10+ Diabetic Targets For Perfect Blood Sugar Control
Achieving perfect blood sugar control is a multifaceted endeavor for individuals with diabetes. It involves not only managing blood glucose levels but also considering various factors that impact overall health and the progression of the disease. Here are 10+ diabetic targets that individuals with diabetes should focus on for optimal blood sugar control, along with the importance of a holistic approach to diabetes management:
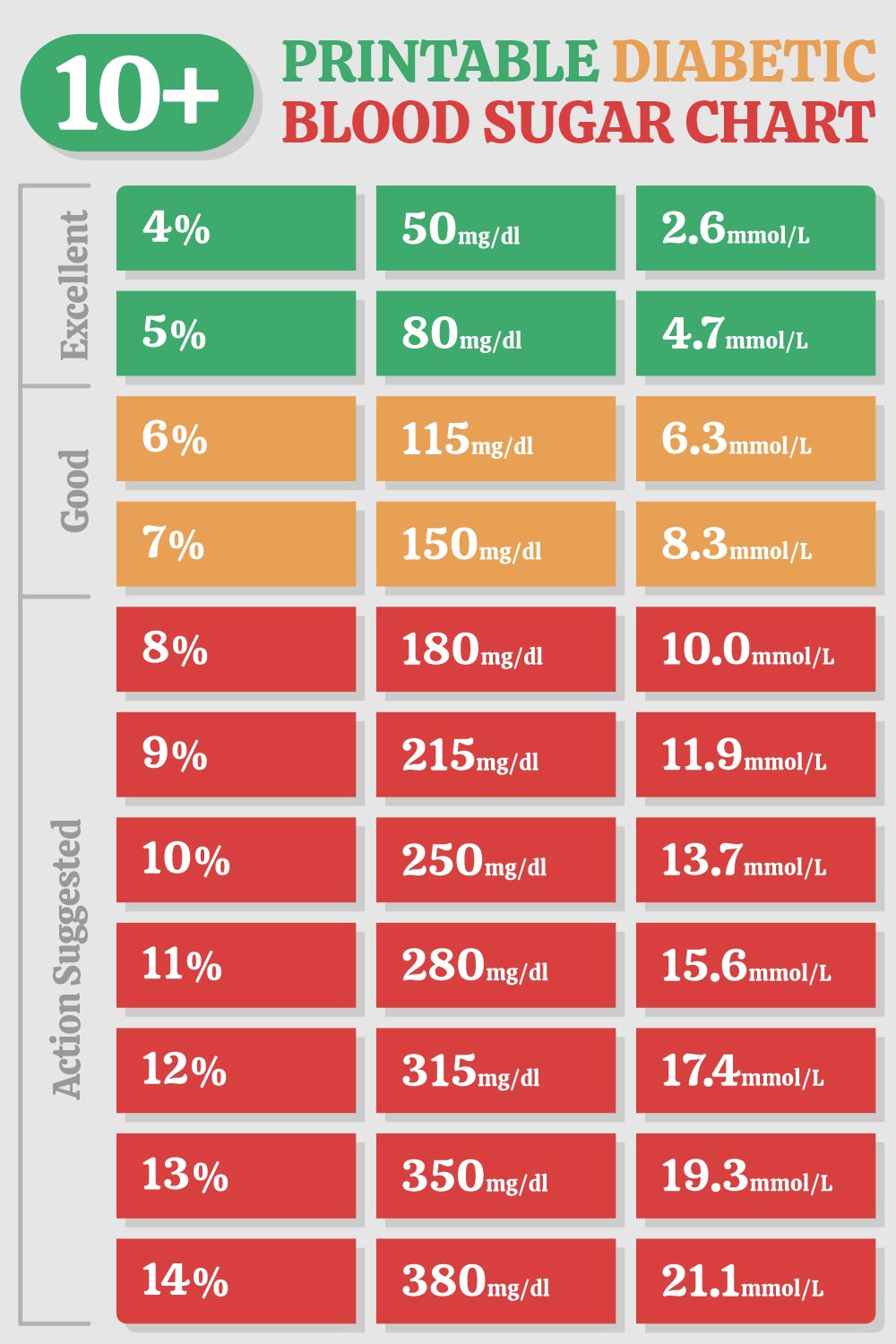
1. HbA1c Levels
- Target: Less than 7% for most adults, as recommended by the American Diabetes Association (ADA), though targets can be individualized based on factors like age, comorbidities, disease duration, life expectancy, and the presence of cardiovascular disease.
- Importance: HbA1c provides an average of blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months, serving as a critical marker for diabetes control.
2. Fasting Blood Glucose
- Target: 80-130 mg/dL for adults, according to the ADA, before eating, and less than 180 mg/dL after meals.
- Importance: Monitoring fasting glucose helps in assessing the body’s ability to manage blood sugar levels when not eating.
3. Postprandial (After Meal) Blood Glucose
- Target: Less than 180 mg/dL, as per ADA guidelines.
- Importance: Postprandial glucose monitoring helps in understanding how the body reacts to different foods and in adjusting meal plans accordingly.
4. Blood Pressure Control
- Target: Less than 130⁄80 mmHg, according to the ADA and American Heart Association (AHA).
- Importance: High blood pressure is a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, which are major complications of diabetes.
5. Lipid Profiles
- Target: LDL (bad) cholesterol < 100 mg/dL, HDL (good) cholesterol > 40 mg/dL for men and > 50 mg/dL for women, and triglycerides < 150 mg/dL.
- Importance: Dyslipidemia (abnormal levels of lipids) increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in diabetic patients.
6. Body Mass Index (BMI)
- Target: Between 18.5 and 24.9, though this may vary slightly based on ethnic background and body composition.
- Importance: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of complications and improves insulin sensitivity.
7. Physical Activity
- Target: At least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on 2 or more days a week.
- Importance: Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, helps with weight management, and reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
8. Smoking Cessation
- Target: Complete cessation of smoking and avoidance of secondhand smoke.
- Importance: Smoking exacerbates cardiovascular risks and worsens diabetes control.
9. Healthy Diet
- Target: A balanced diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium, and high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Importance: A healthy diet helps with weight management, improves blood glucose control, and reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
10. Mental Health and Stress Management
- Target: Regular engagement in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, and seeking professional help when needed.
- Importance: Chronic stress can negatively affect blood glucose control and overall well-being.
11. Regular Health Check-ups
- Target: Annual comprehensive foot exams, regular eye exams, dental check-ups, and vaccinations as recommended by healthcare providers.
- Importance: Early detection and treatment of complications can significantly improve outcomes.
12. Medication Adherence
- Target: Taking medications as prescribed by healthcare providers, including any necessary adjustments based on ongoing monitoring.
- Importance: Adherence to medication regimens is crucial for achieving and maintaining blood glucose control.
Achieving these targets requires a proactive and multifaceted approach, including lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, and, when necessary, medication. It’s also crucial to work closely with healthcare providers to tailor these targets to individual needs and health status, ensuring the most effective and safe management of diabetes.
What is the primary goal of managing blood sugar levels in diabetes?
+The primary goal of managing blood sugar levels is to keep them as close to normal as possible to delay or prevent diabetes complications, such as heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems.
How often should blood glucose be monitored in diabetes management?
+The frequency of blood glucose monitoring depends on the type of diabetes and the treatment plan. For example, individuals with type 1 diabetes or those using insulin may need to monitor their blood glucose levels several times a day, while those with type 2 diabetes managed through diet and exercise might monitor less frequently.
What role does diet play in achieving perfect blood sugar control?
+Diet plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels. A diet that is balanced, low in added sugars, and high in fiber can help manage blood glucose levels. Working with a registered dietitian or a certified diabetes educator can help develop a personalized meal plan.
Why is physical activity important for diabetes management?
+Physical activity, including both aerobic exercise and strength training, improves insulin sensitivity, which helps the body to use insulin more efficiently, lowering blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity also helps with weight management and reduces the risk of heart disease.
How does stress affect diabetes management?
+Stress can affect blood sugar levels and worsen diabetes symptoms. When the body is under stress, it releases stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can cause blood sugar levels to rise. Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises, can help manage stress and improve diabetes control.
In conclusion, achieving perfect blood sugar control involves setting and working towards multiple targets that encompass not just glucose management but also overall health and wellness. By understanding and addressing these diverse aspects, individuals with diabetes can significantly improve their quality of life and reduce the risk of long-term complications.



