12 Wbc Count Tips For Faster Recovery
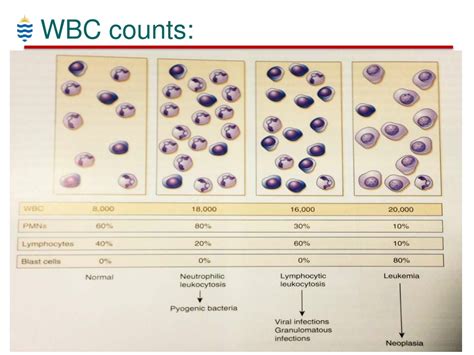
A low white blood cell (WBC) count, also known as leukopenia, can make you more susceptible to infections and slower to recover from illnesses. This is because WBCs are a crucial part of your immune system, helping to fight off invading pathogens and other foreign substances. If you’re experiencing a low WBC count, it’s essential to take proactive steps to support your immune system and promote faster recovery. Here are 12 tips to help you increase your WBC count and get back to full health:
1. Nutrition and Diet
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help support your immune system. Certain foods are particularly beneficial for boosting WBC count, including: - Citrus fruits and berries for their high vitamin C content, which can help stimulate the production of WBCs. - Leafy green vegetables like spinach and kale, rich in folate, which is essential for the production of new cells, including WBCs. - Nuts and seeds for their healthy fats and antioxidant properties. - Fatty fish like salmon, which is rich in vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, both important for immune function.
2. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water is crucial for the proper functioning of all body systems, including the immune system. Adequate hydration helps in the production and circulation of WBCs, ensuring they can reach and combat infections effectively.
3. Exercise Regularly
Moderate exercise can help boost your immune system by increasing the circulation of WBCs. However, it’s essential to avoid overexertion, as excessive exercise can have the opposite effect and weaken your immune system. Activities like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming are excellent choices.
4. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can significantly suppress your immune system, including reducing your WBC count. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help mitigate this effect and support immune function.
5. Get Enough Sleep
Adequate sleep is vital for the health of your immune system. During sleep, your body produces cytokines, which are proteins that help fight off infections and inflammation. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to support your immune system’s function.
6. Avoid Unnecessary Antibiotics
While antibiotics are essential for treating bacterial infections, using them unnecessarily can disrupt the balance of your gut microbiome, which is crucial for immune system function. Always follow your doctor’s advice regarding antibiotic use.
7. Consider Probiotics
Probiotics can help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, supporting your immune system. Foods rich in probiotics include yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables like sauerkraut and kimchi. You can also consider taking probiotic supplements after consulting with your healthcare provider.
8. Limit Alcohol and Tobacco
Both alcohol and tobacco can negatively impact your immune system. Alcohol can impair the function of WBCs, while tobacco smoke can damage the lungs and make them more susceptible to infections. Reducing or eliminating these substances can help support immune health.
9. Get Enough Vitamin D
Vitamin D is important for the regulation of immune cells. You can boost your vitamin D levels through sunlight exposure, supplements, or vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified dairy products. However, always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplements.
10. Reduce Exposure to Toxins
Minimizing your exposure to environmental toxins, such as pesticides and heavy metals, can help protect your immune system. Using protective gear when handling chemicals, choosing organic produce when possible, and filtering your water can reduce your exposure to harmful substances.
11. Stay Up to Date on Vaccinations
Vaccines can help protect you from certain infections by stimulating your immune system to produce WBCs that can recognize and fight specific pathogens. Keeping your vaccinations current is an important part of immune system support.
12. Monitor and Manage Chronic Conditions
Certain chronic conditions, such as diabetes, can affect your immune system. Proper management of these conditions through medication, diet, and lifestyle changes can help minimize their impact on your WBC count and overall immune function.
Conclusion
Recovering from a low WBC count requires a multifaceted approach that includes dietary changes, lifestyle adjustments, and medical interventions when necessary. By incorporating these tips into your daily routine and consulting with healthcare professionals, you can support your immune system and work towards a faster recovery. Remember, every individual’s health journey is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. Patience, persistence, and personalized advice from healthcare providers are key to achieving optimal immune health.
What is the normal range for a WBC count?
+A normal WBC count typically ranges from 4,500 to 11,000 cells per microliter (µL) of blood. However, this range can slightly vary depending on the laboratory conducting the test.
How long does it take to recover from a low WBC count?
+The recovery time from a low WBC count can vary significantly depending on the underlying cause, the severity of the condition, and the effectiveness of the treatment. In some cases, recovery can occur within a few weeks, while in other situations, it may take several months or even longer.
Can supplements help increase WBC count?
+Certain supplements like vitamin C, zinc, and probiotics may help support immune function and potentially increase WBC count. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplements to ensure they are necessary and appropriate for your specific health situation.