Antithyroid Peroxidase Antibody
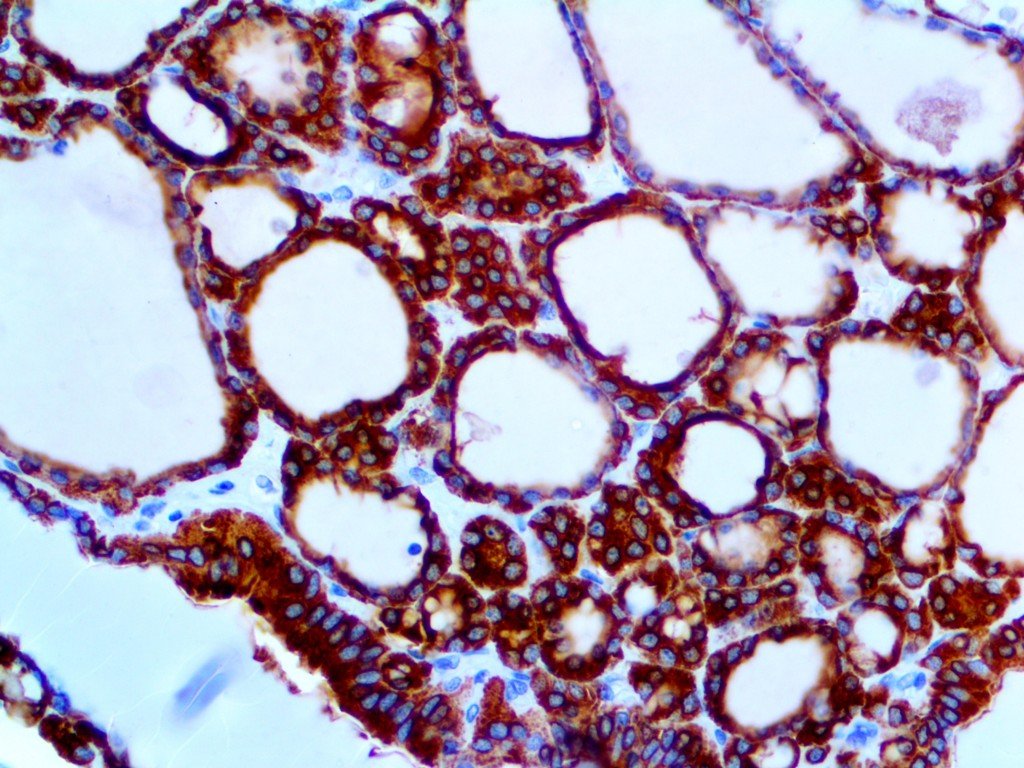
Antithyroid peroxidase (TPO) antibody is a type of autoantibody that is often present in individuals with autoimmune thyroid diseases, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease. To understand the significance of TPO antibodies, it is essential to delve into the role of thyroid peroxidase in thyroid function and the implications of autoimmune responses on thyroid health.
Thyroid peroxidase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the production of thyroid hormones. It catalyzes the oxidation of iodine and its incorporation into thyroglobulin, a protein that serves as a precursor for the synthesis of triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These hormones are vital for regulating metabolism, energy generation, and overall metabolic health.
In autoimmune thyroid diseases, the immune system mistakenly targets the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and damage. The presence of TPO antibodies indicates that the immune system has produced antibodies against thyroid peroxidase, which can disrupt the normal functioning of the thyroid gland. This disruption can lead to decreased production of thyroid hormones, resulting in hypothyroidism, or, in the case of Graves’ disease, an overproduction of thyroid hormones, leading to hyperthyroidism.
Diagnosis and Clinical Significance
The detection of antithyroid peroxidase antibodies is primarily through blood tests. These antibodies are present in the majority of patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, making them a useful diagnostic marker for this condition. However, their presence is not exclusive to Hashimoto’s; they can also be found in patients with Graves’ disease, although to a lesser extent. The level of TPO antibodies can vary widely among individuals and does not directly correlate with the severity of the disease.
The clinical significance of TPO antibodies extends beyond their role as diagnostic markers. Their presence can also be associated with an increased risk of developing thyroid diseases during pregnancy and postpartum thyroiditis. Furthermore, individuals with TPO antibodies, even in the absence of overt thyroid disease, may experience mild thyroid dysfunction or have an increased risk of progressing to overt hypothyroidism over time.
Management and Treatment
The management and treatment of thyroid diseases associated with TPO antibodies depend on the specific condition and its severity. For patients with hypothyroidism due to Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, treatment typically involves thyroid hormone replacement therapy to restore normal levels of T3 and T4. In Graves’ disease, treatments may include antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine ablation, or surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland, with the goal of reducing thyroid hormone production.
Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications
While there is no proven method to prevent autoimmune thyroid diseases, certain lifestyle modifications and preventive measures can help manage the condition and potentially reduce the risk of complications. These include:
- Dietary Changes: Ensuring adequate intake of iodine, selenium, and other micronutrients essential for thyroid function.
- Stress Management: Engaging in stress-reducing activities, as chronic stress can exacerbate autoimmune responses.
- Regular Screening: For individuals with a family history of autoimmune thyroid diseases, regular thyroid function tests can help in early detection and management.
Future Directions and Research
Research into autoimmune thyroid diseases and the role of TPO antibodies is ongoing, with a focus on understanding the underlying mechanisms of these conditions, improving diagnostic techniques, and developing more targeted and effective treatments. Advances in genetics and immunology may provide insights into the risk factors for developing these diseases and potential therapeutic strategies to modulate the immune response and prevent thyroid damage.
FAQs
What are antithyroid peroxidase antibodies?
+Antithyroid peroxidase antibodies are autoantibodies directed against the enzyme thyroid peroxidase, which plays a crucial role in thyroid hormone production. Their presence is a marker of autoimmune thyroid diseases.
How are antithyroid peroxidase antibodies detected?
+Detection is primarily through blood tests that measure the level of these antibodies in the blood.
What conditions are associated with antithyroid peroxidase antibodies?
+These antibodies are most commonly associated with Hashimoto's thyroiditis and can also be present in Graves' disease, indicating autoimmune thyroiditis.
Can the presence of antithyroid peroxidase antibodies predict disease severity?
+The level of TPO antibodies does not directly correlate with disease severity. Instead, they serve as a diagnostic marker and indicator of autoimmune activity.
How are thyroid diseases associated with TPO antibodies managed?
+Management involves replacing thyroid hormones in hypothyroidism and reducing thyroid hormone production in hyperthyroidism, alongside lifestyle modifications and regular monitoring.
In conclusion, antithyroid peroxidase antibodies are a critical marker of autoimmune thyroid diseases, highlighting the complex interplay between the immune system and thyroid function. Understanding the role of these antibodies, along with advances in diagnosis and treatment, can lead to improved management and quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions.