Biopsy Of Cervix

A cervical biopsy is a medical procedure that involves removing a small sample of tissue from the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus in the female reproductive system. The primary purpose of this procedure is to diagnose any abnormalities or potential health risks in the cervix, such as precancerous or cancerous cells.
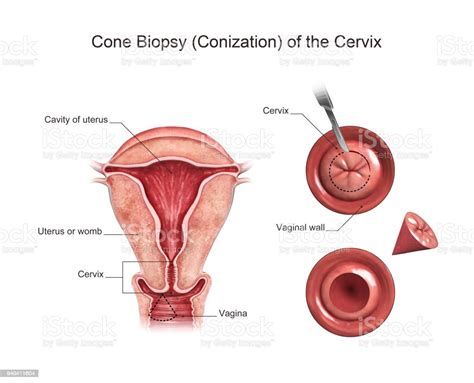
The cervix is a crucial part of the female reproductive system, and it plays a vital role in childbirth and menstruation. The cervix is located at the lower end of the uterus and extends into the vagina. It is approximately 2-3 centimeters in length and has a narrow opening that allows for the passage of menstrual blood and babies during childbirth.
There are several reasons why a doctor may recommend a cervical biopsy. Some of the most common reasons include:
- Abnormal Pap test results: A Pap test, also known as a Pap smear, is a screening test that checks for abnormal cell changes in the cervix. If the results of a Pap test are abnormal, a cervical biopsy may be necessary to further investigate the abnormal cell changes.
- Suspicious cervical lesions: During a pelvic exam, a doctor may notice unusual growths or lesions on the cervix. A cervical biopsy can help determine if these lesions are precancerous or cancerous.
- Cervical cancer symptoms: In some cases, a cervical biopsy may be performed if a woman is experiencing symptoms such as abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, or difficulty urinating.
The procedure for a cervical biopsy is relatively straightforward and can be performed in a doctor’s office or a hospital. The steps involved in the procedure are:
- Preparation: The patient will be asked to undress from the waist down and lie on an examination table.
- _insertion of a speculum: A speculum, which is a metal or plastic instrument, will be inserted into the vagina to hold it open and allow the doctor to see the cervix.
- Visualization: The doctor will use a special microscope or colposcope to visualize the cervix and identify any abnormal areas.
- Removal of tissue sample: The doctor will use a special instrument to remove a small sample of tissue from the abnormal area.
- Stitches or cauterization: Depending on the size and location of the tissue sample, the doctor may use stitches or cauterization to stop any bleeding.
There are different types of cervical biopsies, including:
- Punch biopsy: This is the most common type of cervical biopsy, which involves removing a small sample of tissue using a special instrument.
- Cone biopsy: This type of biopsy involves removing a larger sample of tissue in the shape of a cone.
- Endocervical biopsy: This type of biopsy involves removing tissue from the canal of the cervix.
After the procedure, the tissue sample will be sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results of the biopsy will determine if the abnormal cells are precancerous or cancerous. If the results are abnormal, the doctor may recommend further treatment, such as removal of the abnormal tissue or surgery.
It is essential to note that a cervical biopsy is a relatively safe procedure, but as with any medical procedure, there are potential risks and complications. Some of the possible risks and complications include:
- Bleeding: There may be some bleeding after the procedure, which can be heavy in some cases.
- Infection: There is a risk of infection with any invasive medical procedure.
- Cervical stenosis: In some cases, the cervix may become narrowed or scarred after the procedure, which can cause difficulties with future pregnancies or menstrual cycles.
In conclusion, a cervical biopsy is a medical procedure that involves removing a small sample of tissue from the cervix to diagnose any abnormalities or potential health risks. The procedure is relatively straightforward and can be performed in a doctor’s office or a hospital. While there are potential risks and complications, a cervical biopsy is a crucial diagnostic tool for detecting precancerous or cancerous cells in the cervix.
What is the purpose of a cervical biopsy?
+The purpose of a cervical biopsy is to diagnose any abnormalities or potential health risks in the cervix, such as precancerous or cancerous cells.
What are the different types of cervical biopsies?
+There are several types of cervical biopsies, including punch biopsy, cone biopsy, and endocervical biopsy.
What are the potential risks and complications of a cervical biopsy?
+The potential risks and complications of a cervical biopsy include bleeding, infection, and cervical stenosis.
How is a cervical biopsy performed?
+A cervical biopsy is performed by inserting a speculum into the vagina, visualizing the cervix with a special microscope or colposcope, and removing a small sample of tissue from the abnormal area.
What can I expect after a cervical biopsy?
+After a cervical biopsy, you may experience some bleeding or cramping, and you should follow your doctor's instructions for post-procedure care.
In addition to a cervical biopsy, there are other diagnostic tests that can be used to detect abnormalities in the cervix, including:
- Pap test: A Pap test, also known as a Pap smear, is a screening test that checks for abnormal cell changes in the cervix.
- Colposcopy: A colposcopy is a procedure that uses a special microscope to visualize the cervix and identify any abnormal areas.
- HPV test: An HPV test checks for the presence of high-risk types of human papillomavirus (HPV), which can cause cervical cancer.
It is essential to note that a cervical biopsy is not a substitute for regular Pap tests or other screening tests. Women should follow their doctor’s recommendations for cervical cancer screening and prevention.
In conclusion, a cervical biopsy is a diagnostic tool that can help detect precancerous or cancerous cells in the cervix. While there are potential risks and complications, a cervical biopsy is a crucial procedure for maintaining women’s health and preventing cervical cancer. By understanding the purpose, types, and procedure of a cervical biopsy, women can make informed decisions about their health and take steps to prevent cervical cancer.
According to the American Cancer Society, cervical cancer is one of the most preventable types of cancer, and regular screening tests can help detect abnormal cell changes in the cervix before they become cancerous. Women should follow their doctor's recommendations for cervical cancer screening and prevention to reduce their risk of developing cervical cancer.
By following the recommended screening guidelines and undergoing a cervical biopsy if necessary, women can reduce their risk of developing cervical cancer and maintain good reproductive health.
A cervical biopsy is a diagnostic tool that can help detect precancerous or cancerous cells in the cervix. While there are potential risks and complications, a cervical biopsy is a crucial procedure for maintaining women's health and preventing cervical cancer.
In the end, a cervical biopsy is a vital procedure that can help women maintain good reproductive health and prevent cervical cancer. By understanding the purpose, types, and procedure of a cervical biopsy, women can make informed decisions about their health and take steps to prevent cervical cancer.
Steps to take after a cervical biopsy:
- Follow your doctor’s instructions for post-procedure care.
- Take any prescribed medication as directed.
- Attend any follow-up appointments as scheduled.
- Practice good hygiene and avoid heavy lifting or strenuous activity.