The discovery of the breast cancer gene, specifically the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, has revolutionized our understanding of breast cancer risk and prevention. For decades, women have been searching for answers about their susceptibility to this devastating disease, and genetic testing has provided a crucial tool in the fight against breast cancer. But what exactly do these genes do, and how can understanding your genetic risk help you take proactive steps towards prevention?
The Role of BRCA1 and BRCA2 Genes
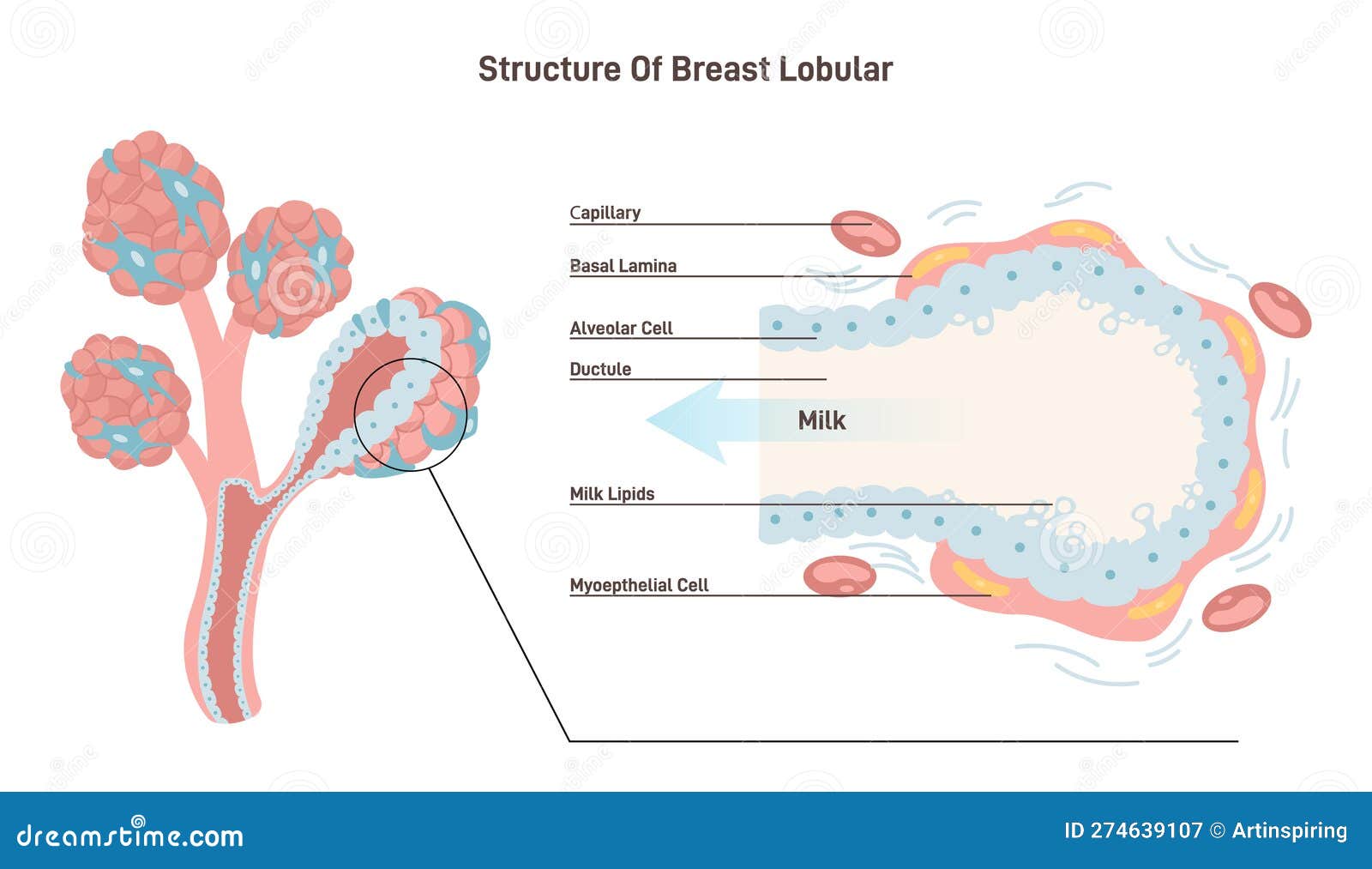
The BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are tumor suppressor genes, responsible for repairing damaged DNA and preventing the growth of cancer cells. When either of these genes is mutated, DNA damage can go unchecked, leading to an increased risk of developing breast, ovarian, and other cancers. Women who inherit a mutated BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene have a significantly higher risk of developing breast cancer, with some studies suggesting that the risk can be as high as 72% for BRCA1 and 69% for BRCA2.
Who Should Get Tested?
Genetic testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2 is not recommended for everyone, but rather for individuals who have a strong family history of breast or ovarian cancer. This includes women who have:
- A first-degree relative (mother, sister, or daughter) with breast cancer
- A first-degree relative with ovarian cancer
- A male relative with breast cancer
- Multiple relatives with breast or ovarian cancer
- Ashkenazi Jewish heritage, as this population is at higher risk for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations
The Genetic Testing Process
The genetic testing process typically involves a simple blood test or saliva sample, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The test looks for specific mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, and results are usually available within several weeks. It’s essential to consult with a genetic counselor before undergoing testing to discuss the potential risks and benefits and to determine whether testing is right for you.
Understanding Your Test Results
If you test positive for a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation, it’s essential to understand that this does not mean you will definitely develop breast cancer. Rather, it indicates that you have a higher risk of developing the disease. Your healthcare provider will work with you to develop a personalized prevention plan, which may include:
- More frequent breast cancer screenings, such as annual mammograms and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Prophylactic surgery, such as a mastectomy or salpingo-oophorectomy (removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes)
- Chemoprevention, such as taking medications to reduce the risk of breast cancer
- Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and limiting alcohol consumption
The Importance of Risk Reduction Strategies
While genetic testing can provide valuable insights into your breast cancer risk, it’s essential to remember that many cases of breast cancer are not linked to genetic mutations. Therefore, it’s crucial for all women to adopt risk-reduction strategies, including:
- Getting regular breast cancer screenings
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise
- Avoiding exposure to environmental toxins and radiation
- Being aware of changes in your breasts and reporting any concerns to your healthcare provider
Regardless of your genetic risk, it's essential to work with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized breast cancer prevention plan. This may include a combination of surveillance, prophylactic surgery, and lifestyle modifications. By taking proactive steps towards prevention, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing breast cancer and improve your overall health and well-being.
Addressing Common Concerns and Misconceptions
One common concern among women considering genetic testing is the potential for emotional distress or anxiety. While it’s natural to feel apprehensive about receiving test results, it’s essential to remember that genetic testing can provide valuable insights into your breast cancer risk and empower you to take proactive steps towards prevention.
Another misconception is that genetic testing is only relevant for women with a strong family history of breast cancer. However, genetic mutations can occur in anyone, regardless of family history. Therefore, it’s essential to discuss your individual risk factors with your healthcare provider and determine whether genetic testing is right for you.
The Future of Genetic Testing and Breast Cancer Prevention
As our understanding of genetics and breast cancer continues to evolve, we can expect to see significant advancements in genetic testing and prevention strategies. For example, researchers are currently exploring the development of new genetic tests that can identify multiple genetic mutations associated with breast cancer risk.
Additionally, there is a growing focus on personalized medicine, which involves tailoring prevention and treatment strategies to an individual’s unique genetic profile and risk factors. By combining genetic testing with advanced imaging technologies and preventive measures, we can significantly reduce the risk of breast cancer and improve treatment outcomes for women diagnosed with the disease.
What is the difference between BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes?
+Both BRCA1 and BRCA2 are tumor suppressor genes that help repair damaged DNA. However, they are located on different chromosomes and have distinct functions. BRCA1 is involved in the repair of double-strand breaks in DNA, while BRCA2 is involved in the repair of single-strand breaks.
Can men get breast cancer if they have a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation?
+Yes, men can develop breast cancer if they have a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation. However, the risk is significantly lower than for women. According to the American Cancer Society, the lifetime risk of breast cancer for men with a BRCA1 mutation is approximately 1.2%, and for those with a BRCA2 mutation, it is approximately 6.8%.
How accurate is genetic testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2?
+Genetic testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2 is highly accurate, with a sensitivity of 95-100% for detecting known mutations. However, it's essential to note that genetic testing may not detect all possible mutations, and a negative test result does not guarantee that you will not develop breast cancer.
In conclusion, understanding your genetic risk for breast cancer can be a powerful tool in the fight against this devastating disease. By knowing your risk, you can take proactive steps towards prevention, including more frequent screenings, prophylactic surgery, and lifestyle modifications. Remember, genetic testing is just one aspect of breast cancer prevention, and all women should adopt risk-reduction strategies to protect their health and well-being.