Amoxicillin & Clavulanate

The combination of amoxicillin and clavulanate, commonly known by the brand name Augmentin, is a potent antibiotic formulation designed to combat a broad spectrum of bacterial infections. This dual-action antibiotic pairs amoxicillin, a penicillin-like medication, with clavulanate, a beta-lactamase inhibitor. The synergy between these two components enhances the effectiveness of amoxicillin by protecting it from degradation by beta-lactamase enzymes, which are produced by certain bacteria to resist the effects of antibiotics like amoxicillin.
Understanding Amoxicillin

Amoxicillin is a widely used antibiotic that belongs to the penicillin class. It functions by interfering with the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, ultimately leading to the death of the bacterial cells. Amoxicillin is effective against a variety of bacterial infections, including those of the skin, ear, nose, throat, and urinary tract. However, its efficacy can be compromised by beta-lactamase-producing bacteria, which can inactivate amoxicillin through enzymatic degradation.
The Role of Clavulanate
Clavulanate is a beta-lactamase inhibitor that, when combined with amoxicillin, extends the spectrum of activity of the antibiotic to include beta-lactamase-producing strains of bacteria. By inhibiting the beta-lactamase enzyme, clavulanate prevents the inactivation of amoxicillin, allowing the antibiotic to reach effective concentrations at the site of infection. This synergy enhances the bactericidal activity of amoxicillin against a broader range of pathogens, including those that would otherwise be resistant due to their ability to produce beta-lactamase.
Clinical Applications
Amoxicillin and clavulanate combination is indicated for the treatment of various bacterial infections, including:
- Respiratory Tract Infections: Such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis, caused by susceptible strains of bacteria.
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infections: Including cellulitis, furuncles, and impetigo.
- Urinary Tract Infections: Caused by susceptible strains of bacteria.
- Dental Infections: Including abscesses and infections of the gums and other tissues around the teeth.
Dosage and Administration
The dosage of amoxicillin and clavulanate combination depends on the type and severity of the infection, as well as the patient’s age, weight, and renal function. It is available in various formulations, including tablets, chewable tablets, and oral suspensions, allowing for flexibility in dosing and administration. The most common dosages range from 250 mg to 500 mg of amoxicillin combined with 125 mg of clavulanate, taken every 8 or 12 hours.
Side Effects and Precautions
While generally well-tolerated, the amoxicillin and clavulanate combination can cause side effects, including but not limited to:
- Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain are common side effects.
- Allergic Reactions: Including rash, itching, and, in severe cases, anaphylaxis.
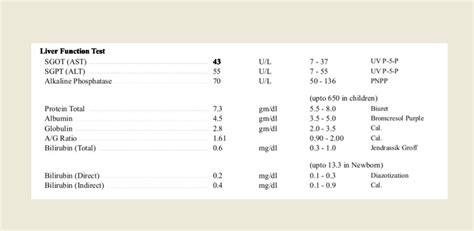
- Hepatic Effects: Elevations in liver enzymes and, rarely, more severe liver dysfunction.
- Interactions with Other Medications: Potential interactions include those with other antibiotics, anticoagulants, and certain oral contraceptives.
It is crucial to use this antibiotic combination under the guidance of a healthcare provider, as misuse or overuse can contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance. Additionally, patients with a history of allergic reactions to penicillins or other beta-lactam antibiotics should use this medication with caution.
Resistance and Future Perspectives
The increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains poses a significant challenge to the effective treatment of infections. The development of resistance to the amoxicillin and clavulanate combination, as with other antibiotics, underscores the need for responsible antibiotic stewardship, including avoiding unnecessary prescriptions and promoting adherence to prescribed treatment regimens. Ongoing research into new antimicrobial agents and strategies to combat resistance is essential for maintaining effective therapeutic options against bacterial infections.
Conclusion
The combination of amoxicillin and clavulanate represents a valuable therapeutic option in the management of bacterial infections. Its broad spectrum of activity, coupled with its generally favorable safety profile, makes it a commonly prescribed antibiotic. However, its effectiveness is contingent upon judicious use and efforts to mitigate the development of resistance. As with all antibiotics, it should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider, with adherence to prescribed dosing regimens and careful monitoring for potential side effects.
What is the primary mechanism by which clavulanate enhances the effectiveness of amoxicillin?
+Clavulanate inhibits beta-lactamase enzymes produced by certain bacteria, thereby preventing the degradation of amoxicillin and allowing it to maintain its bactericidal activity against a broader range of pathogens.
What are the common indications for the use of amoxicillin and clavulanate combination?
+The amoxicillin and clavulanate combination is indicated for the treatment of various bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, urinary tract infections, and dental infections, caused by susceptible strains of bacteria.
What precautions should be taken when prescribing amoxicillin and clavulanate to patients with a history of allergic reactions to penicillins?
+Patients with a history of allergic reactions to penicillins or other beta-lactam antibiotics should use the amoxicillin and clavulanate combination with caution. Healthcare providers should carefully evaluate the risk of an allergic reaction and consider alternative therapeutic options when necessary.