200 Sugar Level Control: Manage Diabetes
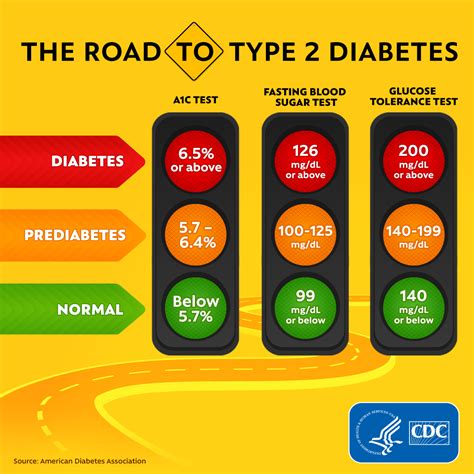
Living with diabetes requires a delicate balance of lifestyle adjustments and medical interventions to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Managing diabetes effectively is crucial to prevent complications and improve the quality of life for individuals with this condition. Blood sugar levels, measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), are a critical indicator of how well diabetes is being managed. The goal for most people with diabetes is to keep their blood sugar levels as close to normal as possible, which typically means a fasting glucose level between 70 and 130 mg/dL and a postprandial (after meal) glucose level below 180 mg/dL.
Understanding the factors that influence blood sugar levels is key to managing diabetes. Diet, physical activity, stress levels, and medication all play significant roles. A diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking, can also improve insulin sensitivity, reducing blood sugar levels. Stress can raise blood sugar levels, so engaging in stress-reducing activities like yoga or meditation can be beneficial. For many people with diabetes, medication is also a crucial part of their management plan, helping to control blood sugar levels when lifestyle changes alone are not enough.
One of the most significant challenges in managing diabetes is the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). Hypoglycemia can occur when too much insulin or oral diabetes medication is taken, when meals are skipped, or when physical activity is increased without adequate food intake. Symptoms of hypoglycemia include shakiness, dizziness, sweating, hunger, headaches, and confusion. Severe cases can lead to loss of consciousness and, if untreated, can be life-threatening. Hyperglycemia, on the other hand, occurs when the body has too little insulin or cannot use it effectively, leading to high blood sugar levels. Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage the heart, eyes, kidneys, nerves, gums, and teeth.
Problem-Solution Framework: Managing Fluctuations
Managing fluctuations in blood sugar levels is critical for people with diabetes. One approach is to implement a continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS), which involves wearing a small sensor under the skin that tracks glucose levels throughout the day. This provides real-time data that can be used to adjust diet, exercise, or medication to maintain blood sugar levels within the target range. Another strategy is to follow a structured eating plan, eating meals and snacks at regular times and choosing foods that are low in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium. Engaging in regular physical activity, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, each week, can also help manage blood sugar levels.
Comparative Analysis: Different Management Approaches
Different management approaches can be effective for different individuals. Some people with diabetes may find that a strict, low-carb diet helps them maintain healthy blood sugar levels, while others may prefer a more balanced approach that includes a variety of food groups. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels can help determine the most effective management plan. For those who are insulin-dependent, learning how to adjust insulin doses based on food intake and physical activity levels can be crucial. Others may find that oral medications or non-insulin injectables are more suitable for their lifestyle and health profile. Working closely with a healthcare provider to tailor a management plan is essential.
Historical Evolution: Advances in Diabetes Management
The management of diabetes has undergone significant evolution over the years, from the discovery of insulin in the 1920s to the advanced insulins and oral medications available today. The introduction of home glucose monitors in the 1970s and 1980s revolutionized diabetes management by allowing individuals to regularly check their blood sugar levels at home. More recently, the development of continuous glucose monitoring systems and insulin pumps has provided real-time data and more precise control over blood sugar levels. Advances in medication, such as the development of GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors, have also expanded treatment options for people with diabetes, offering improved glycemic control with fewer side effects.
Technical Breakdown: Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Understanding blood sugar levels and how they are measured is fundamental to managing diabetes. Blood sugar levels are typically measured using a glucometer, which requires a small drop of blood, usually from a fingerstick, to provide a reading. Continuous glucose monitors, on the other hand, use a sensor inserted under the skin to measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. This provides more detailed information about glucose trends and patterns throughout the day. Interpreting these results accurately and making informed decisions based on them is key to effective diabetes management.
Resource Guide: Empowering Individuals with Diabetes
Empowering individuals with diabetes requires access to comprehensive resources and support. This includes education on diabetes management, nutrition counseling, and physical activity planning. Connecting with a diabetes educator or a registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance on developing a management plan that fits individual needs and lifestyle. Online resources, support groups, and mobile apps can also offer valuable tools and community support, helping individuals with diabetes stay informed, motivated, and connected.
Decision Framework: Making Informed Choices
Making informed choices about diabetes management involves considering several factors, including the type of diabetes, current health status, lifestyle preferences, and treatment goals. For those on insulin or oral medications, understanding how to adjust doses in response to changes in food intake, physical activity, or stress levels is crucial. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and lipid profiles, along with annual comprehensive foot exams and eye exams, can help identify potential complications early. Engaging in open and ongoing communication with healthcare providers about any questions, concerns, or changes in symptoms is also vital.
Conceptual Exploration: The Psychology of Diabetes Management
The psychology of diabetes management plays a significant role in the overall well-being of individuals with diabetes. The chronic nature of the disease and the need for constant vigilance can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and burnout. Developing coping strategies and maintaining a positive mindset can help mitigate these effects. Support from family, friends, and support groups can provide emotional strength and practical help. Engaging in activities that bring joy and fulfillment can also help manage stress and improve quality of life.
FAQ Section
What are the ideal blood sugar levels for someone with diabetes?
+The ideal blood sugar levels can vary depending on the individual and their specific health goals, but generally, most people with diabetes aim for a fasting glucose level between 70 and 130 mg/dL and a postprandial (after meal) glucose level below 180 mg/dL.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels if I have diabetes?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on the type of diabetes, the treatment plan, and the individual's health status. Generally, people with type 1 diabetes or those who use insulin may need to check their blood sugar levels more frequently, up to 4-6 times a day, while those with type 2 diabetes may check less frequently, depending on their medication regimen and health status.
Can diet and exercise alone manage diabetes?
+For some people with type 2 diabetes, diet and exercise may be enough to manage the condition, especially in the early stages or if the condition is mild. However, for many individuals with diabetes, especially those with type 1 diabetes or advanced type 2 diabetes, medication or insulin therapy is necessary in addition to lifestyle changes to achieve and maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
How can I prevent diabetes complications?
+Preventing diabetes complications involves maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels, not smoking, engaging in regular physical activity, and eating a balanced diet. Regular health check-ups and screenings for potential complications, such as nephropathy, retinopathy, and neuropathy, are also crucial.
Are there any new treatments or technologies for diabetes management?
+Yes, there are continuous advancements in diabetes management, including improved insulins, oral medications, continuous glucose monitoring systems, insulin pumps, and the development of bionic pancreas systems that can automatically adjust insulin doses. Research into islet cell transplantation and stem cell therapies also holds promise for future treatments.
Effective diabetes management is a journey that requires dedication, support, and the right information. By understanding the complexities of diabetes, leveraging advances in technology and medication, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals with diabetes can achieve better health outcomes and improve their quality of life. The key to successful management lies in finding a balance that works for each individual, supported by healthcare providers, family, and community resources. As research and technology continue to evolve, the future holds much promise for more effective and personalized approaches to diabetes care.