10+ Hemoglobin A1c Secrets For Accurate Results
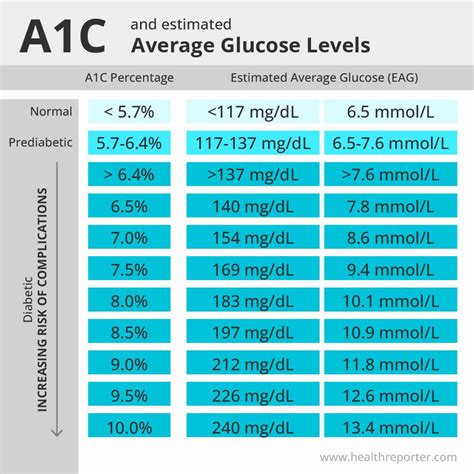
Understanding the intricacies of Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) testing is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals. HbA1c provides a glycemic snapshot, indicating average blood glucose levels over the preceding 2-3 months. This tool is invaluable for diagnosing diabetes, monitoring its management, and assessing the risk of developing complications associated with the disease. However, achieving accurate HbA1c results requires consideration of several factors, which can be categorized into pre-analytical, analytical, and post-analytical phases. Here, we delve into 10+ secrets for ensuring accurate HbA1c results, touching on the nuances of this test and the variables that can influence its outcomes.
1. Understanding Hemoglobin A1c
Hemoglobin A1c is a form of hemoglobin that is bound to glucose. The amount of glucose that binds to hemoglobin is directly proportional to the blood glucose concentration over the lifespan of red blood cells, approximately 120 days. Thus, HbA1c levels provide a reliable indicator of how well diabetes is being managed, with lower values generally indicating better glucose control.
2. Pre-Analytical Considerations
Pre-analytical variables are factors that can affect the test result before the actual analysis takes place. These include the condition of the blood sample, the method of sample collection, and the handling and storage of the sample before analysis. For example, hemolysis (the breaking down of red blood cells) can lead to inaccurate measurements. It’s crucial that blood samples are collected, stored, and transported according to standardized protocols to minimize such effects.
3. Analytical Considerations
The choice of analytical method can significantly impact HbA1c results. Various laboratory methods are available, including ion-exchange high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), immunoassays, and boronate affinity chromatography. Each method has its own set of advantages and limitations, including varying degrees of susceptibility to interference from hemoglobin variants or other substances. Standardization of methods and participation in quality control programs are critical for ensuring accurate and comparable results across different laboratories.
4. Hemoglobin Variants
The presence of hemoglobin variants, such as HbS (sickle hemoglobin), HbC, or HbE, can interfere with some HbA1c assays, leading to inaccurate results. These variants can be common in certain populations, and their presence should be considered when interpreting HbA1c results. In such cases, alternative methods for assessing glycemic control, such as fructosamine testing or continuous glucose monitoring, may be necessary.
5. Red Blood Cell Lifespan
HbA1c reflects average glucose levels over the lifespan of red blood cells. However, conditions that alter red blood cell lifespan, such as hemolytic anemia or blood transfusions, can lead to misleading HbA1c results. In these scenarios, HbA1c may not accurately reflect glycemic control, and other measures should be used in conjunction.
6. Erythropoiesis
Increased erythropoiesis (the production of red blood cells) in response to certain conditions, such as chronic kidney disease or the use of erythropoietin-stimulating agents, can also affect HbA1c levels. This is because the newly produced red blood cells will have fewer glucose molecules attached, potentially lowering the HbA1c measurement even if glucose control has not improved.
7. Altered Iron States
Both iron deficiency and iron overload can affect HbA1c measurements, depending on the specific analytical method used. Iron deficiency, for instance, can lead to an overestimation of HbA1c by some assays, while iron overload may have varying effects depending on the method.
8. Liver Disease
Certain liver conditions can influence HbA1c levels. For example, liver cirrhosis can decrease HbA1c, possibly due to reduced glucose attached to hemoglobin or changes in red blood cell turnover. On the other hand, conditions like liver disease can sometimes lead to hyperglycemia, which would increase HbA1c levels.
9. Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) can complicate the interpretation of HbA1c results. CKD can lead to alterations in red blood cell lifespan and changes in erythropoiesis, both of which can affect HbA1c measurements. Furthermore, certain medications used in CKD management might also influence glycemic control and HbA1c levels.
10. Precision and Bias
Understanding the precision (repeatability) and bias (accuracy) of the HbA1c assay used is critical. Participating in external quality assessment programs can help laboratories ensure that their results are accurate and comparable to international standards.
11. Reference Ranges
Finally, it’s essential to be aware of the reference ranges used for HbA1c interpretation. These can vary slightly between laboratories, and understanding these ranges is crucial for accurately interpreting results. For diabetes diagnosis, an HbA1c of 6.5% or higher is commonly used, while for monitoring, targets may vary depending on individual patient factors, such as risk of hypoglycemia, disease duration, life expectancy, resources, and support system.
Conclusion
Achieving accurate HbA1c results is multifaceted, involving not just the choice of analytical method but also careful consideration of pre-analytical and post-analytical factors. Understanding the nuances of HbA1c testing, including its limitations and the various factors that can influence results, is essential for healthcare professionals and patients alike. By recognizing these complexities, we can better utilize HbA1c as a powerful tool in the diagnosis and management of diabetes, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes.
What does Hemoglobin A1c measure?
+Hemoglobin A1c measures the average blood glucose levels over the preceding 2-3 months by assessing the percentage of glucose that has bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells.
Why are pre-analytical considerations important for HbA1c testing?
+Pre-analytical considerations, such as sample collection and handling, are critical because they can affect the condition of the blood sample and thus the accuracy of the HbA1c measurement.
How do hemoglobin variants affect HbA1c results?
+Hemoglobin variants can interfere with some HbA1c assays, potentially leading to inaccurate results. The choice of analytical method is crucial in individuals known to have hemoglobin variants.
By considering these secrets and nuances of HbA1c testing, healthcare providers can make more informed decisions about diabetes management, and individuals can better understand their condition and how to manage it effectively.



