11 Human Body Temp C Secrets For Better Health
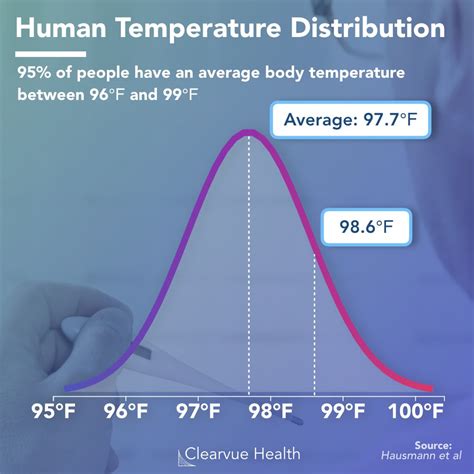
The human body temperature, typically around 37°C (98.6°F), is a vital sign that can indicate overall health and wellbeing. However, there are many secrets and nuances to body temperature that can affect our health in profound ways. Let’s delve into 11 human body temperature secrets that can help us better understand our bodies and improve our health.
1. Normal Body Temperature Range
The average body temperature is often cited as 37°C, but it’s essential to understand that normal body temperature can vary from person to person and throughout the day. A range of 36.5°C to 37.5°C (97.7°F to 99.5°F) is generally considered normal. This variation is crucial for understanding when your body temperature might be indicating an issue.
2. Temperature Regulation
The hypothalamus acts as the body’s thermostat, regulating body temperature through mechanisms like sweating and shivering. Understanding how your body regulates temperature can provide insights into your metabolic health and overall bodily functions.
3. Circadian Rhythms and Body Temperature
Body temperature naturally fluctuates throughout the day, peaking in the late afternoon and decreasing during sleep. This fluctuation is part of our natural circadian rhythm and can influence sleep quality, hormone secretion, and metabolic rate.
4. The Impact of Exercise
Exercise can significantly raise body temperature due to increased metabolic rate and muscle activity. Monitoring body temperature during and after exercise can help in understanding individual limits and preventing overheating, which can lead to heat exhaustion or heatstroke.
5. Diet and Body Temperature
Certain foods, especially those high in protein, can increase metabolic rate and thus raise body temperature slightly. Additionally, spicy foods can make you feel hotter due to the dilation of blood vessels close to the skin’s surface. Understanding the thermal effect of food can help in managing weight and metabolic health.
6. Hormonal Influence on Body Temperature
Hormonal changes, such as those experienced during menopause or pregnancy, can affect body temperature. For example, some women may experience hot flashes during menopause, which can significantly alter their perception of body temperature.
7. Stress and Body Temperature
Stress can lead to a slight increase in body temperature due to the release of stress hormones like adrenaline, which prepares the body for ‘fight or flight’ by increasing heart rate and metabolism.
8. The Role of Sleep
Poor sleep quality or sleep disorders can disrupt the body’s natural temperature regulation, leading to fluctuations in body temperature. A cooler body temperature is associated with deeper sleep, highlighting the importance of a comfortable sleeping environment for health.
9. Age and Body Temperature
As people age, their ability to regulate body temperature can become less efficient. Older adults may be more susceptible to hypothermia or heat-related illnesses due to decreased metabolism, reduced activity levels, and potential chronic health conditions.
10. Medications and Body Temperature
Certain medications can affect body temperature regulation. For example, some antidepressants and blood pressure medications can interfere with the body’s ability to cool down, potentially leading to heat-related illnesses.
11. Monitoring Body Temperature for Health
Regularly monitoring body temperature, especially during illness or when experiencing symptoms like fever, can provide crucial insights into health status. Digital thermometers offer accurate and quick readings, making it easier to track temperature fluctuations over time.
Conclusion
Body temperature is a complex aspect of human health, influenced by a myriad of factors including circadian rhythms, diet, exercise, and hormonal changes. By understanding these nuances, individuals can better appreciate the intricacies of their bodily functions and take proactive steps towards maintaining optimal health.
FAQ Section
What is considered a normal range for body temperature?
+A normal body temperature range is generally considered to be between 36.5°C and 37.5°C (97.7°F to 99.5°F), though it can vary slightly from person to person.
How does exercise affect body temperature?
+Exercise increases body temperature due to the increased metabolic rate and muscle activity. It’s essential to stay hydrated and monitor body temperature during and after exercise to prevent overheating.
Can diet influence body temperature?
+Yes, diet can influence body temperature. Foods high in protein can increase metabolic rate, slightly raising body temperature. Additionally, spicy foods can make you feel hotter due to vessel dilation near the skin’s surface.
How does sleep affect body temperature regulation?
+Poor sleep quality can disrupt the body’s natural temperature regulation. A cooler body temperature is associated with deeper sleep, emphasizing the importance of a comfortable sleeping environment for overall health.
What role does stress play in body temperature?
+Stress can lead to a slight increase in body temperature due to the release of stress hormones like adrenaline, which increases heart rate and metabolism as part of the ‘fight or flight’ response.
Can age affect how well the body regulates temperature?
+Yes, aging can affect the body’s ability to regulate temperature. Older adults may have a harder time maintaining their body temperature, making them more susceptible to hypothermia or heat-related illnesses.



