130 Blood Sugar
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, and a level of 130 mg/dL is considered elevated, falling into the category of hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar. This condition can be a precursor to more serious health issues, including diabetes and cardiovascular disease, if not properly managed. Understanding the causes, consequences, and management strategies for elevated blood sugar levels is essential for individuals aiming to maintain good health.
Causes of Elevated Blood Sugar
Elevated blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, occurs when the body either cannot produce enough insulin, cannot effectively use the insulin it produces, or a combination of both. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that allows cells in the body to absorb glucose from the bloodstream and use it for energy. Several factors can contribute to high blood sugar levels, including:
- Diabetes: Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can lead to high blood sugar levels. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, resulting in a lack of insulin production. Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance (where the body’s cells do not respond to insulin as they should) and impaired insulin secretion.
- Prediabetes: A condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. It often precedes type 2 diabetes.
- Obesity: Excess body fat, particularly around the abdominal area, can lead to insulin resistance.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of regular physical activity can contribute to insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels.
- Stress: Physical or emotional stress can raise blood sugar levels.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can increase blood sugar levels.
- Sleep Deprivation: Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to insulin resistance.
Consequences of High Blood Sugar
High blood sugar levels over an extended period can have serious health consequences. Some of the complications and risks associated with elevated blood sugar include:
- Diabetic Neuropathy: Damage to the nerves, which can cause pain, numbness, or a tingling sensation in the hands and feet.
- Diabetic Retinopathy: A condition that can lead to blindness if left untreated.
- Diabetic Nephropathy: Kidney damage that can lead to chronic kidney disease or kidney failure.
- Foot Damage: Nerve damage, cuts, and blisters can become serious infections if not managed properly.
- Cardiovascular Disease: High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes.
- Hearing Impairment: Research suggests that diabetes may be linked to an increased risk of hearing loss.
Management of Elevated Blood Sugar
Managing high blood sugar levels involves a combination of lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication. Key strategies include:
- Dietary Changes: Eating a healthy, balanced diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium, and high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Foods with a low glycemic index are recommended as they digest slowly and do not cause a spike in blood sugar levels.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days a week.
- Weight Management: If overweight or obese, losing weight can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels.
- Stress Management: Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
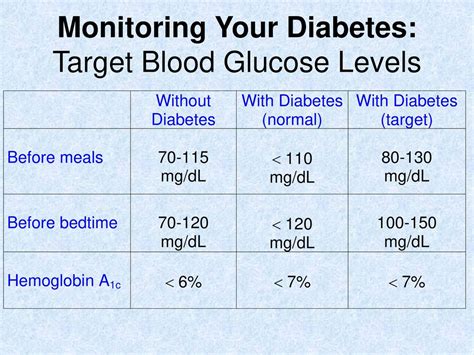
- Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels: Regularly checking blood sugar levels to understand how different factors affect them and making adjustments accordingly.
- Medication and Insulin Therapy: For some, medication or insulin therapy may be necessary to manage blood sugar levels. This should be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Implementing a Balanced Lifestyle
Implementing a balanced lifestyle is key to managing elevated blood sugar levels. This includes:
Conclusion
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is a critical component of overall health and well-being. Understanding the causes of elevated blood sugar, recognizing the potential consequences of unmanaged hyperglycemia, and implementing effective management strategies can help individuals mitigate risks and improve their quality of life. With the right combination of dietary changes, physical activity, stress management, and, when necessary, medication, individuals can effectively manage their blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of developing more serious health conditions.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
+Symptoms of high blood sugar include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, cuts or wounds that are slow to heal, and tingling or numbness in the hands and feet. However, some people may not exhibit any noticeable symptoms, making regular blood sugar checks crucial.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on the individual’s health status and the advice of their healthcare provider. Generally, people with diabetes are advised to check their blood sugar levels at least four times a day, but this can vary based on factors such as medication regimen, diet, and physical activity level.
Can high blood sugar levels be managed without medication?
+Yes, in many cases, high blood sugar levels can be managed through lifestyle changes alone, including dietary adjustments, increased physical activity, weight loss if necessary, and stress reduction techniques. However, for some individuals, especially those with diabetes, medication or insulin therapy may be necessary to achieve and maintain normal blood sugar levels.