Tibial Thrust Vs Cranial Drawer
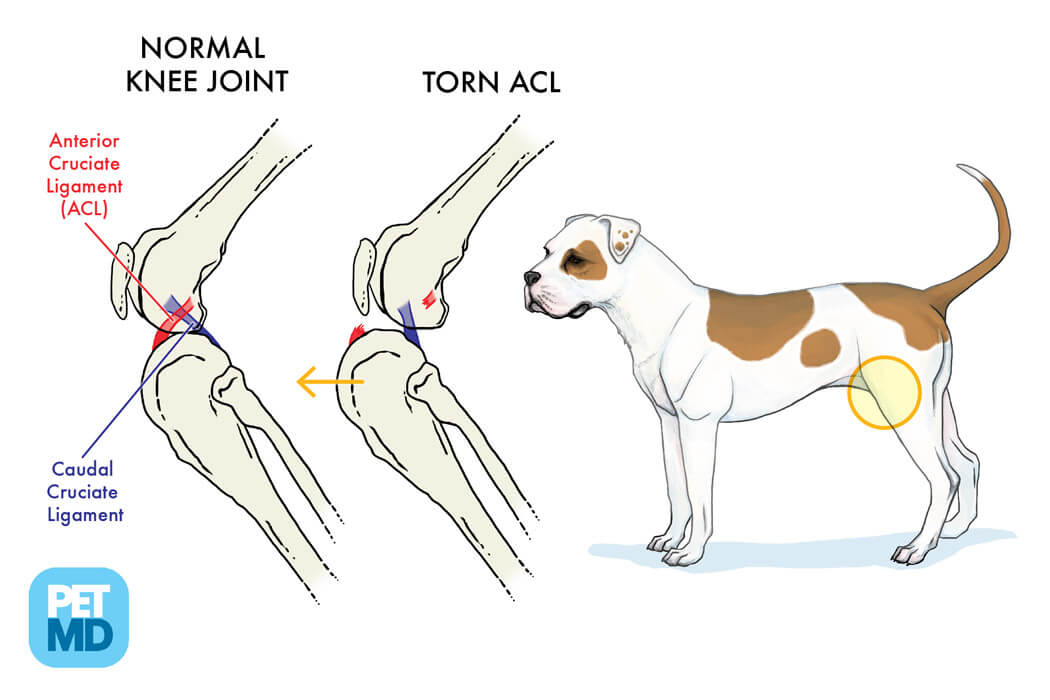
Tibial Thrust Vs Cranial Drawer - Web the cranial cruciate ligament (known as the anterior cruciate ligament or acl in people) is one of several ligaments in the stifle (knee) that connect the femur (thigh bone) to the tibia (shin bone). Web the magnitude of the cranial tibial thrust is a function of external ground reaction forces, internal muscular forces, and the slope of the tibial plateau. Web the loss of these normal findings indicates periarticular fibrosis, joint effusion or both. The cranial drawer assessment is best done on the laterally recumbent animal. Another sign referred to as tibial thrust, may be elicited as well.
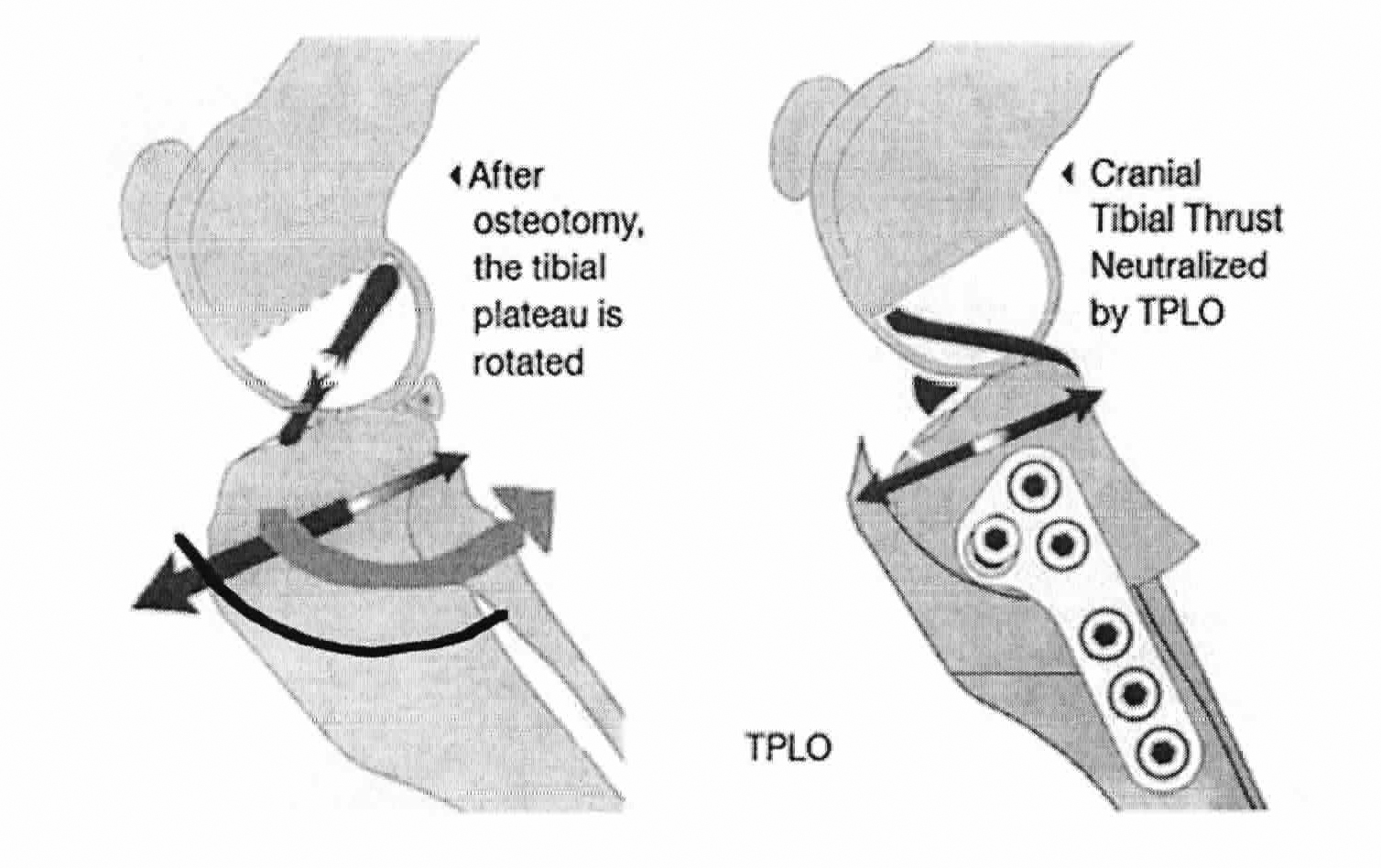
Web tibial plateau leveling osteotomy (tplo) or tibial tuberosity advancement (tta) are commonly used surgical techniques for correction of cranial cruciate ligament (ccl) rupture in dogs. Web increasing tibial loads in the tibial plateau leveled crcl deficient stifle increased caudal tibial thrust.(6) the cranial drawer sign may still be present after tplo surgery. At this time, there was absent cranial drawer and tibial thrust with marked periarticular fibrosis of the stifle. When cranial tibial thrust exceeds the tensile strength of a healthy cranial cruciate ligament or a weakened, degenerative cranial cruciate ligament, the ligament completely or partially. Web instability of the stifle is commonly demonstrated through the cranial drawer test and tibial compression test. Pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. For the tibial thrust test, the dog often stands (it is less stressful) and your veterinarian will hold the femur (thigh bone) stable while bending the foot.
Drawer Test Bruin Blog
The tta procedure results in a stable stifle joint and eliminates the drawer sign. Seven months later, the dog was reexamined, and arthroscopy was performed on the contralateral stifle. Prevent the tibia from sliding forward.
PPT Knee Orthopaedic Tests PowerPoint Presentation, free download
The more severely affected limb clinically had a tplo performed. This force is called “tibial thrust” and the job of the ccl is to prevent this motion. Web increasing tibial loads in the tibial plateau.
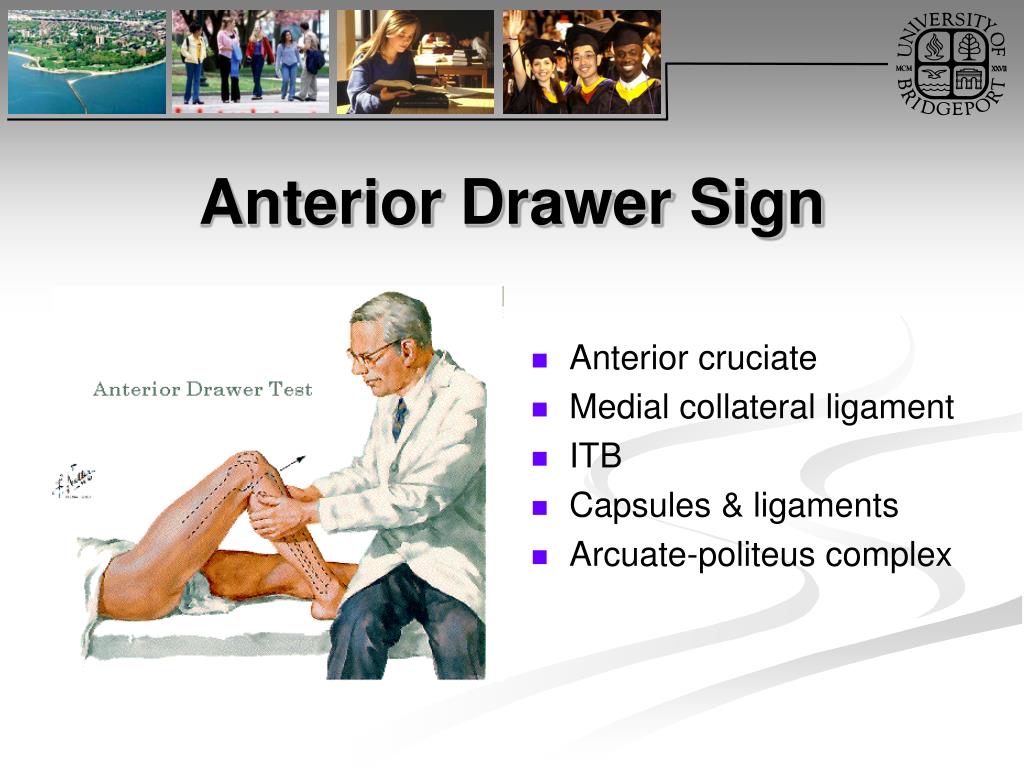
Anterior Drawer Test for ACL How to Perform the Anterior Drawer Test
It is performed by applying a force to the tibia while holding the femur stable, thereby. This systematic review aims to investigate whether one technique is superior to the other. Web the tibial thrust test.
Tibial Plateau Leveling Osteotomy
Web increasing tibial loads in the tibial plateau leveled crcl deficient stifle increased caudal tibial thrust.(6) the cranial drawer sign may still be present after tplo surgery. This systematic review aims to investigate whether one.
A most cranial point of the tibial plateau B most caudal point of the
The cranial drawer test is performed most commonly and tends to be the mainstay of testing for stifle instability by general veterinarians. Web a stable partial tear has cranial drawer and cranial tibial thrust that.
Representative scheme of forces acting on stifle joint before (A) and
Web once the ligament tears to a certain degree the tibia can be manually manipulated to show instability in what is called the “cranial drawer test” in which the tibia can be moved forward in.
Bones of the Lower Limb Anatomy and Physiology I
The cranial drawer test is performed most commonly and tends to be the mainstay of testing for stifle instability by general veterinarians. Your pet’s doctor will take the results from the drawer sign test into.
Tibia alignment Varus (1a), normal (1b), and varus (1c) knee. Red
Cranial cruciate ligament (crcl) rupture is the most common cause of hindlimb lameness in dogs. Clinical signs clinical signs are different in intensity according to the degree and duration of crcl partial rupture. Web in.
ACL and CCL diagram provided by PetMD
Sliding of the distal femur over the proximal tibia Web the technique relies on a cranial advancement of the tibial tuberosity after an osteotomy of the tibial crest. The advancement of the tibial tuberosity not.
Anatomical landmarks and corresponding reference systems. LE Lateral
Your pet’s doctor will take the results from the drawer sign test into consideration when determining a treatment plan for your dog. Web tibial plateau leveling osteotomy (tplo) or tibial tuberosity advancement (tta) are commonly.
Tibial Thrust Vs Cranial Drawer Web definitive diagnosis of rupture of the ccl demands an assessment of stifle joint stability by means of the cranial “drawer” test, the tibial compression test, or both tests. Clinical signs clinical signs are different in intensity according to the degree and duration of crcl partial rupture. Unstable partial tears have more instability than a stable partial tear and typically have instability equal to or less than dogs with a. For the tibial thrust test, the dog often stands (it is less stressful) and your veterinarian will hold the femur (thigh bone) stable while bending the foot. Cranial cruciate ligament (crcl) rupture is the most common cause of hindlimb lameness in dogs.