Blood Sugar Regular
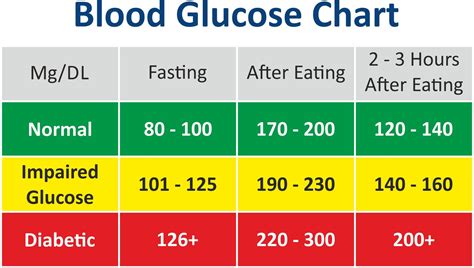
Maintaining regular blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary source of energy for the body’s cells, and its levels are regulated by insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. When blood sugar levels are irregular, it can lead to a range of health issues, from mild symptoms like fatigue and dizziness to more severe complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
To comprehend the importance of regular blood sugar levels, it’s essential to understand how glucose functions in the body. After consuming a meal, the digestive system breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. In response, the pancreas releases insulin, facilitating the entry of glucose into cells, where it’s used for energy production or stored for future use. In individuals with diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or is unable to effectively use the insulin it produces (Type 2 diabetes), leading to high blood sugar levels.
Consequences of Irregular Blood Sugar Levels
Irregular blood sugar levels can have significant consequences on the body. Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, can lead to symptoms such as increased thirst and urination, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds. If left unmanaged, hyperglycemia can cause more severe complications, including:
- Cardiovascular Disease: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes.
- Kidney Damage: The kidneys may become overworked, filtering excess glucose from the blood, potentially leading to kidney failure.
- Nerve Damage: High blood sugar can damage nerves, causing numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet.
On the other hand, hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, can cause symptoms such as shakiness, dizziness, and confusion. Severe hypoglycemia can lead to loss of consciousness, seizures, and even death.
Strategies for Maintaining Regular Blood Sugar Levels
Fortunately, there are several strategies for maintaining regular blood sugar levels. These include:
- Healthy Diet: Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid sugary drinks and foods high in added sugars, salt, and unhealthy fats.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises to help manage stress levels.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Regularly check blood sugar levels to identify patterns and make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.
- Medication Adherence: If prescribed medication, take it as directed by a healthcare provider to help regulate blood sugar levels.
Lifestyle Changes for Blood Sugar Management
In addition to the strategies mentioned above, several lifestyle changes can help manage blood sugar levels. These include:
- Getting Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity.
- Staying Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help the body regulate blood sugar levels and prevent dehydration.
- Limiting Alcohol Consumption: Avoid excessive alcohol consumption, as it can affect blood sugar levels and interact with diabetes medications.
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, and other complications associated with diabetes.
By implementing these strategies and making informed lifestyle choices, individuals can effectively manage their blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of complications and promoting overall health and well-being.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
+The symptoms of high blood sugar include increased thirst and urination, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds. If left unmanaged, high blood sugar can lead to more severe complications, such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
How can I maintain regular blood sugar levels?
+Maintaining regular blood sugar levels can be achieved through a combination of a healthy diet, regular physical activity, stress management, monitoring blood sugar levels, and medication adherence. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as getting enough sleep, staying hydrated, limiting alcohol consumption, and quitting smoking can also help manage blood sugar levels.
What are the risks of unmanaged blood sugar levels?
+Unmanaged blood sugar levels can lead to severe complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and even death. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a plan for managing blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of these complications.


