Bursitis In Elbow
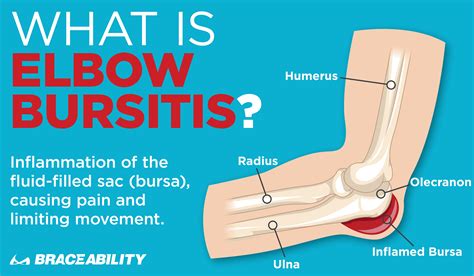
The elbow, a complex joint that connects the humerus (upper arm bone), radius, and ulna (forearm bones), plays a pivotal role in enabling a wide range of movements, from flexion and extension to rotation. Despite its resilience, the elbow can be susceptible to various injuries and conditions, one of which is bursitis. Elbow bursitis, also known as olecranon bursitis, is a common condition characterized by inflammation of the bursae—small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the joints and reduce friction between bones, tendons, and muscles.
Understanding Bursae and Their Role
To grasp the concept of bursitis, it’s essential to understand the role of bursae in the body. Bursae are located in areas where muscles and tendons glide over bones, acting as buffers to prevent friction and allow for smooth movement. In the elbow, the olecranon bursa is situated at the back of the elbow, covering the olecranon (the bony tip of the elbow) and facilitating the movement of the ulna (one of the forearm bones) as it rotates around the humerus (the upper arm bone). The health and functionality of these bursae are crucial for maintaining pain-free and efficient movement of the elbow joint.
Causes and Risk Factors of Elbow Bursitis
Elbow bursitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Repetitive Motion: Engaging in activities that involve repetitive elbow movements, such as lifting, throwing, or bending, can lead to irritation and inflammation of the bursae.
- Direct Trauma: A fall onto the elbow or a direct blow to the elbow can cause bursitis by irritating the bursae and leading to inflammation.
- Infection: In rare cases, bursitis can be caused by an infection. This usually occurs when the skin over the olecranon is broken, allowing bacteria to enter the bursa and cause infection.
- Conditions Like Rheumatoid Arthritis: Individuals with conditions that affect the joints, such as rheumatoid arthritis, are at a higher risk of developing bursitis due to the underlying inflammatory nature of these diseases.
Symptoms of Elbow Bursitis
The symptoms of elbow bursitis can vary in severity but typically include:
- Swelling: The elbow may appear swollen, particularly over the olecranon.
- Pain: Pain at the back of the elbow, which can worsen with movement or pressure.
- Redness and Warmth: The skin over the affected area may become red and feel warm to the touch, especially if there’s an infection.
- Limited Mobility: Inflammation can lead to stiffness, making it difficult to bend or straighten the elbow.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing elbow bursitis usually involves a physical examination to assess swelling, redness, and warmth around the elbow, as well as to evaluate the range of motion. In some cases, a doctor may order imaging tests, like X-rays or an MRI, to rule out other conditions. If there’s suspicion of an infection, a fluid sample may be taken from the bursa for analysis.
Treatment for elbow bursitis depends on the cause and severity of the condition. Common approaches include:
- Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (RICE): To reduce pain and inflammation.
- Medication: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or prescription medications to manage pain and inflammation. Antibiotics may be prescribed if the bursitis is caused by a bacterial infection.
- Physical Therapy: To maintain range of motion and strengthen the muscles around the elbow.
- Aspiration: In some cases, the doctor may drain the bursa to relieve pressure and pain.
- Surgery: Rarely, surgical removal of the bursa may be necessary, especially if other treatments fail or if the bursitis is caused by an infection that doesn’t respond to antibiotics.
Prevention Strategies
While not all cases of elbow bursitis can be prevented, certain precautions can reduce the risk:
- Proper Equipment Use: Ensure that any equipment used for sports or activities fits properly and is used correctly to avoid putting unnecessary strain on the elbow.
- Gradual Increase in Activity: Avoid sudden increases in physical activity. Gradually increase the intensity and duration of activities to allow the body to adapt.
- Protective Gear: Use protective gear, such as elbow pads, during activities that may pose a risk of falling or direct blows to the elbow.
- Good Hygiene and Wound Care: Properly care for any cuts or wounds around the elbow to prevent infection.
Elbow bursitis, while uncomfortable and potentially disabling, can often be treated effectively with rest, appropriate medical care, and, in some cases, physical therapy. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and adopting preventive measures can help in managing and recovering from this condition, thereby restoring the full functionality and comfort of the elbow joint.
What are the primary causes of elbow bursitis?
+The primary causes of elbow bursitis include repetitive motion, direct trauma to the elbow, infection, and underlying conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis. These factors can lead to the inflammation of the bursae, which are small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the joints and reduce friction.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How is elbow bursitis typically diagnosed?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Diagnosis of elbow bursitis usually involves a physical examination to assess symptoms such as swelling, redness, and warmth, as well as to evaluate the range of motion of the elbow. Imaging tests like X-rays or MRI may be ordered to rule out other conditions. In cases of suspected infection, a fluid sample may be taken from the bursa for analysis.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What are the common treatment options for elbow bursitis?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Treatment for elbow bursitis may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), medication to manage pain and inflammation, physical therapy to maintain range of motion and strengthen the muscles around the elbow, aspiration to drain the bursa, and in severe cases, surgery to remove the bursa.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Can elbow bursitis be prevented?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>While not all cases of elbow bursitis can be prevented, certain precautions can reduce the risk. These include using proper equipment for activities, gradually increasing the intensity and duration of physical activities, wearing protective gear during high-risk activities, and practicing good hygiene and wound care to prevent infections.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What is the outlook for individuals with elbow bursitis?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>The outlook for individuals with elbow bursitis is generally positive, with most cases responding well to treatment. However, the duration of recovery can vary depending on the severity of the condition, the effectiveness of the treatment, and the individual's overall health. In some cases, especially if left untreated or if treatment is delayed, elbow bursitis can lead to complications such as chronic pain, limited mobility, or persistent inflammation.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>