Broken Radial Head
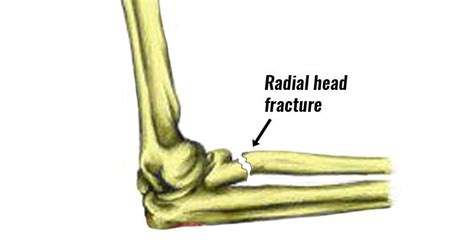
The radial head, a crucial component of the elbow joint, plays a vital role in facilitating rotation, flexion, and extension of the forearm. When this bone fractures, it can significantly impede an individual’s ability to perform everyday activities, leading to substantial discomfort and pain. A broken radial head, also known as a radial head fracture, is a common injury that can occur due to various reasons, including trauma, falls, or sports-related accidents.
To comprehend the severity and implications of a radial head fracture, it is essential to understand the anatomy of the elbow joint. The elbow consists of three bones: the humerus (upper arm bone), the radius, and the ulna (forearm bones). The radial head, located at the top of the radius, articulates with the humerus and the ulna, enabling smooth movement of the forearm. When a fracture occurs, it can disrupt this intricate mechanism, leading to compromised joint function and mobility.
Causes and Risk Factors
Radial head fractures can result from various causes, including:
- Falls: Direct blows to the elbow or falls onto an outstretched hand can transmit force up the forearm, leading to a fracture.
- Sports injuries: Participating in sports that involve throwing, catching, or falling, such as football, basketball, or gymnastics, increases the risk of radial head fractures.
- Trauma: Car accidents, bicycle accidents, or other high-impact collisions can cause a fracture.
- Weakened bones: Osteoporosis or other conditions that weaken the bones can increase the likelihood of a radial head fracture.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of a broken radial head may vary depending on the severity of the fracture. Common signs include:
- Severe pain in the elbow, forearm, or wrist
- Swelling, bruising, or redness around the elbow
- Limited mobility or stiffness in the elbow or forearm
- Crepitus (grinding or clicking sensation) when moving the elbow
- Weakness or numbness in the forearm, hand, or fingers
To diagnose a radial head fracture, a healthcare professional will typically perform a physical examination, assess medical history, and order imaging tests, such as:
- X-rays: To confirm the presence and severity of the fracture.
- CT scans: To provide more detailed images of the bone and surrounding tissue.
- MRI: To assess soft tissue damage, such as ligament or tendon injuries.
Treatment Options
Treatment for a broken radial head depends on the severity of the fracture, the patient’s overall health, and their lifestyle. The primary goals of treatment are to alleviate pain, restore function, and prevent long-term complications.
- Conservative management: Mild fractures may be treated with immobilization, pain management, and physical therapy to maintain joint mobility.
- Surgery: More severe fractures may require surgical intervention to:
- Reduce and stabilize the fracture (open reduction and internal fixation).
- Remove fragmented bone pieces (radial head resection).
- Replace the damaged radial head with a prosthetic (radial head arthroplasty).
- Rehabilitation: Post-operative rehabilitation or physical therapy is crucial to regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected arm.
Complications and Prevention
While treatment can effectively manage a broken radial head, potential complications may arise, including:
- Nonunion or malunion: The bone fails to heal properly, leading to persistent pain and limited mobility.
- Arthritis: Fracture fragments or joint instability can cause degenerative changes, leading to arthritis.
- Nerve damage: Surrounding nerves may be injured, resulting in numbness, tingling, or weakness.
To prevent radial head fractures, it is essential to:
- Maintain strong bones: Engage in regular exercise, such as weight-bearing activities, to strengthen the bones.
- Use proper protective gear: Wear protective equipment, such as elbow pads, when participating in sports or activities that involve falls or impacts.
- Practice fall prevention: Improve balance, strength, and flexibility to reduce the risk of falls.
What are the most common causes of radial head fractures?
+Falls, sports injuries, and trauma are the most common causes of radial head fractures.
How long does it take to recover from a radial head fracture?
+Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the fracture and treatment. Generally, it can take several weeks to several months to regain full mobility and strength.
Can radial head fractures be prevented?
+While some fractures may be unavoidable, maintaining strong bones, using protective gear, and practicing fall prevention techniques can reduce the risk of radial head fractures.
In conclusion, a broken radial head is a significant injury that requires prompt medical attention. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and prevention of long-term complications. By taking proactive steps to maintain strong bones and prevent falls, individuals can reduce their risk of experiencing a radial head fracture.