Abo And Rh: Understand Blood Types
The human body is composed of numerous complex systems, each playing a vital role in maintaining our overall health. One such system is the circulatory system, which is responsible for transporting essential nutrients, oxygen, and hormones throughout the body. At the core of this system are the blood types, which are categorized based on the presence or absence of specific antigens on the surface of red blood cells. The ABO and Rh blood types are the most critical factors in determining an individual’s blood group.
To comprehend the intricacies of blood types, it’s essential to delve into the history of blood transfusions. The concept of transfusing blood dates back to the 17th century, but it wasn’t until the early 20th century that scientists began to understand the importance of blood types. In 1901, Austrian physician Karl Landsteiner discovered the ABO blood group system, which categorizes blood into four main groups: A, B, AB, and O. This breakthrough led to a significant reduction in transfusion-related complications and paved the way for modern blood banking.
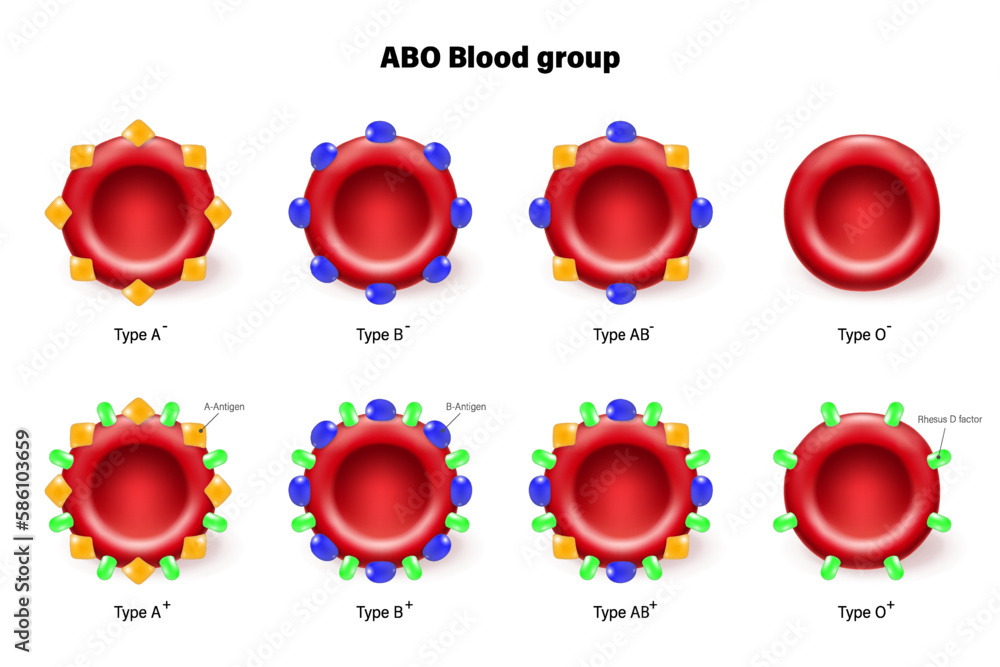
The ABO blood group system is based on the presence or absence of two antigens, A and B, on the surface of red blood cells. Antigens are substances that can trigger an immune response, and in the context of blood types, they determine whether an individual’s blood is compatible with another person’s blood. The four ABO blood groups are:
- Group A:Has A antigens on the surface of red blood cells
- Group B:Has B antigens on the surface of red blood cells
- Group AB:Has both A and B antigens on the surface of red blood cells
- Group O:Has neither A nor B antigens on the surface of red blood cells
In addition to the ABO blood group system, the Rh blood type system is another crucial factor in determining blood compatibility. The Rh system is based on the presence or absence of the RhD antigen on the surface of red blood cells. If an individual has the RhD antigen, they are considered Rh-positive, while those without it are considered Rh-negative. The combination of ABO and Rh blood types results in a total of eight possible blood groups:
- A+ (A and Rh-positive)
- A- (A and Rh-negative)
- B+ (B and Rh-positive)
- B- (B and Rh-negative)
- AB+ (AB and Rh-positive)
- AB- (AB and Rh-negative)
- O+ (O and Rh-positive)
- O- (O and Rh-negative)
Understanding blood types is vital in various medical contexts, including blood transfusions, organ transplantation, and pregnancy. Incompatible blood types can lead to severe reactions, including hemolysis, which is the destruction of red blood cells. For instance, if an individual with type A blood receives type B blood, their immune system will recognize the B antigens as foreign and attack the transfused blood cells.
In the context of pregnancy, blood types can play a critical role in ensuring the health of both the mother and the fetus. If an Rh-negative mother is carrying an Rh-positive fetus, there is a risk of Rh incompatibility. This occurs when the mother’s immune system produces antibodies against the RhD antigen on the fetus’s red blood cells, which can lead to hemolysis. To prevent this, Rh-negative mothers are typically administered Rh immunoglobulin during pregnancy and after delivery.
The discovery of blood types has revolutionized the field of transfusion medicine, enabling healthcare professionals to provide safe and effective blood transfusions. However, it's essential to continue researching and understanding the complexities of blood types to improve patient outcomes and develop new treatments for blood-related disorders.
In conclusion, the ABO and Rh blood types are fundamental components of the human circulatory system, and understanding their intricacies is crucial in various medical contexts. By recognizing the importance of blood types and their role in maintaining our health, we can appreciate the complexity and beauty of the human body.
What are the main differences between ABO and Rh blood types?
+The ABO blood group system categorizes blood into four main groups (A, B, AB, and O) based on the presence or absence of A and B antigens, while the Rh blood type system is based on the presence or absence of the RhD antigen.
Why is it essential to match blood types during transfusions?
+Matching blood types is critical to prevent an immune response against the transfused blood, which can lead to severe reactions, including hemolysis.
Can an individual's blood type change over time?
+No, an individual's blood type is determined by their genetics and remains the same throughout their life.
The study of blood types is a fascinating field that continues to evolve with advancements in medical research and technology. By exploring the intricacies of ABO and Rh blood types, we can gain a deeper understanding of the human body and develop new treatments for blood-related disorders. As we continue to uncover the secrets of blood types, we may uncover new and innovative ways to improve patient outcomes and save lives.