Alt Low Blood Test: Fix It Fast
The mystery of abnormal blood test results can be a daunting experience for many individuals. One common concern is an Alt (Alanine Transaminase) low blood test result. But before we dive into the intricacies of this enzyme and its implications, let’s first understand the broader context of liver health and the role that Alt plays in it.
Liver health is a critical aspect of our overall well-being. The liver acts as a filter, detoxifying harmful substances, metabolizing drugs, and producing vital proteins. Among the various enzymes that indicate liver health, Alanine Transaminase (Alt) is one of the key markers. It is an enzyme found primarily in the liver but also in smaller amounts in the kidneys, heart, and muscles. The level of Alt in the blood is a crucial indicator of liver damage or disease.
Understanding Alt Levels
When we talk about an Alt low blood test result, it refers to a level of Alanine Transaminase that is lower than what is considered the normal range. Normally, the range for Alt is between 0-40 U/L, though this can slightly vary depending on the lab and the individual’s specific conditions. An unusually low level of Alt might not necessarily indicate a health issue, as the normal range can vary among individuals. However, significant deviations from the expected range, whether high or low, can signal potential health concerns.
Causes of Low Alt Levels
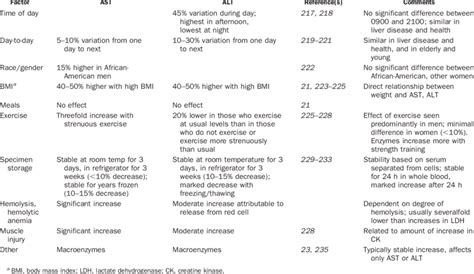
Several factors can contribute to low Alt levels. One of the primary reasons is the presence of certain nutrients and vitamins, such as vitamin B6, which can influence Alt production and metabolism. Some individuals might naturally have lower Alt levels due to genetic factors. Additionally, certain medications can affect Alt levels, either by enhancing liver function and reducing enzyme production or by directly interfering with the metabolic pathways involving Alt.
Moreover, low Alt levels can sometimes be indicative of an underlying condition that affects the liver’s ability to produce this enzyme. For example, conditions such as starvation or malnutrition can lead to decreased production of various enzymes, including Alt, due to the lack of necessary building blocks for enzyme synthesis.
Impact of Low Alt Levels
While high Alt levels are more commonly associated with liver damage or disease, low levels can also have implications for health, albeit less directly. For instance, a significant reduction in Alt could potentially affect the liver’s efficiency in detoxifying harmful substances or metabolizing drugs, although this would depend on the severity of the decrease and the presence of other liver enzymes.
Furthermore, understanding the context of low Alt levels is crucial. An isolated low result may not necessarily warrant concern, especially if the individual is otherwise healthy and shows no symptoms of liver disease. However, if low Alt levels are accompanied by other abnormalities in liver function tests or symptoms indicative of liver dysfunction, it could signal a need for further investigation.
Addressing Low Alt Levels
If an individual has been notified of low Alt levels, the first step is not to panic. The next course of action would typically involve a consultation with a healthcare provider to assess the overall health context and potentially conduct further tests. These tests might include additional liver function tests, such as aspartate transaminase (AST) levels, bilirubin, and alkaline phosphatase, to gain a comprehensive view of liver health.
In some cases, addressing low Alt levels might involve dietary changes, ensuring adequate intake of nutrients that support liver health and enzyme production. This could include increasing consumption of foods rich in vitamin B6, among other nutrients. However, any dietary adjustments should be made under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure they are appropriate and beneficial.
Conclusion
Low Alt levels in a blood test can be a source of confusion and concern for individuals. While it’s essential to understand the implications of such results, it’s equally important to contextualize them within overall health. Often, low Alt levels may not indicate a serious health issue but rather reflect individual variations, nutritional factors, or the effects of certain medications. By consulting with healthcare professionals and potentially undergoing further evaluation, individuals can better understand their specific situation and take appropriate steps to maintain optimal liver health.
What is the normal range for Alt levels in the blood?
+The normal range for Alt (Alanine Transaminase) levels in the blood is typically between 0-40 U/L, though this can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the individual's specific conditions.
Can low Alt levels indicate a health problem?
+While low Alt levels are less commonly associated with liver disease than high levels, significant deviations from the normal range can sometimes signal underlying health issues. These could include nutritional deficiencies, genetic predispositions, or the effects of certain medications.
How can I address low Alt levels?
+Addressing low Alt levels typically involves consulting with a healthcare provider to assess overall health and potentially conduct further tests. Dietary changes, under professional guidance, might also be recommended to ensure adequate intake of nutrients supporting liver health and enzyme production.
In navigating the complexities of liver health and understanding the implications of low Alt levels, it’s crucial to approach the situation with a blend of caution and informed awareness. By doing so, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining optimal liver function and overall well-being.



