Blood Clot Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a complex and delicate process, and one of the many potential complications that can arise is the formation of blood clots. Blood clots, also known as thrombosis, occur when the blood thickens and forms a clump that can block blood flow. During pregnancy, the risk of developing blood clots is higher due to various physiological changes that take place in the body.
One of the main reasons for the increased risk of blood clots during pregnancy is the change in blood clotting factors. The body produces more clotting factors, such as fibrinogen, to prepare for the possibility of bleeding during childbirth. While this is a natural and necessary process, it can also increase the risk of blood clots forming in the legs, lungs, or other parts of the body. According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), the risk of blood clots is approximately 1 in 1,000 pregnancies.
Another factor that contributes to the increased risk of blood clots during pregnancy is the compression of blood vessels. As the uterus expands, it can put pressure on the veins in the legs and pelvis, which can cause blood to flow more slowly and increase the risk of clotting. This is particularly true for women who are carrying multiple fetuses or have a history of blood clots.
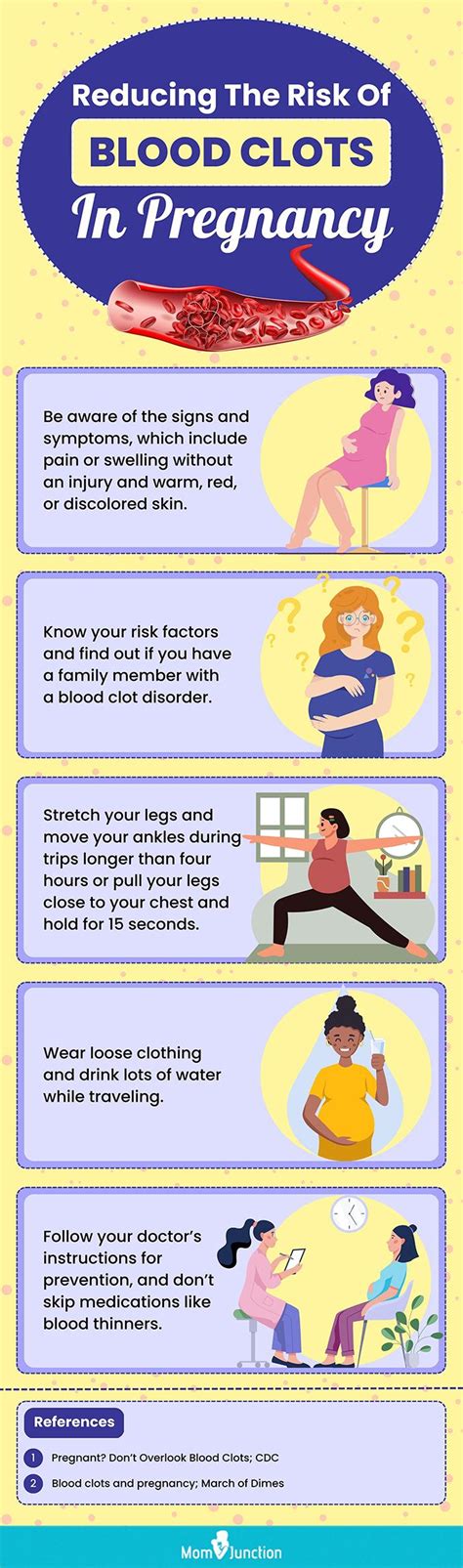
The symptoms of blood clots during pregnancy can vary depending on the location and severity of the clot. Some common symptoms include swelling, redness, and pain in the legs, as well as shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing up blood. It’s essential for pregnant women to be aware of these symptoms and seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of them.
The diagnosis of blood clots during pregnancy typically involves a combination of physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. A doctor may perform a physical exam to check for signs of swelling, redness, or tenderness in the legs. They may also order blood tests to check for clotting factors and other markers of blood clots. Imaging studies, such as ultrasound or CT scans, may be used to confirm the presence of a blood clot.
The treatment of blood clots during pregnancy depends on the location and severity of the clot. In some cases, anticoagulant medications, such as heparin or low-molecular-weight heparin, may be prescribed to prevent the clot from growing and causing further complications. In severe cases, hospitalization and close monitoring may be necessary to ensure the health and safety of both the mother and the fetus.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water
- Wear compression stockings to improve blood flow
- Avoid crossing legs or ankles, which can restrict blood flow
- Take regular breaks to stretch and move around, especially during long periods of sitting or standing
- Get regular exercise, such as walking or swimming, to improve circulation
In addition to these preventive measures, pregnant women can also reduce their risk of blood clots by managing other health conditions, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity. Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and getting regular prenatal care can also help to minimize the risk of complications during pregnancy.
The relationship between blood clots and pregnancy is complex, and more research is needed to understand the underlying causes and risk factors. However, by being aware of the risks and taking preventive measures, women can reduce their chances of developing blood clots during pregnancy and ensure a healthy outcome for both themselves and their babies.
What are the symptoms of blood clots during pregnancy?
+The symptoms of blood clots during pregnancy can include swelling, redness, and pain in the legs, as well as shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing up blood.
How can I reduce my risk of blood clots during pregnancy?
+To reduce your risk of blood clots during pregnancy, stay hydrated, wear compression stockings, avoid crossing your legs or ankles, take regular breaks to stretch and move around, and get regular exercise.
What are the treatment options for blood clots during pregnancy?
+The treatment options for blood clots during pregnancy depend on the location and severity of the clot and may include anticoagulant medications, hospitalization, and close monitoring.
In conclusion, blood clots during pregnancy are a serious complication that can have significant consequences for both the mother and the fetus. By understanding the risks and taking preventive measures, women can reduce their chances of developing blood clots and ensure a healthy outcome for both themselves and their babies. It’s essential for pregnant women to be aware of the symptoms and seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of them. With proper care and attention, the risk of blood clots during pregnancy can be minimized, and women can have a healthy and successful pregnancy.