12+ Goiter Symptoms To Know Today
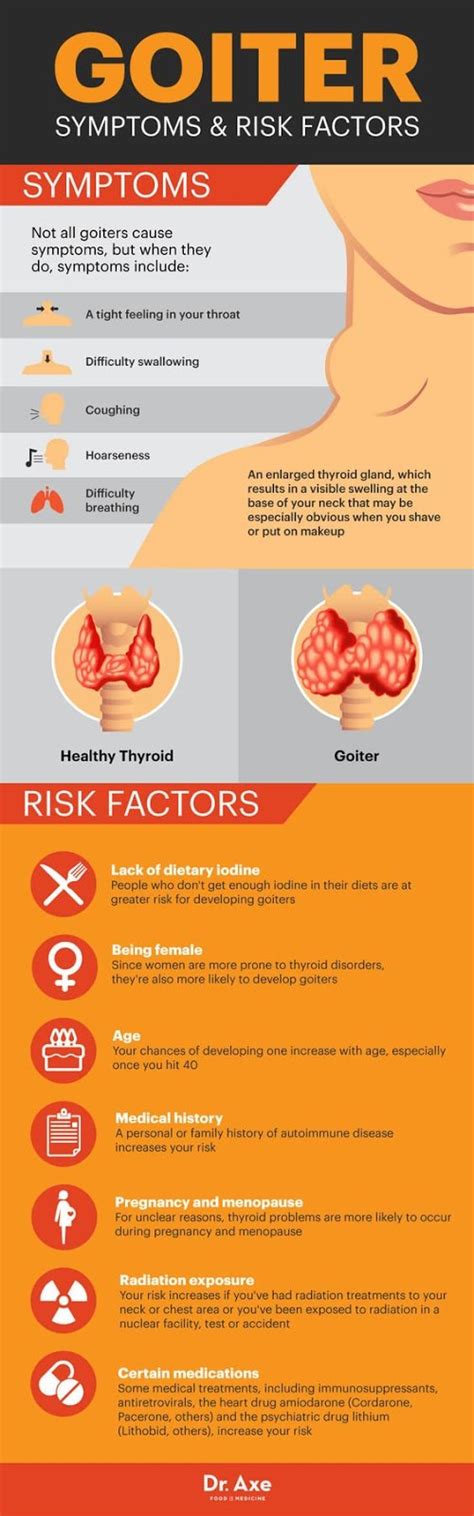
The thyroid gland, a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including growth, development, and metabolism. However, when the thyroid gland becomes inflamed or enlarged, it can lead to a condition known as goiter. Goiter symptoms can vary in severity and may develop gradually over time, making it essential to be aware of the signs and seek medical attention if you suspect you have a thyroid issue.
One of the primary causes of goiter is a lack of iodine in the diet, which is essential for the production of thyroid hormones. Other potential causes include thyroid nodules, thyroid cancer, and certain medications. In some cases, goiter can be a symptom of an underlying condition, such as hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) or hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid). Understanding the underlying cause of goiter is crucial in determining the appropriate course of treatment.
Common Goiter Symptoms
- Enlargement of the Thyroid Gland: The most noticeable symptom of goiter is the swelling of the thyroid gland, which can cause the neck to appear swollen or bulging.
- Neck Discomfort: As the thyroid gland enlarges, it can cause discomfort or pain in the neck, which may worsen when swallowing or turning the head.
- Difficulty Swallowing: The enlarged thyroid gland can put pressure on the esophagus, leading to difficulty swallowing or a sensation of food getting stuck in the throat.
- Breathing Difficulties: In severe cases, the enlarged thyroid gland can compress the trachea, leading to breathing difficulties or shortness of breath.
- Coughing: The pressure on the trachea can also cause coughing, which may be dry and persistent.
- Fatigue: Hypothyroidism, a common underlying cause of goiter, can cause fatigue, weakness, and a general feeling of being unwell.
- Weight Gain: An underactive thyroid gland can lead to weight gain, particularly in the midsection of the body.
- Cold Intolerance: People with hypothyroidism may feel cold even in mild temperatures, as the thyroid gland plays a role in regulating body temperature.
- Dry Skin: Hypothyroidism can cause dry, rough skin, which may be accompanied by hair loss and brittle nails.
- Memory Problems: Some people with goiter may experience memory problems, difficulty concentrating, or depression.
- Menstrual Irregularities: Women with goiter may experience changes in menstrual cycles, including heavier or lighter periods, or irregular ovulation.
- Muscle Weakness: The thyroid gland plays a role in regulating muscle strength, and an underactive thyroid gland can lead to muscle weakness or aches.
Advanced Symptoms
In addition to these common symptoms, some people with goiter may experience more advanced symptoms, such as:
- Thyroid Nodules: The growth of nodules on the thyroid gland, which can be benign or cancerous.
- Thyroid Cancer: In rare cases, goiter can be a symptom of thyroid cancer, which requires prompt medical attention.
- Hyperthyroidism: An overactive thyroid gland can cause symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and increased appetite.
Treatment Options
Treatment for goiter depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to regulate thyroid hormone levels, while in other cases, surgery may be necessary to remove part or all of the thyroid gland.
Step-by-Step Treatment Approach
- Medical Evaluation: A thorough medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause of goiter.
- Medication: Prescription of medication to regulate thyroid hormone levels, if necessary.
- Surgery: Surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland, if necessary.
- Follow-up Care: Regular follow-up care to monitor thyroid hormone levels and adjust treatment as needed.
Prevention
While goiter can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics and underlying medical conditions, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet that includes iodine-rich foods, such as seafood and dairy products, can help support thyroid health.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help flush out toxins and support overall health.
- Manage Stress: Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as yoga or meditation, can help manage stress and support thyroid health.
What are the most common causes of goiter?
+The most common causes of goiter include iodine deficiency, thyroid nodules, and thyroid cancer. Other potential causes include certain medications and underlying medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
How is goiter diagnosed?
+Goiter is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as thyroid function tests and imaging studies.
Can goiter be prevented?
+While goiter can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics and underlying medical conditions, maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle can help reduce your risk. Eating a balanced diet that includes iodine-rich foods and staying hydrated can help support thyroid health.
In conclusion, goiter is a complex condition that requires prompt medical attention. By understanding the common symptoms, underlying causes, and treatment options, you can take the first step towards managing your thyroid health and preventing long-term complications. Remember to maintain a healthy diet and lifestyle, and seek medical attention if you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above.


