Amox Clav 875 125
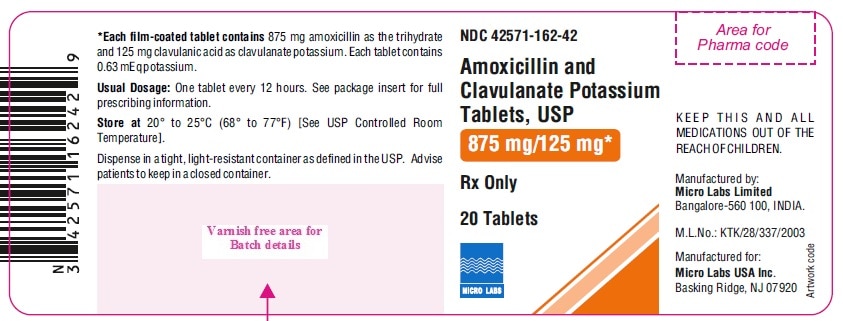
Augmentin, commonly known by its generic name Amoxicillin/Clavulanate or simply as Amox Clav, is a widely prescribed antibiotic. The “875 125” denomination refers to the specific strengths of the two active components in the formulation: 875mg of Amoxicillin and 125mg of Clavulanic Acid. This combination is designed to combat a broader spectrum of bacterial infections by overcoming resistance mechanisms that some bacteria may have developed against Amoxicillin alone.
Introduction to Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is a penicillin-type antibiotic that works by stopping the growth of bacteria. It interferes with the formation of the bacterial cell wall, which is essential for the survival of the bacteria. This action is effective against a wide variety of bacterial infections, including those affecting the respiratory tract, skin, and urinary tract.
Role of Clavulanic Acid
Clavulanic Acid is a beta-lactamase inhibitor that, when combined with Amoxicillin, extends its spectrum of activity. Many bacteria produce beta-lactamase enzymes, which can inactivate Amoxicillin and other penicillins, rendering them ineffective. Clavulanic Acid inhibits these enzymes, thereby protecting Amoxicillin from degradation and allowing it to continue its antibacterial action against bacteria that would otherwise be resistant.
Indications for Use
The Amox Clav 875 125 formulation is typically prescribed for more severe infections or those caused by bacteria that are more likely to be resistant to Amoxicillin alone. Common indications include:
- Respiratory Tract Infections: Such as community-acquired pneumonia, acute bacterial sinusitis, and acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis.
- Skin and Skin Structure Infections: Including bacterial infections of the skin, soft tissues, and bones.
- Urinary Tract Infections: Such as pyelonephritis and uncomplicated urinary tract infections.
Administration and Dosage
The dosage of Amox Clav 875 125 is usually taken orally, every 12 hours, with or without food. However, it is recommended to be taken at the start of a meal to minimize gastrointestinal side effects. The total duration of treatment depends on the type and severity of the infection, typically ranging from 7 to 14 days.
Side Effects and Precautions
While generally well-tolerated, Amox Clav can cause side effects, including but not limited to diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and allergic reactions. Severe reactions can include anaphylaxis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis, although these are rare. It is essential to monitor for signs of Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) infection, which can cause diarrhea and colitis, and to report any severe or persistent side effects to a healthcare provider.
Resistance and Stewardship
The rise of antibiotic resistance is a global concern, and the misuse or overuse of antibiotics like Amox Clav contributes to this problem. It is crucial to use antibiotics responsibly, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, and to complete the full prescribed course unless otherwise directed.
Conclusion
Amox Clav 875 125 is a powerful antibiotic combination that provides an effective treatment option for a wide range of bacterial infections. Its efficacy against beta-lactamase-producing bacteria makes it a valuable resource in the fight against antibiotic resistance. However, its use must be carefully managed to ensure that it remains effective for future generations.
What is the primary mechanism of action of Amoxicillin in Amox Clav 875 125?
+Amoxicillin works by inhibiting the formation of the bacterial cell wall, which is essential for bacterial survival.
Why is Clavulanic Acid added to Amoxicillin in the formulation of Amox Clav 875 125?
+Clavulanic Acid acts as a beta-lactamase inhibitor, protecting Amoxicillin from degradation by beta-lactamase enzymes produced by certain bacteria, thereby extending its spectrum of activity.
What are common indications for the use of Amox Clav 875 125?
+Common indications include respiratory tract infections, skin and skin structure infections, and urinary tract infections caused by susceptible bacteria.