Atrial Appendage Closure: Reduce Stroke Risk
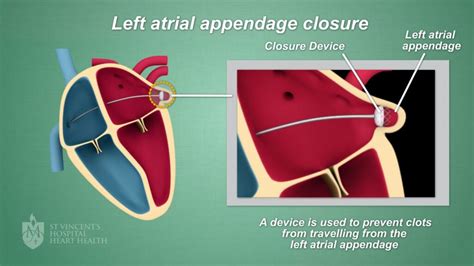
The atrial appendage, a small pouch attached to the upper chamber of the heart, has been identified as a significant source of blood clots that can lead to stroke in individuals with atrial fibrillation, a common heart rhythm disorder. Atrial fibrillation affects millions of people worldwide, and the risk of stroke associated with this condition is a major concern. Recent advances in medical technology have led to the development of a minimally invasive procedure known as atrial appendage closure, which aims to reduce the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation.
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke Risk
Atrial fibrillation is a type of irregular heartbeat that can lead to the formation of blood clots in the atrial appendage. These clots can break loose and travel to the brain, causing a stroke. The risk of stroke in individuals with atrial fibrillation is significantly higher than in those with a normal heart rhythm. According to the American Heart Association, atrial fibrillation increases the risk of stroke by four to five times. The atrial appendage is thought to be responsible for approximately 90% of thromboembolic events in patients with atrial fibrillation.
Atrial Appendage Closure: A Minimally Invasive Solution
Atrial appendage closure is a procedure that involves the insertion of a small device into the atrial appendage to prevent blood clots from forming and breaking loose. The device, typically made of a metal or fabric mesh, is designed to seal off the atrial appendage, reducing the risk of stroke. The procedure is usually performed under general anesthesia and takes approximately one to two hours to complete. The device is inserted through a small incision in the groin and guided to the heart using a catheter.
Atrial appendage closure is a game-changer for patients with atrial fibrillation who are at high risk of stroke. By sealing off the atrial appendage, we can significantly reduce the risk of stroke and improve the quality of life for these patients.
Benefits of Atrial Appendage Closure
The benefits of atrial appendage closure are numerous. The procedure has been shown to reduce the risk of stroke by approximately 70% in patients with atrial fibrillation. Additionally, the procedure can reduce the risk of bleeding associated with long-term anticoagulation therapy, which is often prescribed to patients with atrial fibrillation to prevent stroke. Atrial appendage closure can also improve the quality of life for patients with atrial fibrillation, allowing them to return to normal activities without the fear of stroke.
Comparative Analysis: Atrial Appendage Closure vs. Anticoagulation Therapy
Atrial appendage closure and anticoagulation therapy are two different approaches to reducing the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. Anticoagulation therapy involves the use of medications to prevent blood clots from forming in the atrial appendage. While anticoagulation therapy is effective in reducing the risk of stroke, it can also increase the risk of bleeding. Atrial appendage closure, on the other hand, is a one-time procedure that can provide long-term protection against stroke without the need for ongoing anticoagulation therapy.
| Approach | Risk Reduction | Risk of Bleeding |
|---|---|---|
| Atrial Appendage Closure | 70% | Low |
| Anticoagulation Therapy | 60% | High |
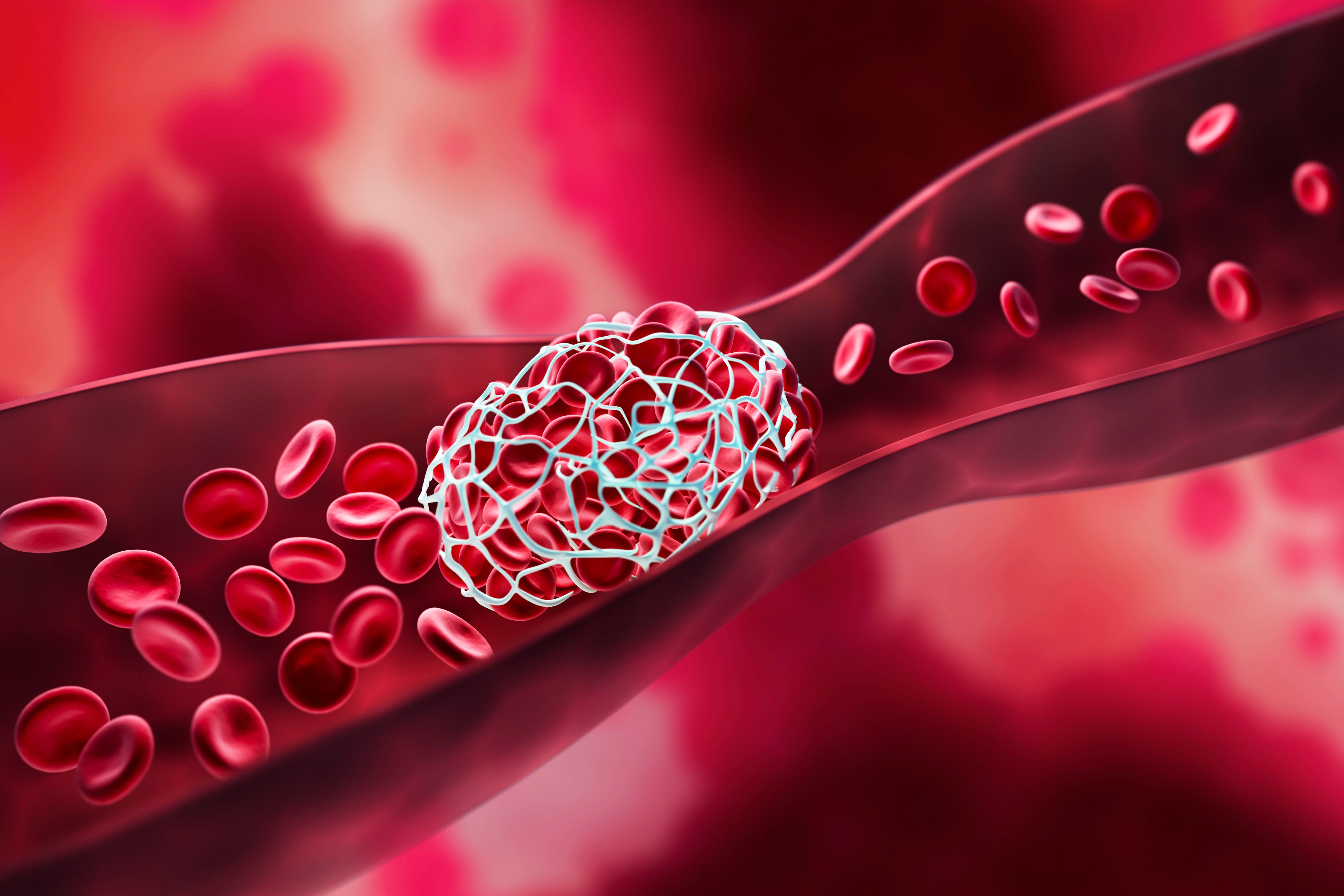
Future Trends: Advancements in Atrial Appendage Closure
The field of atrial appendage closure is rapidly evolving, with new devices and techniques being developed to improve the safety and efficacy of the procedure. One of the most promising advancements is the development of newer generation devices that are designed to be more effective and easier to implant. Additionally, researchers are exploring the use of atrial appendage closure in combination with other treatments, such as catheter ablation, to provide comprehensive care for patients with atrial fibrillation.
Steps to Atrial Appendage Closure
- Patient selection: Identify patients who are at high risk of stroke and are suitable candidates for atrial appendage closure.
- Procedure preparation: Prepare the patient for the procedure, including administering anesthesia and inserting a catheter into the groin.
- Device insertion: Insert the device into the atrial appendage using a catheter.
- Device deployment: Deploy the device to seal off the atrial appendage.
- Post-procedure care: Monitor the patient for any complications and provide post-procedure care.
Decision Framework: Is Atrial Appendage Closure Right for You?
Atrial appendage closure is a highly effective procedure for reducing the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. However, it may not be suitable for everyone. Patients who are considering atrial appendage closure should discuss the following factors with their doctor:
- Risk of stroke: Patients who are at high risk of stroke may benefit from atrial appendage closure.
- Bleeding risk: Patients who are at high risk of bleeding may not be suitable candidates for atrial appendage closure.
- Other medical conditions: Patients with other medical conditions, such as heart valve problems or coronary artery disease, may require additional treatments.
Pros and Cons of Atrial Appendage Closure
- Pros:
- Reduces the risk of stroke by approximately 70%
- Minimally invasive procedure
- Can reduce the risk of bleeding associated with long-term anticoagulation therapy
- Cons:
- May not be suitable for patients with other medical conditions
- Requires a catheter to be inserted into the groin
- May require post-procedure care and monitoring
FAQ Section
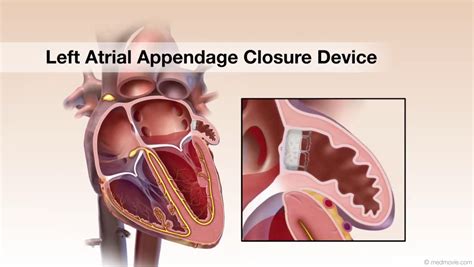
What is atrial appendage closure, and how does it work?
+Atrial appendage closure is a minimally invasive procedure that involves the insertion of a small device into the atrial appendage to prevent blood clots from forming and breaking loose. The device seals off the atrial appendage, reducing the risk of stroke.
Who is a suitable candidate for atrial appendage closure?
+Patients who are at high risk of stroke and have atrial fibrillation are suitable candidates for atrial appendage closure. However, the decision to undergo the procedure should be made in consultation with a doctor, taking into account individual factors and medical history.
What are the benefits of atrial appendage closure compared to anticoagulation therapy?
+Atrial appendage closure can reduce the risk of stroke by approximately 70%, which is comparable to anticoagulation therapy. However, atrial appendage closure can also reduce the risk of bleeding associated with long-term anticoagulation therapy, making it a preferable option for some patients.
What are the potential complications of atrial appendage closure?
+Potential complications of atrial appendage closure include bleeding, infection, and damage to the heart or surrounding tissues. However, these complications are rare, and the procedure is generally considered safe.
How long does the atrial appendage closure procedure take, and what is the recovery time?
+The atrial appendage closure procedure typically takes approximately one to two hours to complete. The recovery time is usually short, with most patients able to return home the same day or the next day.



