12 Blood Sugar Test Tips For Better Health
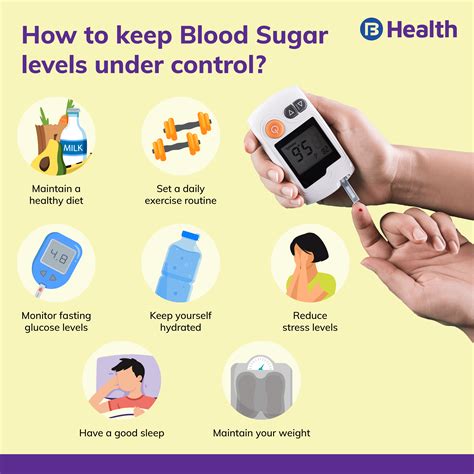
Monitoring blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of managing diabetes and maintaining overall health. The process involves pricking your finger with a lancet to collect a small blood sample, which is then analyzed by a glucose meter to determine your blood sugar level. While the task may seem straightforward, there are several tips and best practices to keep in mind to ensure you’re getting accurate readings and making the most of your testing routine.
Choosing the Right Glucose Meter
The first step in blood sugar testing is selecting a reliable glucose meter. With numerous options available on the market, it’s essential to consider factors such as accuracy, ease of use, and additional features that might be important to you, such as Bluetooth connectivity for syncing with your smartphone or a large display for better readability. Look for meters that have been certified by reputable organizations, ensuring they meet certain standards for accuracy.
Understanding Your Targets
Before you start testing, it’s crucial to understand what your blood sugar targets are. These can vary based on the time of day, your health status, and the type of diabetes you have (if you have diabetes). Generally, before meals, your blood sugar should be between 70 and 130 mg/dL, and less than 180 mg/dL after meals. However, your healthcare provider may give you specific targets based on your individual needs.
Preparing for a Test
Preparation is key to getting an accurate reading. Ensure your hands are clean and dry, as dirt or moisture can interfere with the test results. Remove any lotion or oil from your hands, as these can also affect the reading. If you’re testing after a meal, wait for the recommended time frame, usually 1 to 2 hours after eating, to get a true reading of how your body is handling the glucose from the meal.
Selecting the Right Lance and Technique
The lancet you use can impact the comfort and effectiveness of your blood sugar testing. Choose a lancet with a fine needle and adjustable depth setting to minimize discomfort. The technique is also crucial; typically, the side of your fingertip is recommended because it’s less painful and has fewer nerve endings. However, it’s essential to rotate the sites to avoid irritating any one area too much.
Recording Your Results
Keeping a log of your blood sugar readings is vital for understanding patterns and trends in your blood sugar levels. This can be done manually in a journal or digitally through an app that syncs with your glucose meter. Recording the time of day, what you ate, and any physical activity before the test can also provide valuable context for your readings.
Managing Stress
Stress can significantly impact blood sugar levels, causing them to rise. This makes managing stress a crucial part of diabetes management and blood sugar control. Techniques such as deep breathing, yoga, and meditation can help reduce stress levels and, consequently, help stabilize blood sugar.
Hydration and Its Impact
Being well-hydrated is essential for overall health, and it also plays a role in blood sugar management. Sometimes, the body can mistake thirst for hunger, leading to unnecessary snacking that can impact blood sugar levels. Drinking enough water can help prevent this and support the body’s natural processes for regulating blood sugar.
Exercise and Blood Sugar
Regular physical activity is a cornerstone of diabetes management. Exercise can lower blood sugar levels and improve your body’s ability to use insulin. However, it’s essential to monitor your blood sugar before, during, and after exercise to understand how different activities affect your levels and to prevent hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), especially during prolonged or intense exercise sessions.
Nutrition and Meal Planning
What you eat has a direct impact on your blood sugar levels. Understanding the glycemic index of foods, which measures how quickly foods raise blood sugar levels, can help you make informed dietary choices. Additionally, working with a dietitian or using meal planning resources can provide personalized recommendations for managing blood sugar through nutrition.
Travel Considerations
When traveling, especially across different time zones, it’s crucial to consider how this might affect your blood sugar testing routine and medication schedule. Keep your glucose meter and supplies easily accessible, and be aware of any travel restrictions on the transportation of diabetes supplies.
Backup Planning
Always have a backup plan in case something goes wrong. This could mean having an extra glucose meter and supplies in a different location, knowing where to buy supplies in an emergency, or having a list of emergency contacts.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems (CGMS)
For some individuals, especially those with type 1 diabetes or those who experience significant fluctuations in blood sugar levels, a Continuous Glucose Monitoring System (CGMS) might be recommended. These devices provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day and night, offering detailed insights into how different factors (like food, exercise, and sleep) impact blood sugar levels.
What is the ideal blood sugar level before meals?
+How often should I test my blood sugar?
+The frequency of blood sugar testing depends on several factors, including the type of diabetes you have, your treatment plan, and how well your blood sugar levels are controlled. Typically, individuals with type 1 diabetes or those using insulin may need to test more frequently than those with type 2 diabetes who are managing their condition through diet and oral medications.
Can I use any lancet for blood sugar testing?
+No, it's recommended to use a lancet specifically designed for blood sugar testing. These lancets are typically finer and designed to cause less discomfort. They also come in different gauges (thicknesses), and some allow for depth adjustment, which can help reduce pain.
How does exercise affect blood sugar levels?
+Regular physical activity can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. However, the immediate effect of exercise on blood sugar can vary depending on the intensity and duration of the activity. It's essential to monitor blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise to understand how physical activity impacts your levels and to prevent hypoglycemia.
Can stress impact blood sugar levels?
+Yes, stress can significantly impact blood sugar levels. When you're under stress, your body releases hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can cause your blood sugar to rise. Managing stress through techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga can help mitigate this effect and support overall blood sugar management.
How does hydration affect blood sugar control?
+Staying hydrated is crucial for overall health and can also play a role in blood sugar management. Sometimes, thirst can be mistaken for hunger, leading to unnecessary eating that can impact blood sugar levels. Drinking enough water can help regulate blood sugar levels and support the body's natural functions.
In conclusion, managing blood sugar levels effectively involves a combination of regular testing, healthy lifestyle choices, and awareness of how different factors can impact your levels. By understanding these elements and working closely with your healthcare team, you can develop a personalized plan that helps you maintain better control over your blood sugar and supports your overall health and well-being. Whether you’re living with diabetes or aiming to prevent its onset, the right approach to blood sugar management can make a significant difference in your quality of life.