Blood Sugar Over 200
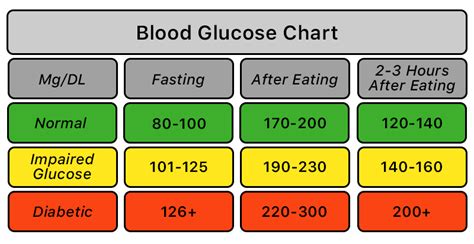
Having a blood sugar level over 200 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) is a significant concern, as it indicates hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar. This condition can be dangerous and requires immediate attention, especially for individuals with diabetes. Understanding the implications, causes, and management strategies for high blood sugar levels is crucial for maintaining health and preventing complications.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar levels are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) and are an essential indicator of how well the body is managing glucose, the primary source of energy for cells. In a healthy individual, blood glucose levels typically range from 70 to 110 mg/dL throughout the day, with some variations depending on when the last meal was consumed and the physical activity level. However, for people with diabetes or prediabetes, managing these levels is a daily challenge.
Risks Associated with High Blood Sugar
High blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, occurs when the body has too much glucose in the blood. This can happen for several reasons, including consuming more carbohydrates than the body can handle, not taking enough diabetes medication, or experiencing stress and illness, which can raise blood sugar levels. If left untreated, hyperglycemia can lead to serious health issues, including:
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): A life-threatening condition that occurs when the body produces high levels of blood acids called ketones.
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS): A serious condition most commonly seen in people with type 2 diabetes, where the body tries to get rid of the excess glucose through urine, leading to severe dehydration.
- Damage to Organs: Over time, high blood sugar can damage the heart, eyes, kidneys, nerves, teeth, and gums.
Managing High Blood Sugar
Managing high blood sugar involves a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and monitoring. Here are some strategies for bringing down high blood sugar levels:
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps the kidneys flush out excess glucose through urine.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Dietary Changes: Eating smaller, more balanced meals can help manage blood sugar spikes. Focus on whole foods, vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Medication: For individuals with diabetes, following the prescribed medication regimen is crucial. This may include insulin or oral medications that help lower blood sugar.
- Stress Reduction: Stress can raise blood sugar levels. Engaging in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help.
- Monitoring: Regularly checking blood sugar levels helps identify patterns and allows for timely interventions to prevent levels from getting too high.
Preventing High Blood Sugar Episodes
Prevention is key to managing diabetes and avoiding the risks associated with high blood sugar. Here are some preventive measures:
- Regular Health Check-ups: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol can help prevent complications.
- Healthy Weight Maintenance: Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and helps manage the condition if you already have it.
- Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol: Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can worsen diabetes management and increase the risk of complications.
Seek Medical Help
If you experience any of the following symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical help immediately:
- High blood sugar levels above 250 mg/dL
- Severe thirst or dry mouth
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Cuts or wounds that are slow to heal
- Tingling or numbness in the hands and feet
- Recurring skin, gum, or bladder infections
prompting for immediate medical evaluation if symptoms persist or worsen.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
+Symptoms can include severe thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts or wounds. If you're experiencing any of these, it's crucial to check your blood sugar level and consult with your healthcare provider.
How can I quickly lower my blood sugar?
+Drinking water, engaging in light physical activity, and following your prescribed medication regimen can help lower your blood sugar. It's also essential to identify and avoid triggers that cause high blood sugar levels.
Can high blood sugar be prevented?
+Yes, preventive measures such as maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet, exercising regularly, not smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption can significantly reduce the risk of developing high blood sugar and related complications.
Balancing blood sugar levels is a delicate task that requires patience, dedication, and the right guidance. By understanding the causes, risks, and management strategies for high blood sugar, individuals can take proactive steps towards a healthier life, minimizing the risk of complications and maximizing their well-being.



