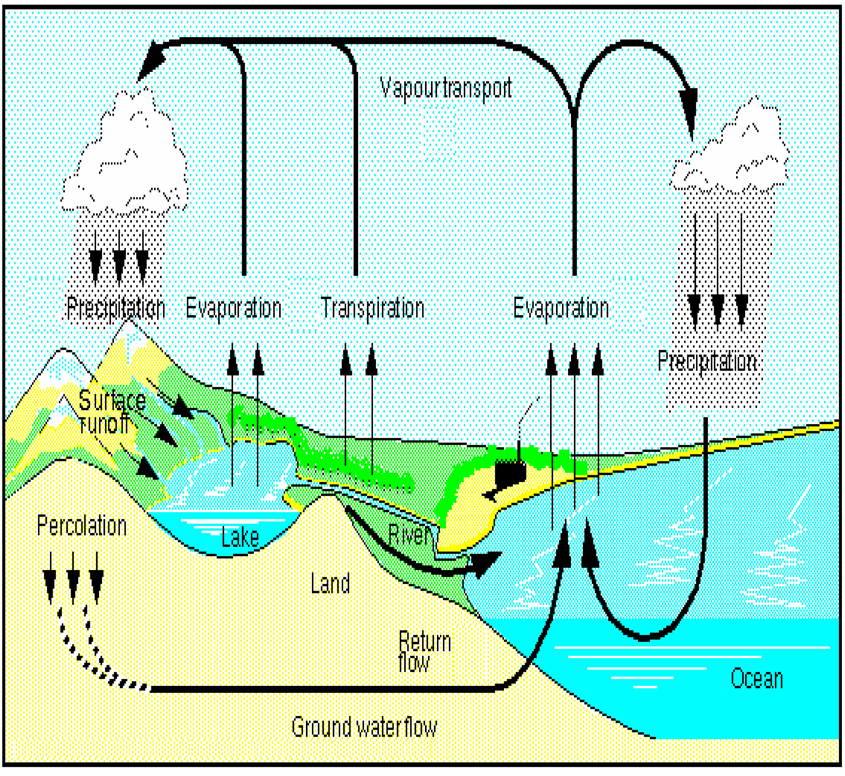
(ii) another part flows over the surface in rivers and ultimately reaches sea or ocean. Web the water, or hydrologic, cycle describes the pilgrimage of water as water molecules make their way from the earth’s.
WATER CYCLE The Process that Provides ALL THE WATER You Use
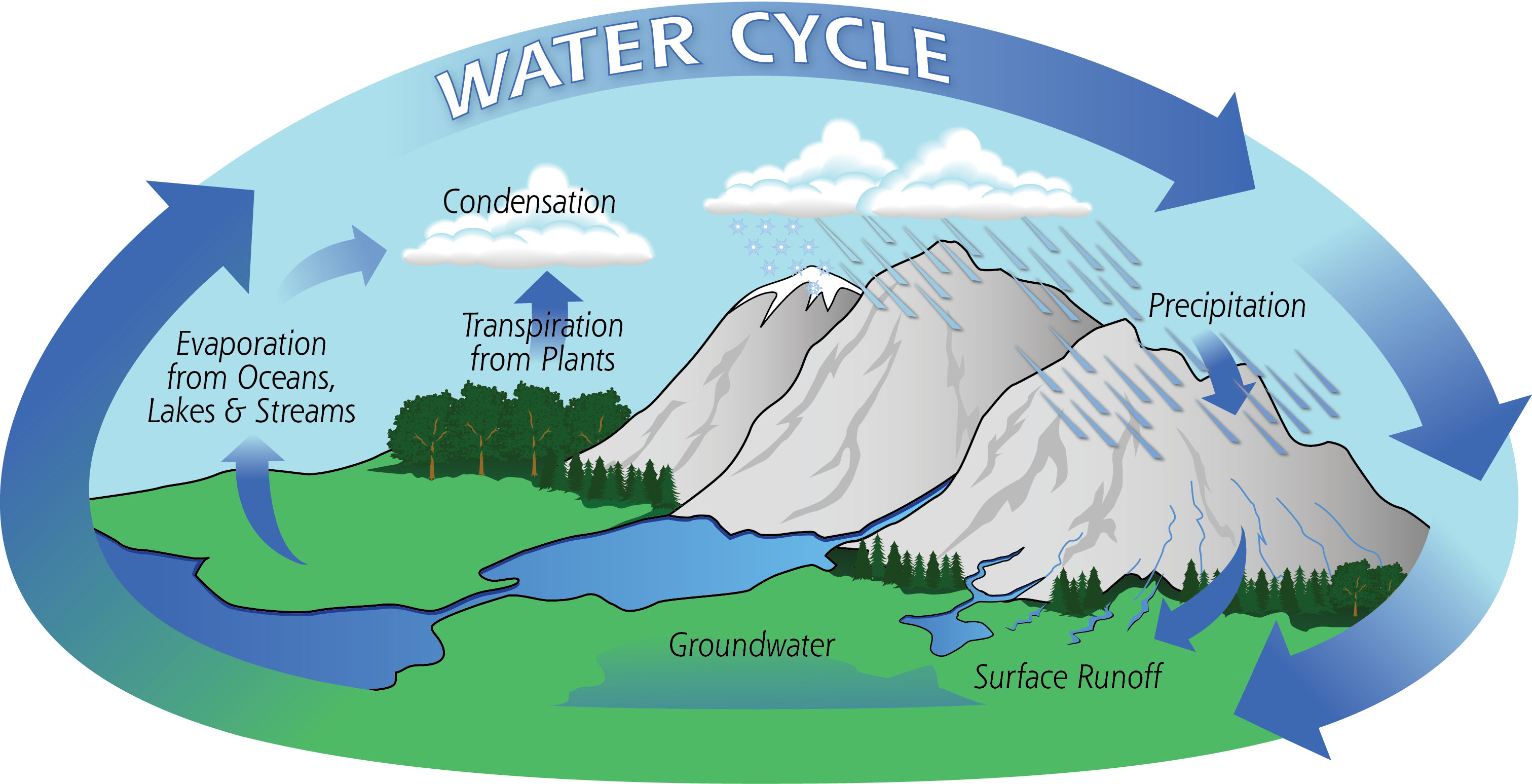
Web the hydrologic cycle begins with the evaporation of water from the surface of the ocean. Web hydrological cycle can be defined as the continuous process of exchange of water from the earth surface to.
The hydrologic (water) cycle GeoKansas
(i) one part directly returns to the air as water vapour by evaporation and transpiration from plants. Web overview of water moving through the hydrologic cycle, or water cycle: Web the water cycle, also known.
water cycle Definition, Steps, Diagram, & Facts Britannica
Web the water cycle, or hydrologic cycle, is driven by the sun’s energy. Web the water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous.
Hydrosphere The water cycle Britannica
It evaporates from earth's surface as water vapour, which condenses in the atmosphere, forming clouds and precipitation, which falls to the land and flows through lakes, rivers, and oceans, from which water evaporates as the.
Hydrologic Cycle
Web the water, or hydrologic, cycle describes the pilgrimage of water as water molecules make their way from the earth’s surface to the atmosphere and back again, in some cases to below the surface. Get.
FileSimple Water Cycle.JPG
Web beginner intermediate advanced sources/usage: It evaporates from earth's surface as water vapour, which condenses in the atmosphere, forming clouds and precipitation, which falls to the land and flows through lakes, rivers, and oceans, from.
What is Water?
Our interactive diagrams allow you to mouse around the parts of the water cycle and view explanations, pictures, and more. Most of the earth’s water sources, such as rivers, lakes, oceans and underground sources, etc..
Water Cycle Definition & Steps Explained With Simple Diagram
Web our newest diagram, released in 2022, depicts the global water cycle, as well as how human water use affects where water is stored, how it moves, and how clean it is. It is also.
Hydrological Cycle
The rain water that falls on the ground surface is divided into three parts: Web the hydrologic cycle, also known as the water cycle, is the series of processes that water goes through during its.
Draw The Hydrological Cycle Click one of the levels above to start exploring! Web our newest diagram, released in 2022, depicts the global water cycle, as well as how human water use affects where water is stored, how it moves, and how clean it is. This gigantic system, powered by energy from the sun, is a continuous exchange of moisture between the oceans, the atmosphere, and the land. 96.5% of the water on earth is saltwater and is held in oceans. The oceans are the lowest.