10 Walking Pneumonia Facts For Faster Recovery
Walking pneumonia, also known as atypical pneumonia, is a type of pneumonia that is not caused by the traditional pneumonia bacteria. Instead, it is usually caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae, a type of bacteria that is different from the ones that cause traditional pneumonia. Walking pneumonia is called “walking” because its symptoms are often mild enough that one can still be walking around and carrying out daily activities, unlike traditional pneumonia which can be severe and require hospitalization.
One of the key challenges with walking pneumonia is that its symptoms can be similar to those of a cold or flu, making it difficult to diagnose. However, understanding the facts about walking pneumonia can help in seeking the right treatment and ensuring a faster recovery. Here are 10 important facts about walking pneumonia:
Causes and Risk Factors: Walking pneumonia is most commonly caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. It can affect anyone but is more common among school-aged children and young adults. Crowded living conditions, such as those found in schools, dormitories, and military barracks, can increase the risk of spreading the infection.
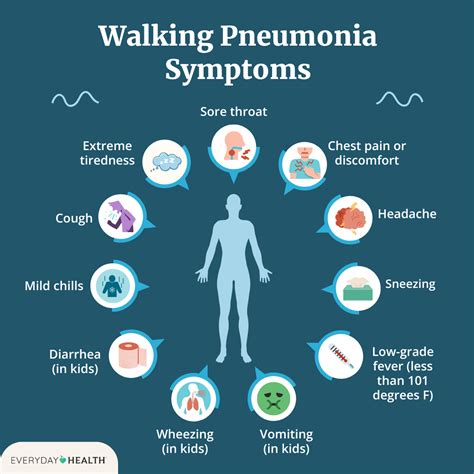
Symptoms: The symptoms of walking pneumonia can be mild and may resemble those of a cold or flu. They include cough, sore throat, fever, headache, and fatigue. In some cases, symptoms can be more severe, and individuals may experience chest pain, difficulty breathing, or a persistent cough that produces mucus.
Transmission: Walking pneumonia is contagious and can be spread through droplets that are released when an infected person coughs or sneezes. It can also be spread by touching surfaces that have the bacteria on them and then touching one’s mouth, nose, or eyes.
Diagnosis: Diagnosing walking pneumonia can be challenging because its symptoms are similar to those of other respiratory infections. A healthcare provider may use a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests such as chest X-rays and blood tests to diagnose walking pneumonia.
Treatment: The treatment for walking pneumonia usually involves antibiotics, which are effective against the bacteria that cause the infection. It’s crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by the healthcare provider, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
Recovery Time: The recovery time for walking pneumonia can vary depending on the severity of the symptoms and the effectiveness of the treatment. Generally, people start to feel better within a few days of starting antibiotic treatment, but full recovery may take a couple of weeks.
Complications: While walking pneumonia is typically mild, it can lead to complications in some cases, especially in older adults or people with underlying health conditions. Possible complications include bronchitis, sinus infections, and in rare cases, more severe respiratory infections.
Prevention: Preventing the spread of walking pneumonia involves practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently, covering the mouth when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with people who are infected. Getting plenty of rest, eating a healthy diet, and not smoking can also help in preventing respiratory infections.
Vaccination: There is no vaccine specifically for Mycoplasma pneumoniae, the bacteria that cause walking pneumonia. However, practicing good hygiene and following preventive measures can reduce the risk of infection.
Self-Care: Self-care is an important part of recovering from walking pneumonia. This includes resting, drinking plenty of fluids to stay hydrated, using a humidifier to relieve cough and congestion, and avoiding irritants such as smoke and pollution. Over-the-counter medications can help manage symptoms such as fever and cough, but it’s essential to follow the advice of a healthcare provider.
In conclusion, understanding the causes, symptoms, transmission, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of walking pneumonia is crucial for managing the condition effectively. By being aware of these aspects, individuals can seek timely medical attention, adhere to the prescribed treatment, and take necessary precautions to prevent the spread of the infection, ultimately leading to a faster recovery.
What are the primary symptoms of walking pneumonia?
+The primary symptoms of walking pneumonia include cough, sore throat, fever, headache, and fatigue. In some cases, individuals may experience more severe symptoms such as chest pain, difficulty breathing, or a persistent cough that produces mucus.
How is walking pneumonia diagnosed?
+Diagnosing walking pneumonia involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests such as chest X-rays and blood tests. Since the symptoms can be similar to those of other respiratory infections, a thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider is necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
What is the typical treatment for walking pneumonia?
+The typical treatment for walking pneumonia involves antibiotics that are effective against Mycoplasma pneumoniae, the bacteria that cause the infection. Completing the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by the healthcare provider is crucial for ensuring that the infection is fully cleared.
Can walking pneumonia be prevented?
+While there is no vaccine for walking pneumonia, practicing good hygiene such as frequent hand washing, covering the mouth when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals can help reduce the risk of infection. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and adequate rest, can help in preventing respiratory infections.
What are some common complications of walking pneumonia?
+Walking pneumonia can lead to complications such as bronchitis, sinus infections, and in rare cases, more severe respiratory infections. These complications are more likely to occur in older adults or individuals with underlying health conditions. Early diagnosis and treatment can help in preventing these complications.
How long does it take to recover from walking pneumonia?
+The recovery time for walking pneumonia can vary but generally, individuals start to feel better within a few days of starting antibiotic treatment. Full recovery may take a couple of weeks. It's essential to follow the healthcare provider's advice and complete the full course of antibiotics to ensure a complete recovery.
By understanding these facts and taking proactive steps, individuals can better manage walking pneumonia, reduce the risk of complications, and ensure a faster recovery. Remember, if symptoms persist or worsen, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly.