Acetaminophen Hydrocodone 5325
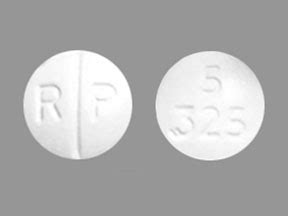
The combination of acetaminophen and hydrocodone, often referred to by the numbers “5⁄325” or variations thereof (such as 5325, which might indicate a different dosage form or strength but generally refers to a combination of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen), is a prescription medication used to relieve moderate to moderately severe pain. This medication combines an opioid analgesic (hydrocodone) with a non-opioid analgesic (acetaminophen) to provide more effective pain relief than either medication could provide alone.
Hydrocodone is a semi-synthetic opioid derived from codeine and thebaine, which are naturally occurring substances extracted from the opium poppy. It works by binding to opioid receptors in the brain, spinal cord, and other areas, altering the perception of and response to pain. Hydrocodone has a relatively rapid onset of action and is effective for treating short-term, acute pain conditions, as well as chronic pain when used under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Acetaminophen, on the other hand, is a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic that works centrally in the brain to relieve pain and reduce fever. While its precise mechanism of action is less understood than that of hydrocodone, it’s thought to act by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins in the brain, substances that cause pain and fever.
The combination of hydrocodone and acetaminophen in medications like Vicodin (which contains 5mg hydrocodone bitartrate and 300mg acetaminophen per tablet, but can vary in strength) has been widely used to manage pain that is not adequately relieved by other means. However, due to the potential for abuse, dependence, and side effects associated with opioids, this medication is carefully monitored and regulated.
Usage and Precautions
When prescribed this medication, patients must follow the dosage instructions carefully. The medication should be taken by mouth as directed, usually every 4 to 6 hours as needed. It is crucial not to exceed the recommended dose, as this can lead to increased risk of serious side effects.
Hydrocodone-acetaminophen combination products can cause significant side effects, including but not limited to:
- CNS (Central Nervous System) Depression: Drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, and impaired cognitive performance. This effect can impair the ability to perform potentially hazardous activities.
- Constipation: This is one of the most common side effects, due to the opioid component of the medication.
- Nausea and Vomiting: While this can be an issue, particularly when first starting the medication, tolerance to these effects often develops.
- Physical Dependence and Tolerance: Long-term use can lead to physical dependence and addiction. The body gets used to the presence of the opioid, leading to withdrawal symptoms if the medication is stopped abruptly.
- Liver Damage: High doses of acetaminophen can cause liver damage, particularly when combined with alcohol or other liver-damaging substances.
Given the potential risks and side effects, especially those related to hydrocodone, medical professionals and patients alike must be vigilant about usage. Patients should not drive a car or operate machinery until they know how this medication affects them. Also, the sharing of this medication with others, especially children and pets, must be strictly avoided.
Misuse, Abuse, and Overdose Risks
The misuse and abuse of hydrocodone-acetaminophen combination products can lead to serious health consequences, including overdose and death. Abuse involves taking the drug in ways not intended by the prescriber, such as taking it more frequently, in higher doses, or by a different method (e.g., crushing and snorting). This behavior is particularly problematic due to the potent opioid component.
The symptoms of overdose can include:
- Confusion or drowsiness
- Cold, clammy skin
- Bluish tinge around the mouth and lips
- Heart rate and breathing rate that are slower than normal
- Shallow breathing
- Low blood pressure
- Constricted (pinpoint) pupils
In case of an overdose, emergency services should be contacted immediately. Overdose can lead to respiratory failure, which might result in death if not promptly addressed.
Management of Chronic Pain
The management of chronic pain with opioids requires a thoughtful approach that balances the potential benefits of pain relief against the risks. Long-term use of opioids, including hydrocodone-acetaminophen combinations, is typically reserved for situations where pain cannot be managed with other options or when those options are not tolerated.
Healthcare providers closely monitor patients for signs of dependency, abuse, and side effects. Strategies to minimize risks include using the lowest effective dose, limiting the duration of therapy when possible, and regularly reassessing the need for ongoing opioid therapy.
Role in Nationwide Opioid Crisis
The role that hydrocodone-acetaminophen products, among other opioids, have played in the opioid crisis is a subject of significant discussion. Misuse and overprescription of opioid medications have contributed to widespread addiction, overdose, and death. Efforts to combat this issue include educational campaigns, stricter prescribing guidelines, and development of alternative pain management strategies.
Conclusion
In summary, hydrocodone-acetaminophen (e.g., 5325, or variations indicating different strengths or formulations) is a potent medication for the management of moderate to moderately severe pain. While effective, its potential for abuse, dependence, and serious side effects necessitates careful use and monitoring. As society and the medical community navigate the complexities of pain management within the context of the opioid crisis, this medication remains a tool for healthcare professionals when used judiciously and with attention to patient safety.
FAQ Section
What are the main components of the hydrocodone-acetaminophen combination medication?
+This medication combines hydrocodone, an opioid analgesic, with acetaminophen, a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic. Together, they provide effective relief from moderate to moderately severe pain.
What are the primary risks associated with using hydrocodone-acetaminophen combination products?
+The primary risks include the potential for abuse and addiction due to the opioid component, as well as the risk of liver damage from high doses of acetaminophen. Additionally, side effects like CNS depression, constipation, nausea, and vomiting can occur.
How can the misuse and abuse of hydrocodone-acetaminophen combination products be prevented or minimized?
+Prevention involves careful prescribing practices, patient education about the risks, monitoring for signs of dependence or abuse, and using alternative pain management strategies whenever possible. Additionally, programs for the proper disposal of unused medication can help prevent diversion.
What are the symptoms of an overdose on hydrocodone-acetaminophen, and what should one do in case of suspected overdose?
+Symptoms can include confusion, drowsiness, cold and clammy skin, shallow breathing, and constricted pupils. In case of suspected overdose, emergency services should be contacted immediately. Rescue breathing or CPR may be necessary if the person is not breathing or not breathing normally.
Are there any specific guidelines for the management of chronic pain with hydrocodone-acetaminophen combinations?
+Guidelines recommend using the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible, closely monitoring patients for signs of dependence or abuse, and regularly reassessing the need for ongoing opioid therapy. Alternative pain management strategies should be considered when feasible.