Blood Under A Nail
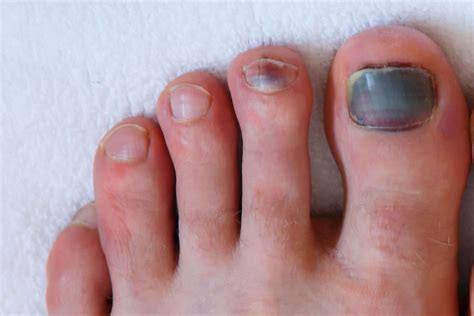
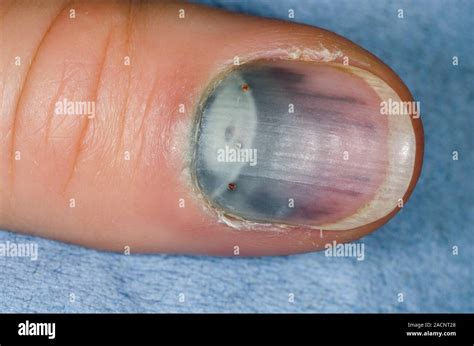
Subungual hematoma, commonly known as blood under a nail, is a condition that occurs when blood accumulates underneath a fingernail or toenail. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including trauma, injury, or certain medical conditions. The blood that collects under the nail can cause pain, discomfort, and discoloration, and if left untreated, can lead to further complications.
One of the primary causes of subungual hematoma is direct trauma to the nail, which can occur from a sudden impact, such as hitting one’s finger with a hammer or dropping a heavy object on the toe. This type of injury can cause blood vessels under the nail to rupture, leading to bleeding and accumulation of blood under the nail. In addition to trauma, certain medical conditions, such as psoriasis, eczema, or diabetes, can increase the risk of developing subungual hematoma.
Symptoms of subungual hematoma can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Mild cases may only cause minor discomfort and discoloration, while more severe cases can lead to intense pain, swelling, and even nail loss. In some cases, the accumulated blood can put pressure on the nail, causing it to lift off the nail bed or even fall off completely. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Diagnosis of subungual hematoma typically involves a physical examination and medical history. A healthcare professional will examine the affected nail and assess the severity of the condition. In some cases, additional tests, such as X-rays or ultrasound, may be required to rule out underlying conditions or complications.
Treatment for subungual hematoma depends on the severity of the condition. Mild cases can be managed with self-care measures, such as applying ice to reduce pain and swelling, elevating the affected limb, and taking over-the-counter pain medication. In more severe cases, medical treatment may be necessary, which can include drainage of the accumulated blood, application of topical antibiotics, or even surgical removal of the nail.
Prevention is key to avoiding subungual hematoma. Taking measures to protect the nails from trauma, such as wearing protective gear when engaging in activities that involve risk of injury, can help reduce the risk of developing this condition. Additionally, maintaining good foot and hand hygiene, avoiding excessive exposure to chemicals, and managing underlying medical conditions can also help prevent subungual hematoma.
In some cases, subungual hematoma can be a sign of an underlying fungal infection. Fungal infections, such as onychomycosis, can cause changes in the appearance of the nail, including thickening, brittleness, or discoloration. If left untreated, fungal infections can lead to further complications, including the spread of the infection to other parts of the body.
What are the common causes of subungual hematoma?
+Common causes of subungual hematoma include direct trauma to the nail, certain medical conditions, such as psoriasis or eczema, and fungal infections.
How is subungual hematoma diagnosed?
+Diagnosis of subungual hematoma typically involves a physical examination and medical history. Additional tests, such as X-rays or ultrasound, may be required to rule out underlying conditions or complications.
What are the treatment options for subungual hematoma?
+Treatment for subungual hematoma depends on the severity of the condition. Mild cases can be managed with self-care measures, while more severe cases may require medical treatment, including drainage of the accumulated blood or surgical removal of the nail.
In conclusion, subungual hematoma is a condition that requires prompt medical attention to prevent further complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage and prevent this condition. It’s essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time, as subungual hematoma can be a sign of an underlying condition that requires proper evaluation and treatment.
Advanced cases of subungual hematoma may require more extensive treatment, including surgical intervention. In these cases, a healthcare professional may need to drain the accumulated blood or remove the nail to promote healing and prevent further complications. It’s essential to follow post-treatment care instructions carefully to ensure proper healing and prevent infection.
Historically, subungual hematoma has been recognized as a condition that can have significant implications for overall health. In ancient civilizations, nail disorders were often seen as a sign of underlying health issues, and treatment approaches varied depending on the perceived cause of the condition. Today, we understand that subungual hematoma can be caused by a variety of factors, including trauma, medical conditions, and fungal infections, and treatment approaches are tailored to address the underlying cause of the condition.
The future of subungual hematoma treatment is likely to involve the development of new technologies and therapies that can promote healing and prevent complications. Researchers are currently exploring the use of advanced materials and techniques, such as platelet-rich plasma therapy, to promote nail growth and reduce the risk of infection. As our understanding of the condition evolves, we can expect to see the development of more effective treatment options that can improve outcomes for individuals affected by subungual hematoma.
| Causes of Subungual Hematoma | Symptoms | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|
| Direct trauma to the nail | Pain, discomfort, and discoloration | Self-care measures, medical treatment, or surgical intervention |
| Certain medical conditions, such as psoriasis or eczema | Swelling, redness, and nail loss | Topical antibiotics, anti-fungal medications, or corticosteroids |
| Fungal infections | Changes in nail appearance, including thickening or brittleness | Surgical removal of the nail or oral anti-fungal medications |
In the context of medical practice, subungual hematoma is a condition that requires careful evaluation and treatment. Healthcare professionals must consider the underlying cause of the condition, as well as the individual’s overall health status, when developing a treatment plan. By taking a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment, healthcare professionals can help individuals affected by subungual hematoma manage their symptoms and prevent further complications.
Ultimately, the effective management of subungual hematoma requires a collaborative approach between healthcare professionals and individuals affected by the condition. By working together to develop a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals can reduce their risk of complications and promote healing. As our understanding of the condition continues to evolve, we can expect to see the development of more effective treatment options and improved outcomes for individuals affected by subungual hematoma.