Blood Sugar Chart Guide: Manage Levels
Managing blood sugar levels is a critical aspect of maintaining overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes. A blood sugar chart is a valuable tool that helps track and manage blood glucose levels, providing insights into the body’s response to different foods, physical activity, and medication. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of blood sugar charts, exploring their benefits, how to use them, and practical tips for managing blood sugar levels.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
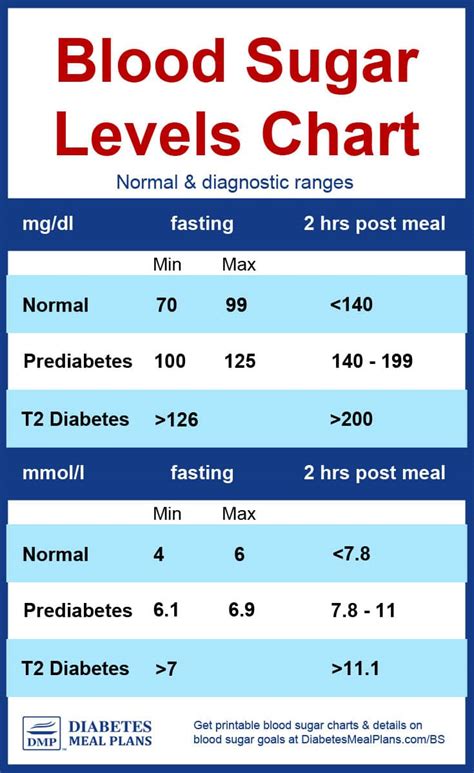
Before diving into the world of blood sugar charts, it’s essential to understand the different blood sugar levels and their implications. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends the following blood sugar targets:
- Fasting blood sugar: 80-130 mg/dL
- Before meals: 70-130 mg/dL
- After meals: Less than 180 mg/dL
- At bedtime: 100-140 mg/dL
What is a Blood Sugar Chart?
A blood sugar chart, also known as a blood glucose log or diary, is a tool used to track and record blood sugar levels over a period. It typically includes columns for recording the date, time, blood sugar level, and any notable events, such as meals, exercise, or medication. By monitoring blood sugar levels, individuals can identify patterns, trends, and areas for improvement, enabling them to make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication.
Benefits of Using a Blood Sugar Chart
Using a blood sugar chart offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved blood sugar control: By tracking blood sugar levels, individuals can identify patterns and trends, enabling them to make adjustments to their diet, exercise, and medication.
- Enhanced self-awareness: A blood sugar chart helps individuals develop a deeper understanding of how their body responds to different foods, physical activity, and medication.
- Better communication with healthcare providers: A blood sugar chart provides valuable information for healthcare providers, enabling them to make informed decisions about treatment plans and medication adjustments.
- Increased motivation: Tracking progress and seeing improvements in blood sugar control can be a powerful motivator, encouraging individuals to continue making healthy lifestyle choices.
How to Use a Blood Sugar Chart
Using a blood sugar chart is a straightforward process that involves:
- Recording blood sugar levels: Use a glucometer to measure blood sugar levels at designated times, such as before and after meals, and at bedtime.
- Noting events and activities: Record any notable events, such as meals, exercise, or medication, to help identify patterns and trends.
- Analyzing data: Review the blood sugar chart regularly to identify areas for improvement and make adjustments to diet, exercise, and medication as needed.
- Sharing with healthcare providers: Bring the blood sugar chart to healthcare appointments to provide valuable insights and inform treatment decisions.
Practical Tips for Managing Blood Sugar Levels
In addition to using a blood sugar chart, the following tips can help individuals manage their blood sugar levels:
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Engage in regular physical activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate blood sugar levels and support overall health.
- Manage stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, to help mitigate the impact of stress on blood sugar levels.
Advanced Blood Sugar Management Techniques
For individuals with diabetes or those who require more advanced blood sugar management, the following techniques may be helpful:
- Continuous glucose monitoring: Use a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) to track blood sugar levels throughout the day and night.
- Insulin therapy: Work with a healthcare provider to develop an insulin therapy plan that meets individual needs.
- Carb counting: Track carbohydrate intake to better manage blood sugar levels and make informed decisions about food choices.
Conclusion
Managing blood sugar levels is a critical aspect of maintaining overall health, and a blood sugar chart is a valuable tool that can help individuals track and manage their blood glucose levels. By understanding the benefits of using a blood sugar chart, how to use it, and practical tips for managing blood sugar levels, individuals can take control of their health and make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication. Remember to consult with a healthcare provider before making any significant changes to your treatment plan.
FAQ Section
What is the normal range for blood sugar levels?
+The normal range for blood sugar levels is between 70-130 mg/dL before meals and less than 180 mg/dL after meals.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of blood sugar checks depends on individual needs and healthcare provider recommendations. Typically, individuals with diabetes check their blood sugar levels before and after meals, and at bedtime.
Can I use a blood sugar chart to track my progress?
+What are the benefits of using a blood sugar chart?
+The benefits of using a blood sugar chart include improved blood sugar control, enhanced self-awareness, better communication with healthcare providers, and increased motivation to make healthy lifestyle choices.
Can I use a blood sugar chart to manage my insulin therapy?
+How can I get started with using a blood sugar chart?
+To get started with using a blood sugar chart, consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best approach for individual needs. Choose a blood sugar chart that meets your needs, and start tracking blood sugar levels and notable events. Review the chart regularly to identify areas for improvement and make adjustments to diet, exercise, and medication as needed.