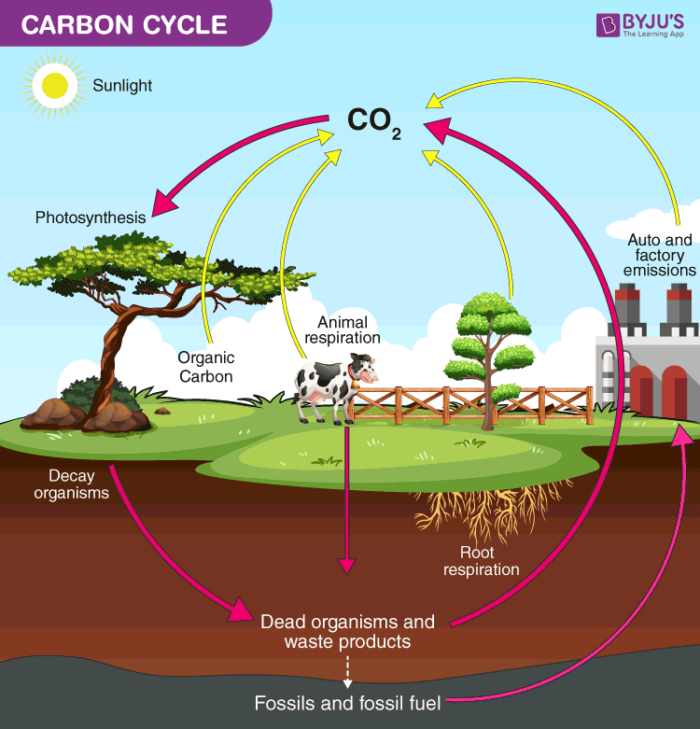
Drawing Carbon Cycle
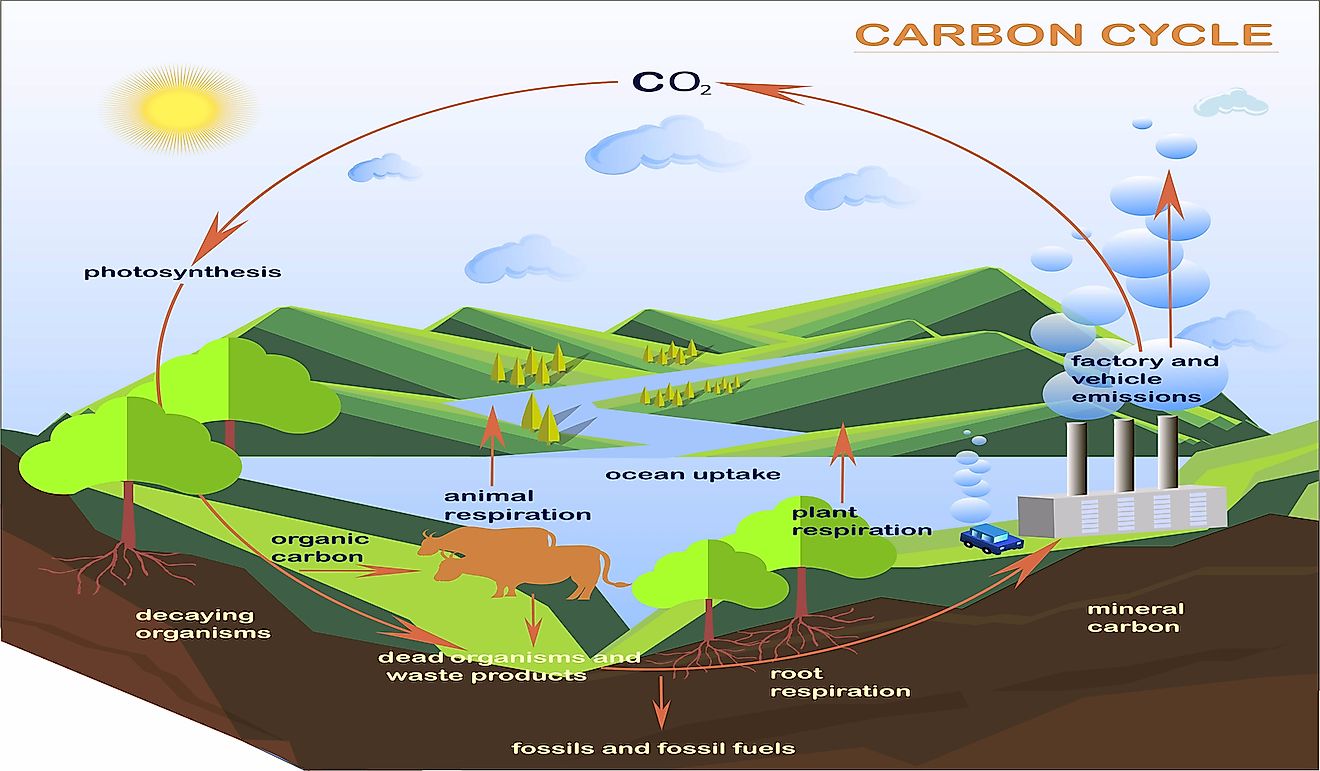
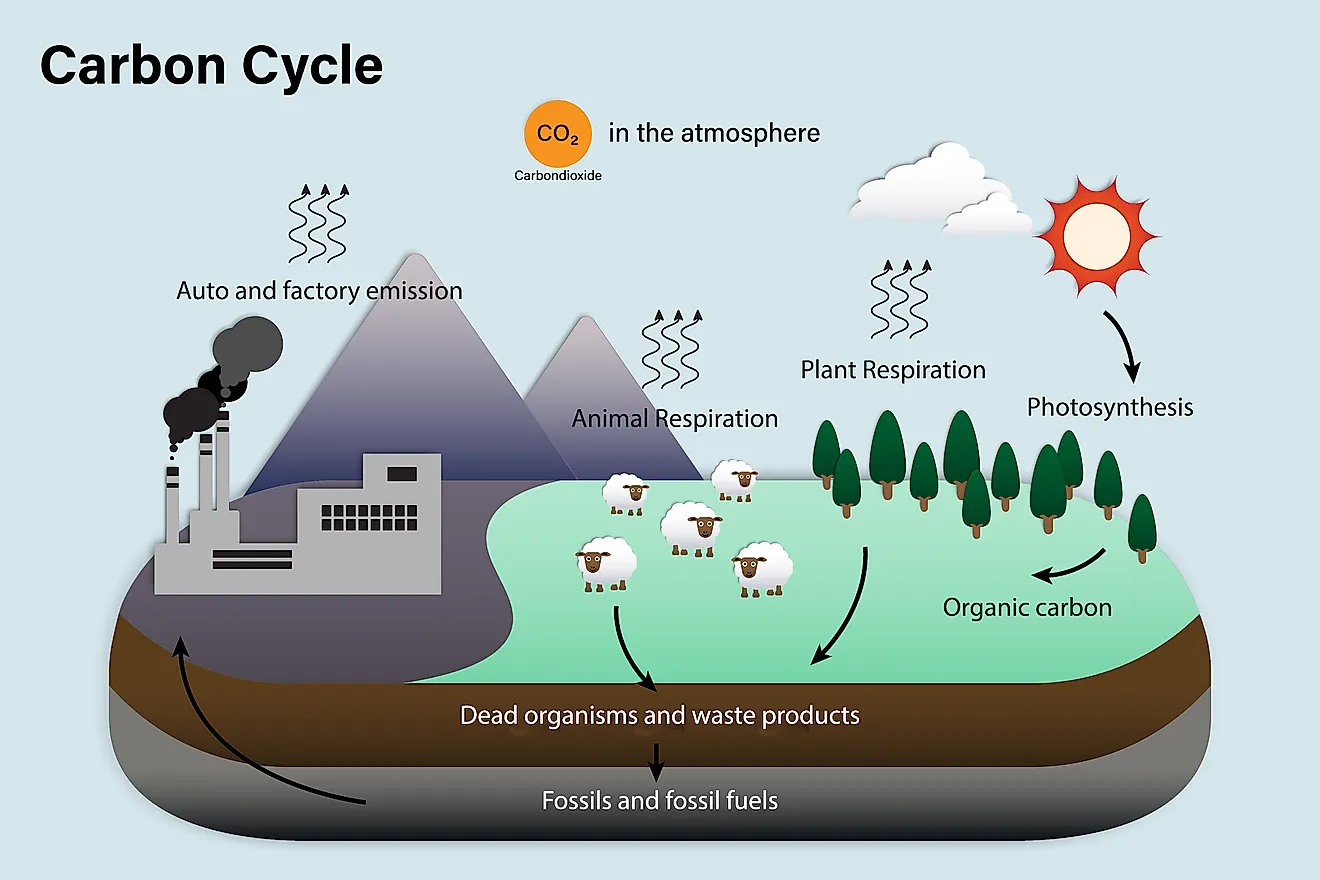
Drawing Carbon Cycle - All of the atoms that are building blocks of living things are a part of biogeochemical cycles. Web carbon cycle shows the movement of carbon in elemental and combined states on earth. Web the carbon cycle is a biogeochemical cycle through which the carbon moves among the biosphere (living organisms), geosphere (earth’s crust), pedosphere (earth’s soil layer), hydrosphere (water bodies), and earth’s atmosphere. They learn how carbon atoms travel through the geological (ancient) carbon. Carbon is the fourth most abundant element in the universe.
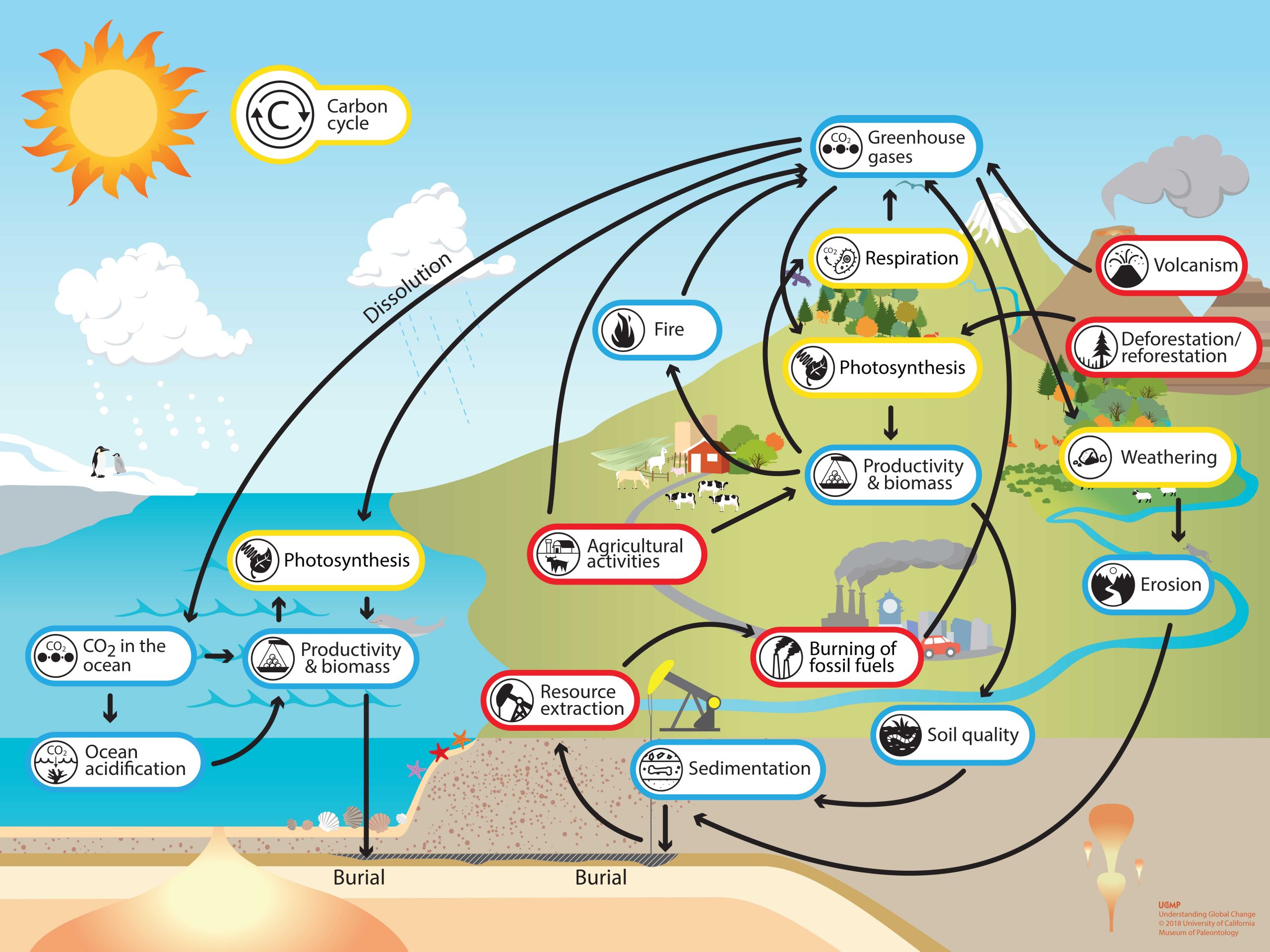
Web the ocean plays an important part in the carbon cycle. We are made of carbon, we eat carbon, and our civilizations—our economies, our homes, our means of transport—are built on carbon. The entire carbon cycle is shown in figure 1. Web the carbon cycle is the process that moves carbon between plants, animals, and microbes; Locate the carbon cycle icon and identify other earth system processes and phenomena that cause changes to, or are affected by, the cycling of carbon. Click the image on the left to open the understanding global change infographic. At the top of the drawing above the clouds there is a label of carbon dioxide in atmosphere.
What Is The Carbon Cycle?
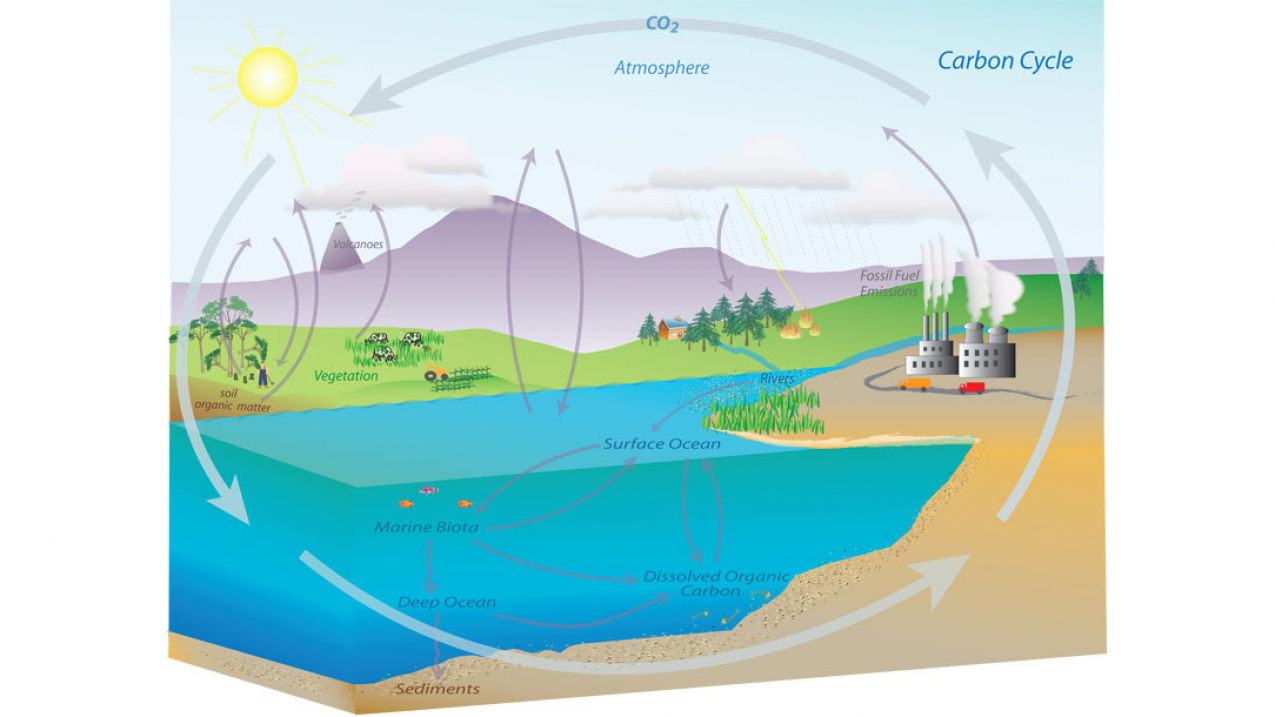
Diagram of the carbon cycle. There are arrows pointing from air sea gas exchange, human emissions, and a volcano pointing towards carbon dioxide in atmosphere. Web the carbon cycle is the process that moves carbon.
Carbon cycle Understanding Global Change
Web resource collections topics: Overall, the ocean is called a carbon ‘sink’ because it takes up more carbon from the atmosphere than it gives up. Web the ocean plays an important part in the carbon.
The Carbon Cycle UCAR Center for Science Education
Web the carbon cycle is a biogeochemical cycle through which the carbon moves among the biosphere (living organisms), geosphere (earth’s crust), pedosphere (earth’s soil layer), hydrosphere (water bodies), and earth’s atmosphere. Web the carbon cycle.
Carbon cycle National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
There are arrows pointing from air sea gas exchange, human emissions, and a volcano pointing towards carbon dioxide in atmosphere. All of the atoms that are building blocks of living things are a part of.
Carbon Cycle Diagram from NASA Center for Science Education
Web the carbon cycle overlaps the rock cycle. From how to teach the carbon cycle at 11 14, education in chemistry, rsc.li/2p939rc keywords carbon cycle, earth science, atmosphere. Carbon dioxide gas exists in the atmosphere.
Carbon cycle Royalty Free Vector Image VectorStock
Web the carbon cycle is a biogeochemical cycle through which the carbon moves among the biosphere (living organisms), geosphere (earth’s crust), pedosphere (earth’s soil layer), hydrosphere (water bodies), and earth’s atmosphere. This cycle keeps carbon.
Systems Thinking and the Carbon Cycle An Interactive Introduction to
There are also exchanges with the ocean which are only hinted at here. There are arrows pointing from air sea gas exchange, human emissions, and a volcano pointing towards carbon dioxide in atmosphere. © inna.
Carbon Cycle WorldAtlas
Web resource collections topics: Web the carbon cycle is an essential part of how the earth system works. This cycle keeps carbon circulating in the biosphere. Web the carbon cycle overlaps the rock cycle. Click.
Carbon Cycle GLOBE.gov
This cycle keeps carbon circulating in the biosphere. From how to teach the carbon cycle at 11 14, education in chemistry, rsc.li/2p939rc keywords carbon cycle, earth science, atmosphere. Ocean sediments and the rocks they turn.
Carbon Cycle Definition, Process, Diagram Of Carbon Cycle
Web the carbon cycle game and instructions. Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere dissolves in the surface waters of the ocean. Locate the carbon cycle icon and identify other earth system processes and phenomena that cause.
Drawing Carbon Cycle A diagram shows processes within the carbon cycle connected by arrows indicating the flow of carbon within and between the atmosphere, land, and ocean. Carbon is the fourth most abundant element in the universe. The carbon cycle involves plants taking in carbon dioxide, fixing carbon, and creating organic molecules. We are made of carbon, we eat carbon, and our civilizations—our economies, our homes, our means of transport—are built on carbon. The entire carbon cycle is shown in figure 1.