Best Sugar Levels
Maintaining optimal sugar levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. When we refer to sugar levels, we’re primarily talking about blood glucose levels, which are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). The body uses glucose as a primary source of energy, but it must be maintained within a specific range to prevent complications. Understanding what constitutes the best sugar levels and how to achieve them can significantly impact your quality of life.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
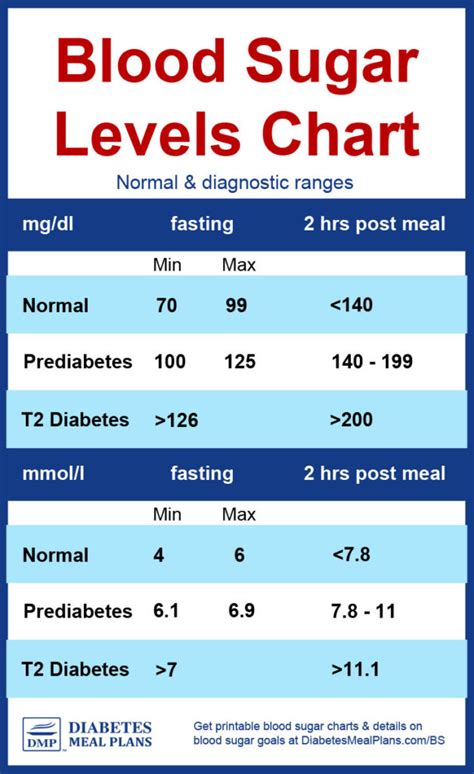
For individuals without diabetes, normal blood sugar levels are typically as follows: - Fasting blood sugar (after not eating for at least 8 hours): Less than 100 mg/dL. - After eating (postprandial): Less than 140 mg/dL 2 hours after a meal.
For people with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) provides guidelines for blood glucose targets, which may slightly vary but generally include: - Before meals: 80-130 mg/dL for adults. - After meals (1-2 hours after beginning of meal): Less than 180 mg/dL.
Importance of Monitoring Sugar Levels
Monitoring and maintaining optimal sugar levels is vital, especially for individuals with diabetes. High blood sugar (hyperglycemia) over time can lead to serious health issues, including heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems. Conversely, low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can be dangerous and even life-threatening if not promptly treated.
Achieving Best Sugar Levels
Achieving and maintaining the best sugar levels involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments and, for some, medication. Here are several strategies:
Dietary Changes: Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit intake of added sugars, saturated fats, and refined carbohydrates.
Regular Physical Activity: Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels and improves insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.
Hydration: Drinking enough water helps the body regulate blood sugar levels and improves overall health.
Stress Management: Stress can affect blood sugar levels. Engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
Medication Adherence: For those with diabetes, taking medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider is crucial for managing blood sugar levels.
Advanced Strategies for Optimal Sugar Levels
For some individuals, especially those with prediabetes or diabetes, more advanced strategies may be necessary: - Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): This involves wearing a small device that tracks glucose levels throughout the day and night, providing valuable insights into how different foods, activities, and times of day affect your glucose levels. - Insulin Therapy: For individuals with diabetes, insulin injections or an insulin pump may be necessary to help regulate blood sugar levels. - Nutritional Counseling: Working with a registered dietitian or a certified diabetes educator can provide personalized dietary advice tailored to your needs and health goals.
Future Trends in Sugar Level Management
The future of managing sugar levels looks promising, with advancements in technology and medical research offering new tools and treatments. For instance: - Artificial Pancreas Systems: These systems automate insulin delivery based on real-time glucose monitoring, aiming to mimic the body’s natural pancreatic function more closely. - Personalized Medicine: Tailoring diabetes management to the individual, considering genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors, could lead to more effective and sustainable control of blood sugar levels.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
There are several misconceptions about sugar levels and diabetes management: - Myth: People with diabetes cannot eat sugar at all. - Reality: While it’s true that individuals with diabetes need to be mindful of their carbohydrate intake, completely eliminating sugar from the diet is not necessary or practical. The focus should be on balancing carbohydrate intake and choosing whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
+Symptoms of high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) can include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, slow healing of cuts and wounds, and frequent infections. If left untreated, high blood sugar can lead to more severe symptoms and complications.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on the type of diabetes you have, your treatment plan, and how well your blood sugar levels are controlled. Generally, people with type 1 diabetes and some with type 2 diabetes may need to check their blood sugar levels multiple times a day, while others may only need to check occasionally.
Can diet and exercise alone treat diabetes?
+For people with type 2 diabetes, diet and exercise can sometimes be enough to manage blood sugar levels, especially if the condition is caught early. However, for many, and especially for those with type 1 diabetes, medication (like insulin) is necessary to control blood sugar levels effectively. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best management plan for your specific situation.
Key Takeaways
- Monitoring and maintaining optimal sugar levels is crucial for overall health.
- Lifestyle adjustments, including diet, exercise, and stress management, play a significant role in achieving and maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
- For individuals with diabetes, medication adherence and, in some cases, advanced strategies like continuous glucose monitoring, may be necessary.
By focusing on comprehensive management of sugar levels and being aware of the most current approaches in diabetes care, individuals can lead healthier, more fulfilling lives. Remember, the key to successful sugar level management is understanding your body’s unique needs and working closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized plan.