8 Newborn Weight Facts For Healthy Babies

Newborn weight is one of the most significant indicators of a baby’s health, and it’s a topic that fascinates new parents and medical professionals alike. While every baby is unique, there are some key facts about newborn weight that can provide valuable insights into a child’s development and well-being. In this article, we’ll delve into eight essential facts about newborn weight, exploring what’s considered normal, how weight affects health, and what factors influence a baby’s birth weight.
Understanding Newborn Weight: A Critical Health Indicator

Newborn weight is a critical indicator of a baby’s health, and it’s closely monitored by healthcare professionals in the days and weeks following birth. A baby’s weight at birth is influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, including the mother’s diet, lifestyle, and overall health during pregnancy. On average, a healthy newborn weighs between 5.5 and 8.8 pounds (2.5 to 4 kilograms), with the average weight for boys being slightly higher than for girls.
Factors Influencing Newborn Weight
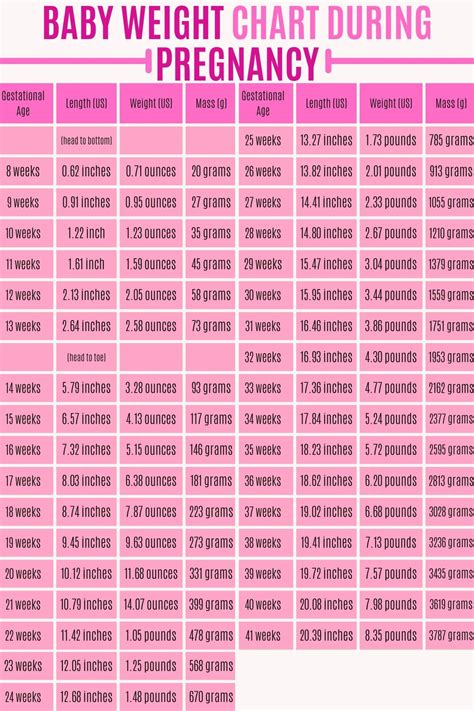
Several factors can influence a baby’s birth weight, including the mother’s weight, age, and health during pregnancy. Women who are overweight or underweight are more likely to have babies with lower or higher birth weights, respectively. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as gestational diabetes or hypertension, can also impact a baby’s weight at birth. Furthermore, factors like the baby’s gestational age, with preterm babies typically weighing less than full-term babies, play a significant role in determining newborn weight.
The Importance of Monitoring Newborn Weight
Monitoring a newborn’s weight is crucial in the first few weeks of life, as it can help identify potential health issues early on. Babies typically lose around 5-10% of their birth weight in the first week, but they should start gaining weight by the second week. If a baby is not gaining weight as expected, it may indicate an issue with feeding, such as difficulty latching or inadequate milk supply, or an underlying medical condition. Healthcare providers closely track a baby’s weight to ensure they’re receiving adequate nutrition and to detect any potential problems.
Newborn Weight Percentiles: What Do They Mean?
Newborn weight percentiles are a way to compare a baby’s weight to that of other babies of the same gestational age. Percentiles are calculated based on a large dataset of birth weights, and they provide a snapshot of a baby’s weight relative to the average. For example, a baby in the 50th percentile for weight is average, while a baby in the 90th percentile is above average. Understanding newborn weight percentiles can help parents and healthcare providers track a baby’s growth and development over time.
The Relationship Between Newborn Weight and Future Health
Research suggests that newborn weight may be linked to future health outcomes, including the risk of obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Babies born with low birth weights (less than 5.5 pounds) may be at higher risk for these conditions, while babies born with high birth weights (over 8.8 pounds) may also face increased risks. However, it’s essential to note that many factors contribute to future health, and newborn weight is just one aspect to consider.
How Newborn Weight Affects Feeding and Nutrition
A baby’s weight at birth can impact their feeding and nutrition needs. For example, babies with low birth weights may require more frequent feedings to ensure they’re receiving adequate calories and nutrients. On the other hand, babies with high birth weights may be at risk for overfeeding, which can lead to digestive issues and other problems. Healthcare providers work closely with parents to develop a feeding plan that meets their baby’s unique needs.
The Role of Genetics in Newborn Weight
Genetics play a significant role in determining a baby’s birth weight, with some families tendency to have larger or smaller babies. However, it’s essential to remember that genetics is just one factor, and many other influences, such as the mother’s health and lifestyle during pregnancy, also contribute to a baby’s weight at birth. Understanding the interplay between genetics and environmental factors can help parents and healthcare providers better appreciate the complexities of newborn weight.
Conclusion: Newborn Weight as a Foundation for Health
In conclusion, newborn weight is a vital indicator of a baby’s health, and it’s influenced by a complex array of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. By understanding the facts about newborn weight, parents and healthcare providers can work together to ensure that babies receive the best possible start in life. Whether a baby is born with a low, average, or high birth weight, monitoring their weight and overall health in the first few weeks and months of life is critical for identifying potential issues and promoting healthy growth and development.
What is considered a normal newborn weight?
+A normal newborn weight is typically considered to be between 5.5 and 8.8 pounds (2.5 to 4 kilograms), with the average weight for boys being slightly higher than for girls.
How often should newborn weight be monitored?
+Newborn weight should be monitored regularly, especially in the first few weeks of life, to ensure that the baby is gaining weight as expected and to detect any potential health issues early on.
What factors can influence a baby’s birth weight?
+Several factors can influence a baby’s birth weight, including the mother’s weight, age, and health during pregnancy, as well as the baby’s gestational age and genetic factors.
How does newborn weight affect future health outcomes?
+Research suggests that newborn weight may be linked to future health outcomes, including the risk of obesity, diabetes, and heart disease, although many factors contribute to future health, and newborn weight is just one aspect to consider.



