10 Smz Tmp Drug Facts For Better Health

In the realm of health and medicine, understanding the specifics of various drugs is crucial for both healthcare professionals and the general public. One such drug that has garnered attention is SMZ-TMP, known in full as Sulfamethoxazole-Trimethoprim. This antibiotic is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections. Here are 10 key facts about SMZ-TMP that can contribute to better health outcomes:
Composition and Mechanism: SMZ-TMP is a combination antibiotic consisting of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim. It works by inhibiting the growth and multiplication of bacteria. Sulfamethoxazole belongs to a class of drugs known as sulfonamides, which work by inhibiting the growth of bacteria by interfering with their ability to produce folic acid, a necessary nutrient for bacterial growth. Trimethoprim enhances this effect by inhibiting the production of tetrahydrofolic acid, further starving the bacteria of necessary nutrients.
Uses: This combination drug is used to treat various types of infections, including urinary tract infections, bronchitis, traveler’s diarrhea, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) skin infections, and certain types of pneumonia. It’s also used for the prevention of infections in people with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS.
Dosage and Administration: The dosage of SMZ-TMP varies depending on the condition being treated and the patient’s age, weight, and kidney function. It is usually taken orally, in tablet or liquid form, with or without food, every 12 hours for 10 to 14 days. It’s crucial to complete the full treatment course, even if symptoms disappear after a few days, to prevent the infection from returning.
Side Effects and Interactions: Like all medications, SMZ-TMP can cause side effects, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and an allergic reaction. Serious side effects can include severe skin reactions, liver damage, and a decrease in blood cells, which can affect the body’s ability to fight infections. It’s also important to note that SMZ-TMP can interact with other medications, such as blood thinners, and decrease their effectiveness or increase the risk of side effects.
Contraindications: There are certain conditions under which SMZ-TMP should not be used. Patients with a known allergy to sulfonamides or trimethoprim should avoid this drug. It’s also contraindicated in patients with severe liver or kidney disease, those with certain blood disorders, and in infants less than 2 months old due to the risk of displacing bilirubin from plasma proteins, potentially leading to kernicterus.
Resistance and Effectiveness: The increasing problem of antibiotic resistance can affect the effectiveness of SMZ-TMP. Resistance rates vary geographically and can be high for certain types of infections. It’s essential for healthcare providers to select antibiotics based on the most current susceptibility data available and for patients to use antibiotics only when prescribed and to complete the full course of treatment to help prevent the development of resistance.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: SMZ-TMP is categorically classified in pregnancy and should be used with caution. It is generally recommended to avoid its use during the last month of pregnancy due to the potential risk of kernicterus in the newborn. Regarding breastfeeding, sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim are excreted in breast milk, and caution should be exercised when administering this drug to a nursing mother, as it may cause kernicterus in the infant.
Pediatric and Geriatric Use: In pediatric patients, the use of SMZ-TMP requires careful consideration of the risks and benefits. It should not be used in infants less than 2 months of age due to the potential risk of kernicterus. For geriatric patients, dosage adjustments may be necessary due to decreased renal function that occurs with age.
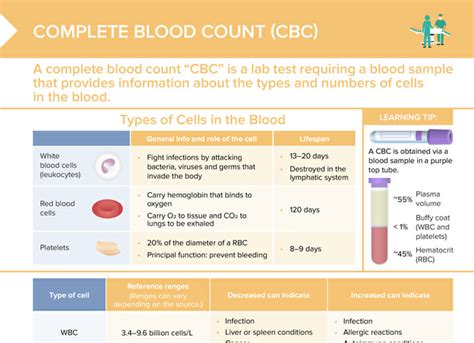
Laboratory Tests and Monitoring: Patients taking SMZ-TMP, especially those on long-term therapy, should have complete blood counts and liver function tests performed regularly. This monitoring helps in the early detection of adverse effects such as leukopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and hepatotoxicity.
Storage and Disposal: SMZ-TMP tablets and suspension should be stored at room temperature, away from moisture and light. The suspension should be shaken well before each use and discarded after the expiration date or after 10 days if not used.
In conclusion, SMZ-TMP is a valuable antibiotic combination for the treatment of a wide range of bacterial infections. However, its use requires careful consideration of patient factors, potential side effects, and the risk of resistance. Understanding these aspects can lead to better health outcomes by ensuring that the drug is used effectively and safely.
What is SMZ-TMP used for?
+SMZ-TMP is used to treat various types of infections, including urinary tract infections, bronchitis, traveler's diarrhea, and certain types of pneumonia. It is also used for the prevention of infections in people with weakened immune systems.
How does SMZ-TMP work?
+SMZ-TMP works by inhibiting the growth and multiplication of bacteria. It does this by interfering with the bacteria's ability to produce folic acid and tetrahydrofolic acid, necessary nutrients for bacterial growth.
What are the potential side effects of SMZ-TMP?
+Potential side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and an allergic reaction. Serious side effects can include severe skin reactions, liver damage, and a decrease in blood cells.
Can SMZ-TMP be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
+SMZ-TMP should be used with caution in pregnancy, especially during the last month, due to the risk of kernicterus in the newborn. For breastfeeding mothers, caution should also be exercised due to the potential risk of kernicterus in the infant.
How should SMZ-TMP be stored and disposed of?
+SMZ-TMP should be stored at room temperature, away from moisture and light. The suspension should be shaken well before each use and discarded after the expiration date or after 10 days if not used.
What is the importance of completing the full course of SMZ-TMP treatment?
+Completing the full course of treatment is crucial to prevent the infection from returning and to prevent the development of antibiotic resistance. Even if symptoms disappear after a few days, the full treatment course should be completed as directed by a healthcare provider.
Understanding these critical aspects of SMZ-TMP can help ensure its safe and effective use, contributing to better health outcomes for those requiring antibiotic treatment.