Anesthesia For Colonoscopy
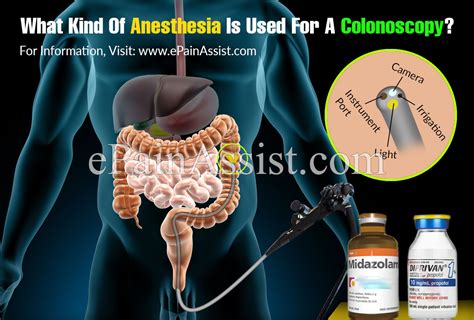
Colonoscopy, a crucial diagnostic and therapeutic procedure for detecting and preventing colorectal cancer, relies heavily on the effective use of anesthesia to ensure patient comfort and safety. The administration of anesthesia for colonoscopy has evolved over the years, with various techniques and agents being employed to minimize discomfort, anxiety, and potential complications. This comprehensive overview aims to delve into the intricacies of anesthesia in colonoscopy, exploring its importance, types, administration techniques, benefits, and potential risks.
Importance of Anesthesia in Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy involves the insertion of a flexible tube with a camera and light on the end into the rectum to visualize the inside of the colon. This procedure can cause significant discomfort and anxiety due to the invasive nature of the examination. Anesthesia plays a pivotal role in reducing the pain and distress associated with colonoscopy, thereby enhancing the overall patient experience. Effective anesthesia allows for a more thorough examination, as patients are more likely to tolerate the procedure without moving, which can obscure the view or cause discomfort.
Types of Anesthesia Used for Colonoscopy
Several types of anesthesia can be used for colonoscopy, each with its own advantages and indications. The choice of anesthesia depends on various factors, including patient health, anxiety levels, and the complexity of the procedure.
- Conscious Sedation: This is the most commonly used form of anesthesia for colonoscopy. It involves the use of medications that induce a state of relaxation and reduce pain, but the patient remains awake and able to respond to commands. Common agents include midazolam, fentanyl, and meperidine.
- Deep Sedation: In some cases, deeper levels of sedation may be required, particularly for patients with high levels of anxiety or those undergoing more complex procedures. This type of sedation is similar to conscious sedation but induces a deeper sleep-like state, from which patients can be easily awakened.
- General Anesthesia: Though less common for routine colonoscopies, general anesthesia may be considered for certain patients, such as those with severe anxiety, previous traumatic experiences, or specific medical conditions that make conscious sedation inappropriate.
Administration Techniques
The administration of anesthesia for colonoscopy is typically performed by a trained healthcare professional, often an anesthesiologist or a gastroenterologist with specialized training in sedation. The technique involves the intravenous administration of the selected anesthetic agents, closely monitoring the patient’s vital signs and level of consciousness to ensure safety and comfort.
Benefits of Anesthesia in Colonoscopy
The benefits of using anesthesia during colonoscopy are multifaceted: - Enhanced Patient Comfort: Reduces pain and discomfort, making the procedure more tolerable. - Increased Patient Satisfaction: By minimizing anxiety and discomfort, patients are more likely to be satisfied with their care. - Improved Procedure Success: A comfortable patient is more likely to remain still, allowing for a more thorough and accurate examination. - Reduced Anxiety: Effective anesthesia can alleviate pre-procedural anxiety, making the experience less stressful for the patient.
Potential Risks and Complications
While anesthesia significantly improves the colonoscopy experience, it is not without potential risks and complications. These include: - Respiratory Depression: A decrease in breathing rate that can be life-threatening if not promptly addressed. - Cardiovascular Complications: Changes in blood pressure and heart rate can occur, particularly in patients with pre-existing heart conditions. - Allergic Reactions: Though rare, allergic reactions to anesthetic agents can happen and must be quickly recognized and managed. - Recovery Time: Patients may experience drowsiness and impaired judgment for several hours after the procedure, requiring accompaniment and avoidance of operating heavy machinery or making important decisions.
Future Directions and Innovations
The field of anesthesia in colonoscopy is continually evolving, with ongoing research into newer, safer anesthetic agents and techniques. Innovations such as the use of propofol, a rapidly acting sedative with a short recovery time, and the development of more sophisticated monitoring technologies aim to further enhance patient safety and comfort.
Conclusion
Anesthesia plays a critical role in the performance of colonoscopy, enabling healthcare providers to conduct thorough examinations while ensuring patient comfort and safety. By understanding the types, benefits, and potential risks of anesthesia used in colonoscopy, patients can better navigate their procedure with confidence, knowing that their comfort and well-being are paramount. As medical science continues to advance, the future of anesthesia in colonoscopy holds promise for even more effective and safe procedures, further solidifying the importance of this diagnostic tool in preventive healthcare.
What are the most common types of anesthesia used for colonoscopy?
+The most common types include conscious sedation and deep sedation, with general anesthesia being less frequently used but still an option for specific cases.
What are the benefits of using anesthesia during colonoscopy?
+The benefits include enhanced patient comfort, increased patient satisfaction, improved procedure success, and reduced anxiety.
What are some potential risks and complications of anesthesia in colonoscopy?
+Potential risks include respiratory depression, cardiovascular complications, allergic reactions, and prolonged recovery times.