Blood Diabetic Levels
Understanding blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals living with diabetes, as well as those who are at risk of developing the condition. Blood glucose levels refer to the amount of glucose present in the blood at any given time. Glucose is a type of sugar that serves as the primary source of energy for the body’s cells. In people with diabetes, the body either cannot produce enough insulin (a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels) or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces, leading to elevated blood glucose levels.
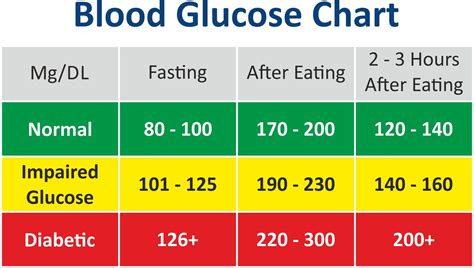
The normal range for blood glucose levels is typically between 70 and 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), though this can vary slightly depending on the timing of the last meal and other factors. For individuals with diabetes, maintaining blood sugar levels within a target range is key to preventing complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems. The target ranges can vary depending on the individual, their health status, and the specific type of diabetes they have (Type 1, Type 2, or gestational diabetes).
Importance of Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels is a critical aspect of diabetes management. It helps individuals understand how different factors such as diet, exercise, stress, and medications affect their blood glucose levels. By keeping track of these levels, individuals can make informed decisions about their daily activities and adjust their treatment plans as needed to prevent both hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), both of which can have serious health consequences.
How to Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
There are several methods to monitor blood sugar levels, including:
Fingerstick Tests: This is the most common method, involving pricking the fingertip with a lancet to draw a small drop of blood, which is then placed on a test strip and read by a glucometer.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): These devices are worn on the body and use a small sensor inserted under the skin to track glucose levels throughout the day and night.
Flash Glucose Monitors: Similar to CGMs, these provide real-time glucose readings but require scanning the sensor with a reader to get the levels.
Target Blood Sugar Levels
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends the following target blood sugar levels for most adults with diabetes:
- Before Meals: 80-130 mg/dL
- After Meals (1-2 hours): Less than 180 mg/dL
However, these targets may be adjusted based on individual factors, such as age, other health conditions, duration of diabetes, life circumstances, and the presence of complications. Pregnant women with gestational diabetes may have different targets. It’s crucial for individuals to work closely with their healthcare providers to establish personalized glucose targets.
Complications of Uncontrolled Blood Sugar Levels
Uncontrolled high blood sugar levels over time can lead to serious complications, including:
- Cardiovascular Disease: High risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular conditions.
- Nerve Damage (Neuropathy): Can cause pain, numbness, or tingling in the hands and feet.
- Kidney Damage (Nephropathy): Can lead to kidney failure.
- Eye Damage (Retinopathy): Can cause blindness.
- Foot Damage: Nerve damage and poor circulation can lead to foot problems, including sores that won’t heal.
Management and Prevention
Managing blood sugar levels involves a combination of lifestyle changes and, for many, medication. Key strategies include:
- Healthy Eating: Following a balanced meal plan that controls carbohydrate intake and focuses on whole, unprocessed foods.
- Regular Physical Activity: Exercise can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Medications: For those who require it, insulin or oral medications can help control blood sugar levels.
- Stress Management: High levels of stress can affect blood sugar control; techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help.
Preventing diabetes, particularly Type 2, involves many of the same strategies. Maintaining a healthy weight, being physically active, and eating a healthy diet can significantly reduce the risk of developing insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes.
Future Trends in Blood Sugar Management
Advancements in technology and medical research are continually improving the management of blood sugar levels. Developments include:
- Artificial Pancreas Systems: Automated systems that use CGM data to adjust insulin doses.
- New Medications: Research into new classes of drugs and novel delivery systems for existing medications.
- Gene Editing and Stem Cell Therapies: Potential future treatments aimed at curing or more effectively managing diabetes.
- Digital Health Platforms: Apps, wearables, and online services that support diabetes management through data tracking, education, and community support.
The management of blood sugar levels is a multifaceted challenge that requires a personalized approach, integrating medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and technological support. As our understanding of diabetes and its management evolves, so too will the tools and strategies available for maintaining healthy blood glucose levels.
What is the normal range for blood glucose levels?
+The normal range for blood glucose levels is typically between 70 and 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), though this can vary slightly depending on the timing of the last meal and other factors.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on the type of diabetes and the individual’s treatment plan. Generally, people with diabetes are advised to check their blood sugar levels at least four times a day, but this can vary based on their specific needs and the recommendations of their healthcare provider.
What are the potential complications of uncontrolled blood sugar levels?
+Uncontrolled high blood sugar levels over time can lead to serious complications, including cardiovascular disease, nerve damage (neuropathy), kidney damage (nephropathy), eye damage (retinopathy), and foot damage. It is crucial to manage blood sugar levels effectively to prevent these complications.
Can lifestyle changes alone manage blood sugar levels?
+For some individuals, particularly those with prediabetes or early-stage Type 2 diabetes, lifestyle changes such as healthy eating, regular physical activity, and weight loss can be sufficient to manage blood sugar levels. However, for others, especially those with Type 1 diabetes or more advanced Type 2 diabetes, medication or insulin therapy may also be necessary.
What role does technology play in managing blood sugar levels?
+Technology plays a significant role in managing blood sugar levels, from continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and flash glucose monitors that provide real-time glucose data, to digital health platforms that offer tracking tools, educational resources, and community support. These technologies can help individuals with diabetes make informed decisions and better manage their condition.