Blood Test For Allergic Reaction
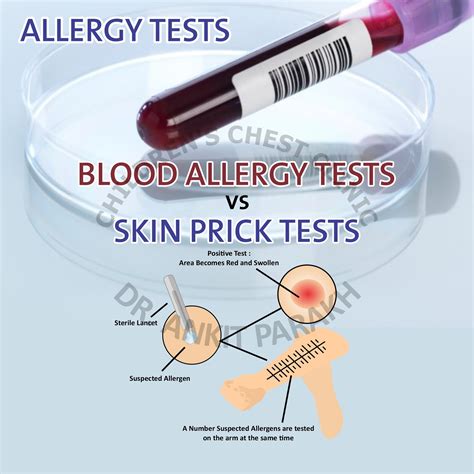
When it comes to identifying an allergic reaction, a blood test can be a valuable tool. Allergic reactions occur when the body’s immune system overreacts to a harmless substance, such as pollen, dust, or certain foods. This overreaction can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to life-threatening reactions. A blood test for an allergic reaction can help doctors diagnose the problem and determine the best course of treatment.
How Blood Tests Work for Allergies
Blood tests for allergies measure the levels of certain antibodies in the blood. Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system in response to the presence of foreign substances. In the case of allergies, the relevant antibodies are immunoglobulin E (IgE). When an allergen enters the body, IgE antibodies bind to it, triggering the release of chemical mediators, such as histamine, which cause allergic symptoms.
The most common blood test used to diagnose allergies is the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or the radioallergosorbent test (RAST). These tests detect the presence of specific IgE antibodies to particular allergens. Another test, known as the ImmunoCAP test, is also widely used for its high sensitivity and specificity in detecting IgE antibodies.
Process of Taking a Blood Test
The process of taking a blood test for an allergic reaction is relatively straightforward. Here’s what you can expect:
- Preparation: You might be asked to avoid taking certain medications that could affect the test results, such as antihistamines, for a few days before the test.
- Drawing Blood: A healthcare professional will clean your arm with an antiseptic, tie a band around your upper arm to locate a vein, and then insert a needle into the vein to draw a blood sample. You might feel a slight pinch when the needle goes in.
- After the Test: The band is removed, and pressure is applied to the area where the needle was inserted to stop any bleeding. A bandage might be applied.
- Waiting for Results: The blood sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis. Results can take a few days to come back.
Understanding Blood Test Results
If the blood test shows the presence of IgE antibodies to a specific allergen, it indicates that you are allergic to that substance. However, the presence of IgE antibodies does not always mean you will react to the allergen. It’s also possible to have a false negative result, where the test does not detect an allergy that you actually have.
Types of Allergies Diagnosed by Blood Tests
Blood tests can diagnose a wide range of allergies, including but not limited to:
- Food Allergies: Such as allergies to peanuts, tree nuts, fish, shellfish, milk, eggs, wheat, and soy.
- Insect Sting Allergies: Allergies to stings from bees, wasps, hornets, yellow jackets, and fire ants.
- Environmental Allergies: Such as allergies to dust mites, mold, and pet dander.
- Drug Allergies: Reactions to certain medications.
Limitations and Considerations
While blood tests are a powerful diagnostic tool, they have limitations. They might not detect every type of allergy, and sometimes the results can be unclear or misleading. Furthermore, having a positive result for an allergen does not necessarily mean you will experience symptoms upon exposure to that allergen. Therefore, blood tests are often used in conjunction with a physical examination, medical history, and sometimes skin prick tests to make a comprehensive diagnosis.
Treatment and Management
Once an allergy is diagnosed through a blood test, the primary treatment involves avoiding exposure to the allergen as much as possible. Depending on the severity of the allergy, medication such as antihistamines might be prescribed to manage symptoms, and in severe cases, an emergency epinephrine injector (like an EpiPen) may be recommended.
Future Directions in Allergy Diagnosis
Advancements in medical technology are continually improving the diagnosis and management of allergies. More precise and less invasive tests are being developed to help diagnose allergies earlier and more accurately. Additionally, research into the desensitization and treatment of allergies through immunotherapy offers hope for those suffering from severe allergies.
Conclusion
Blood tests for allergic reactions play a crucial role in diagnosing and managing allergies. By understanding how these tests work and what their results mean, individuals can better navigate the process of identifying and dealing with their allergies. While there are limitations to blood tests, they remain a fundamental tool in the toolkit of allergy diagnosis, helping healthcare providers and patients work together to build a healthier, safer life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most common blood test for allergies?
+The most common blood tests for allergies are the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and the radioallergosorbent test (RAST), which detect specific IgE antibodies.
How long does it take to get the results of a blood test for allergies?
+Results can vary, but generally, it takes a few days to a week to receive the results of a blood test for allergies.
Can blood tests diagnose all types of allergies?
+No, blood tests cannot diagnose all types of allergies. They are primarily used for diagnosing IgE-mediated allergies and may not detect other types of allergic reactions.
What is the next step after a positive allergy blood test result?
+After a positive result, the next steps typically involve avoiding the allergen as much as possible and potentially starting a treatment plan, which might include medication or immunotherapy, as recommended by a healthcare provider.