10+ Sedimentation Rate Secrets For Better Health
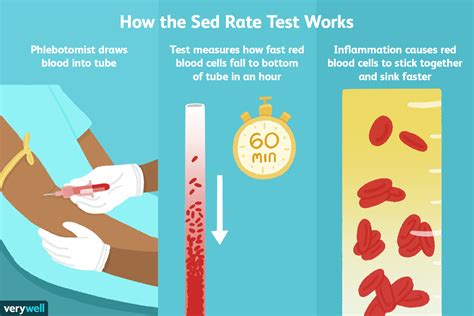
Sedimentation rate, often referred to as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), is a blood test that measures how quickly erythrocytes (red blood cells) settle at the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. It indirectly measures how much inflammation is in the body. The sedimentation rate is a simple yet powerful tool for diagnosing and monitoring various conditions, including inflammatory diseases, infections, and cancers. Understanding the secrets behind sedimentation rates can provide valuable insights into achieving better health.
What Influences Sedimentation Rate?
Several factors can influence sedimentation rates, including age, gender, and the presence of inflammatory conditions. Generally, women tend to have higher ESR values than men, and ESR increases with age. Pregnancy can also cause an increase in ESR. It’s crucial to understand these baseline variations to accurately interpret sedimentation rate results.
How Is Sedimentation Rate Tested?
The test for sedimentation rate involves taking a blood sample, which is then placed in a vertical tube. The rate at which the red blood cells settle to the bottom of the tube is measured over a specific period, usually one hour. The result is reported in millimeters per hour (mm/h). A higher rate indicates greater inflammation in the body.
Interpreting Sedimentation Rate Results
Interpreting the results of a sedimentation rate test requires careful consideration of the individual’s health context. Generally, a low sedimentation rate indicates a lower level of inflammation, while a high rate may suggest the presence of an inflammatory condition. However, the sedimentation rate is not specific to any particular disease and must be interpreted in conjunction with other diagnostic tests and clinical findings.
Factors That Can Affect Sedimentation Rate Results
- Age and Gender: As mentioned, age and gender can influence ESR values, with higher values often observed in older adults and women.
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy is known to increase ESR due to changes in blood composition and increased fibrinogen levels, which can affect how red blood cells settle.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids and aspirin, can influence ESR by reducing inflammation.
- Technical Issues: The way the blood sample is handled can also affect the ESR result, emphasizing the importance of proper laboratory procedures.
The Significance of Sedimentation Rate in Disease Diagnosis
- Inflammatory Diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus are characterized by elevated sedimentation rates due to chronic inflammation.
- Infections: Bacterial and viral infections can cause an increase in ESR as the body responds with an inflammatory reaction.
- Cancer: Some types of cancer, especially those affecting the blood or bone marrow, can lead to increased ESR.
Lifestyle Modifications to Reduce Inflammation
While the sedimentation rate itself is not directly influenced by lifestyle, reducing inflammation through diet and lifestyle changes can lead to lower ESR values, indicating better health. Strategies include:
- Anti-inflammatory Diet: Consuming foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and fiber can help reduce inflammation.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity has anti-inflammatory effects and can contribute to overall health.
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation and yoga can help manage stress, which is known to contribute to inflammation.
Monitoring Sedimentation Rate for Health Management
For individuals with chronic inflammatory conditions, regular monitoring of the sedimentation rate can be an essential tool for managing their health. It provides a quantitative measure of the level of inflammation, helping healthcare providers adjust treatment plans as necessary.
Sedimentation Rate and Disease Prognosis
In some cases, the sedimentation rate can offer insights into the prognosis of certain diseases. For example, very high ESR values have been associated with a poorer prognosis in various cancers and inflammatory diseases. Monitoring changes in ESR over time can help assess the effectiveness of treatment and disease progression.
Future Directions in Sedimentation Rate Testing
Advancements in technology and laboratory methods continue to refine sedimentation rate testing, making it more accurate and accessible. Automated systems for measuring ESR are becoming more common, reducing the potential for human error and improving turnaround times for results.
Conclusion
The sedimentation rate is a valuable diagnostic tool that offers a window into the body’s inflammatory status. Understanding the factors that influence sedimentation rate, how it’s tested, and its interpretation can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health. By recognizing the role of lifestyle in managing inflammation and the importance of regular monitoring for those with chronic conditions, individuals can take proactive steps towards better health.
What does a high sedimentation rate indicate?
+A high sedimentation rate typically indicates the presence of inflammation in the body, which could be due to a variety of conditions including infections, inflammatory diseases, or cancers.
How can I lower my sedimentation rate?
+Lowering your sedimentation rate involves reducing inflammation in your body. This can be achieved through lifestyle changes such as adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, engaging in regular exercise, managing stress, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Is a sedimentation rate test painful?
+The sedimentation rate test involves a blood draw, which may cause temporary discomfort. However, the procedure is generally quick and minimally invasive.
Can I prepare for a sedimentation rate test?
+Generally, no specific preparation is required for a sedimentation rate test. However, it’s essential to follow any instructions provided by your healthcare provider, which may include fasting or avoiding certain medications before the test.
How often should I get a sedimentation rate test?
+The frequency of sedimentation rate tests depends on your health status and the presence of any underlying conditions. Your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate testing schedule based on your individual needs and medical history.