12 Blood Sugar Levels For Better Health
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, as it directly impacts energy levels, weight management, and the risk of developing chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease. The importance of managing blood sugar cannot be overstated, given its implications on both immediate and long-term health. Understanding what constitutes healthy blood sugar levels and how to manage them is essential for preventing complications and ensuring better health outcomes.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
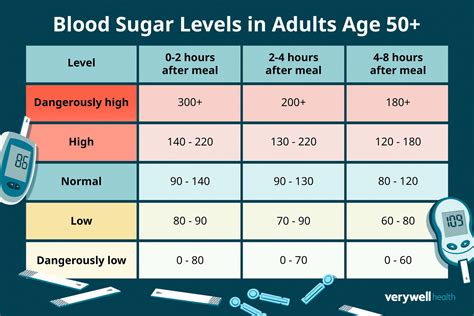
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the body’s primary energy source. It is obtained from the food we eat and is crucial for the proper functioning of the body’s cells. The level of glucose in the blood is measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). To understand whether your blood sugar levels are within a healthy range, it’s essential to know the normal blood sugar levels.
- Fasting Blood Sugar: For individuals without diabetes, normal fasting blood sugar levels are typically between 70 and 99 mg/dL.
- After Eating: Two hours after eating, blood sugar should be below 140 mg/dL for people without diabetes.
Importance of Monitoring Blood Sugar
Monitoring blood sugar levels is vital, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing diabetes. It helps in managing the condition effectively, preventing serious health issues like kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems. Regular monitoring can also indicate how different factors (like food, exercise, and medications) affect blood sugar levels, allowing for personalized adjustments to achieve better health.
Blood Sugar Levels and Health Implications
Understanding the implications of different blood sugar levels is critical. For instance: - High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia): Levels above 180 mg/dL can lead to symptoms like increased thirst and urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. Prolonged high blood sugar can lead to serious complications. - Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia): Levels below 70 mg/dL can cause shakiness, dizziness, sweating, hunger, irritability, confusion, or even loss of consciousness in severe cases.
Strategies for Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Effective management of blood sugar levels involves a combination of lifestyle changes and, if necessary, medication. Key strategies include: - Dietary Changes: Eating a balanced diet that is low in sugar, saturated fats, and salt but high in fiber can help manage blood sugar levels. Foods with a low glycemic index (GI) are particularly beneficial as they cause a slower and smaller rise in blood sugar. - Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps the body use insulin more efficiently, lowering blood sugar levels. Aerobic exercises and strength training are both beneficial. - Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and helps manage existing diabetes. - Stress Management: Chronic stress can affect blood sugar control. Practicing stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help.
Role of Nutrition in Blood Sugar Management
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in managing blood sugar levels. Certain foods and nutrients can help lower blood sugar, while others can cause it to spike. - Fiber-Rich Foods: Foods high in fiber like oats, barley, nuts, legumes, fruits, and vegetables can slow the absorption of sugar and cholesterol into the bloodstream. - Protein and Healthy Fats: Including sources of protein and healthy fats in meals can help regulate blood sugar levels by slowing down the digestion of carbohydrates and thereby reducing the spike in blood glucose. - Hydration: Drinking enough water helps the kidneys flush out toxins, including excess glucose, from the body.
Benefits of Lowering Blood Sugar Levels
For individuals with diabetes or prediabetes, lowering blood sugar levels can significantly reduce the risk of complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision problems. Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels also improves energy levels, supports weight loss, and enhances overall quality of life.
Implementing Sustainable Lifestyle Changes
While managing blood sugar levels requires making significant lifestyle changes, these adjustments can be sustainable and beneficial in the long term. It’s essential to approach these changes gradually, allowing time for the body to adjust. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends can also make the journey towards better health more manageable.
Advanced Blood Sugar Management Techniques
For some individuals, standard management techniques might not be enough. Advanced strategies may include: - Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): This involves wearing a device that tracks glucose levels throughout the day and night, providing detailed insights into how different activities, foods, and medications affect blood sugar. - Insulin Therapy: For individuals with type 1 diabetes and some with type 2 diabetes, insulin injections or an insulin pump may be necessary to manage blood sugar levels.
Future Trends in Blood Sugar Management
The future of blood sugar management looks promising, with ongoing research into new technologies and treatments. Advances in wearable devices, artificial intelligence, and personalized medicine are expected to make managing blood sugar levels more efficient and effective. These innovations will likely provide more precise control over glucose levels, reduce the burden of diabetes management, and improve health outcomes.
Conclusion
Managing blood sugar levels is a critical aspect of achieving and maintaining better health, especially for individuals with diabetes or at risk of developing the condition. Through a combination of dietary changes, regular physical activity, stress management, and, if necessary, medication, individuals can effectively manage their blood sugar levels. As research and technology continue to evolve, the future holds much promise for improved blood sugar management and better health outcomes for all.
What are the risks associated with high blood sugar levels?
+High blood sugar levels can lead to serious health issues, including heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems. Managing blood sugar levels is crucial to prevent these complications and ensure better health outcomes.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on the individual’s health status and the presence of diabetes. Generally, it is recommended to check levels at least once a day, but this may vary based on specific health needs and as advised by a healthcare provider.
What role does diet play in managing blood sugar levels?
+Diet plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels. Eating a balanced diet that is low in sugar, saturated fats, and salt but high in fiber can help regulate blood sugar levels. Choosing foods with a low glycemic index can also help manage blood sugar.
Can exercise help manage blood sugar levels?
+Yes, regular exercise is beneficial for managing blood sugar levels. Physical activity helps the body use insulin more efficiently, which can lower blood sugar levels. Both aerobic exercises and strength training are recommended for optimal benefits.
How does stress affect blood sugar levels?
+Chronic stress can affect blood sugar control by increasing the production of stress hormones like cortisol, which can raise blood sugar levels. Practicing stress-reducing techniques can help manage stress and improve blood sugar control.
What are the benefits of maintaining healthy blood sugar levels?
+Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels can reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes, improve energy levels, support weight management, and enhance overall quality of life. It also reduces the risk of heart disease, kidney failure, and vision problems.