10 Kidney Function Panel Tests For Better Health
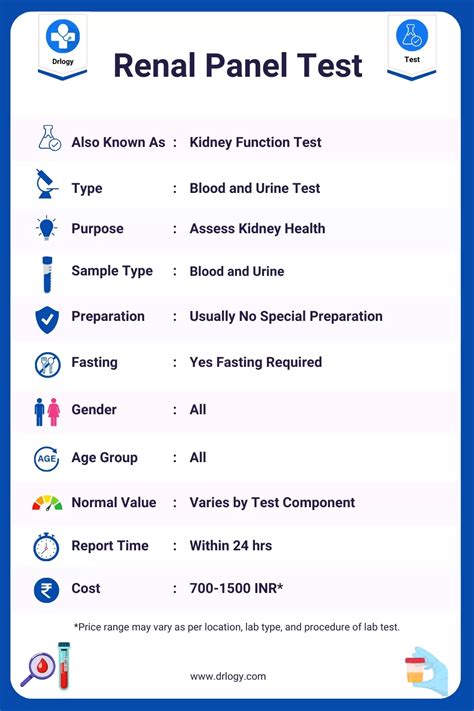
Maintaining optimal kidney function is crucial for overall health, as these vital organs play a central role in filtering waste products, regulating blood pressure, and balancing electrolytes. A kidney function panel test is a comprehensive diagnostic tool that assesses various aspects of kidney health, providing valuable insights into the functioning of these critical organs. This article will delve into the importance of kidney function tests, exploring ten key components that are typically included in a kidney function panel, along with an explanation of their significance and how they contribute to a better understanding of kidney health.
Introduction to Kidney Function Tests
Kidney function tests are designed to evaluate how well the kidneys are performing their duties. These tests can help identify early signs of kidney damage or disease, allowing for timely intervention. The tests included in a kidney function panel can vary slightly depending on the healthcare provider and the specific concerns being addressed, but they generally cover a broad spectrum of kidney functions and related health indicators.
Components of a Kidney Function Panel
A standard kidney function panel includes several tests that provide a comprehensive overview of kidney health. Understanding each component is essential for interpreting test results and making informed decisions about health care.
Creatinine Test: This test measures the level of creatinine in the blood, a waste product from the normal breakdown of muscle tissue. High levels of creatinine indicate impaired kidney function, as the kidneys are not filtering this waste effectively.
Urea Test: Urea is another waste product that the kidneys are responsible for filtering out of the blood. Elevated urea levels can signal kidney dysfunction, although urea levels can also be influenced by factors such as dehydration and heart failure.
Electrolyte Panel: This includes measurements of sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate levels in the blood. The kidneys help regulate these electrolytes, which are crucial for maintaining proper fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contraction.
Calcium and Phosphorus Levels: The kidneys play a key role in regulating the levels of these minerals in the body. Abnormal levels can indicate kidney problems, as the kidneys help activate vitamin D, which is necessary for calcium absorption, and they also excrete excess phosphorus.
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Test: This test measures the amount of urea in the blood. Like the urea test, it helps assess kidney function but can be influenced by factors other than kidney disease, such as a high-protein diet or dehydration.
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR): The GFR is a calculation based on the creatinine test, age, sex, and race. It estimates the percentage of kidney function, providing a direct measure of how well the kidneys are filtering wastes from the blood.
Albumin and Total Protein Tests: These tests measure the levels of albumin and total protein in the blood. Low levels of albumin, in particular, can indicate kidney disease, as the kidneys may be excreting this protein in the urine instead of keeping it in the bloodstream.
Urinalysis: While not strictly a blood test, urinalysis is often included as part of a comprehensive kidney function evaluation. It involves examining the urine for various substances that could indicate kidney dysfunction, such as blood, protein, or glucose.
Phosphate Test: This measures the level of phosphate in the blood. The kidneys help regulate phosphate levels by excreting excess amounts. High levels can indicate kidney problems, among other conditions.
Magnesium Level Test: The kidneys also help regulate magnesium levels in the body. Abnormal magnesium levels can affect muscle and nerve function and may indicate issues with kidney function.
Practical Applications and Health Implications
Understanding the components of a kidney function panel is crucial for maintaining kidney health. By identifying potential issues early, individuals can work with their healthcare providers to implement lifestyle changes or treatments that can help prevent further kidney damage. Regular monitoring of kidney function is particularly important for individuals with risk factors for kidney disease, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or a family history of kidney disease.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of kidney problems is key to effective management and prevention of further damage. Kidney disease often progresses silently, with few symptoms until the disease is advanced. Therefore, regular health check-ups, including kidney function tests for those at risk, are essential for identifying kidney issues before they become severe.
Lifestyle Changes for Kidney Health
In addition to medical interventions, several lifestyle changes can support kidney health. These include maintaining a balanced diet low in salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water, exercising regularly, managing stress, and not smoking. For individuals with specific dietary needs due to kidney disease, working with a dietitian can help tailor a diet that supports kidney health while meeting nutritional needs.
Conclusion
Kidney function panel tests are powerful tools for assessing kidney health and identifying potential issues early. By understanding the components of these tests and their implications, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining optimal kidney function and overall health. Regular monitoring, combined with healthy lifestyle choices, can significantly contribute to preventing kidney disease and its complications, ensuring better health outcomes for individuals at risk.
What are the primary indicators of kidney function in a kidney function panel?
+The primary indicators include creatinine and urea levels, electrolyte balance, and the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), which collectively provide a comprehensive view of how well the kidneys are functioning.
How often should kidney function tests be conducted for individuals with no known kidney issues?
+For individuals with no known kidney issues, kidney function tests are typically part of routine health examinations, the frequency of which can depend on age, overall health, and risk factors. However, annual check-ups are recommended for early detection of potential health issues.
Can lifestyle changes alone reverse early stages of kidney disease?
+Lifestyle changes can significantly slow the progression of kidney disease and, in some cases, may improve kidney function, especially in the early stages. However, the effectiveness of lifestyle changes depends on the severity of the disease, the presence of other health issues, and how promptly interventions are made.
What role does diet play in maintaining kidney health?
+Diet plays a crucial role in maintaining kidney health. A balanced diet that is low in salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help support kidney function. Additionally, for individuals with kidney disease, a customized diet that limits certain nutrients such as protein, phosphorus, and potassium may be necessary to reduce the strain on the kidneys.
How does regular exercise contribute to kidney health?
+Regular exercise is beneficial for overall health, including kidney health. It can help control blood pressure, improve blood sugar levels, and contribute to a healthy weight, all of which can reduce the risk of developing kidney disease or slow its progression if it already exists.
Can kidney function be improved through supplementation or vitamins?
+While certain supplements and vitamins may be beneficial for overall health, their impact on kidney function is more nuanced. Some supplements, especially those containing potassium or phosphorus, can actually be harmful to individuals with kidney disease. Therefore, any supplementation should be discussed with a healthcare provider to ensure it is safe and beneficial.



