When the body is invaded by a pathogen, whether it’s a virus, bacteria, or another type of germ, it can trigger a range of symptoms designed to eliminate the foreign invader. Among the most common and debilitating symptoms are chills, diarrhea, and throwing up, also known as vomiting. These symptoms can be part of the body’s defense mechanism but can also lead to severe dehydration and electrolyte imbalances if not managed properly.
Understanding the Causes
Chills, diarrhea, and vomiting can result from various causes, including but not limited to:
- Viral Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu): This is one of the most common causes, resulting from viruses such as norovirus or rotavirus. It leads to inflammation of the stomach and intestines, causing symptoms like diarrhea, vomiting, and stomach cramps.
- Food Poisoning: Consuming contaminated food or drinks can introduce harmful bacteria, viruses, or parasites into the body. Common culprits include Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria, which can cause severe gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Infections: Beyond the gastrointestinal tract, infections elsewhere in the body (like the respiratory or urinary tract) can also provoke systemic responses such as chills and, in some cases, gastrointestinal upset.
The Role of the Body’s Response
- Chills are often a precursor to fever, indicating that the body is launching an immune response. The shaking or feeling cold, despite being in a warm environment, is the body’s way of generating heat to combat the infection.
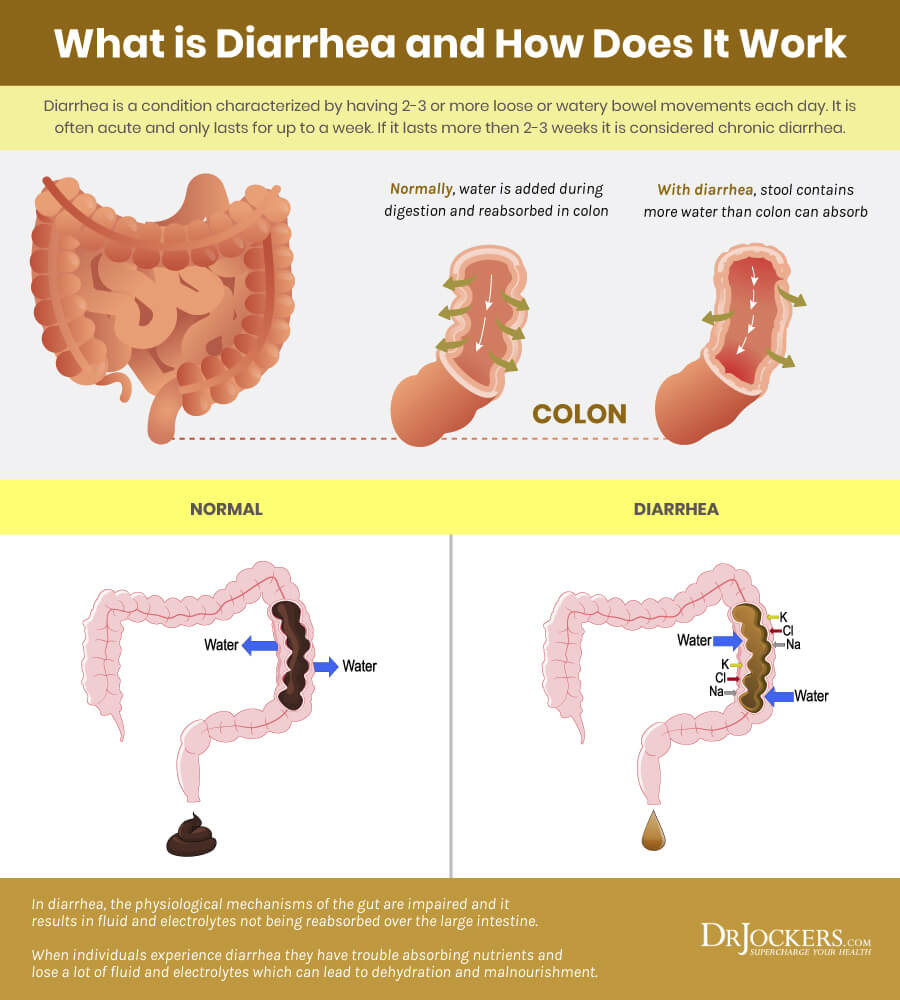
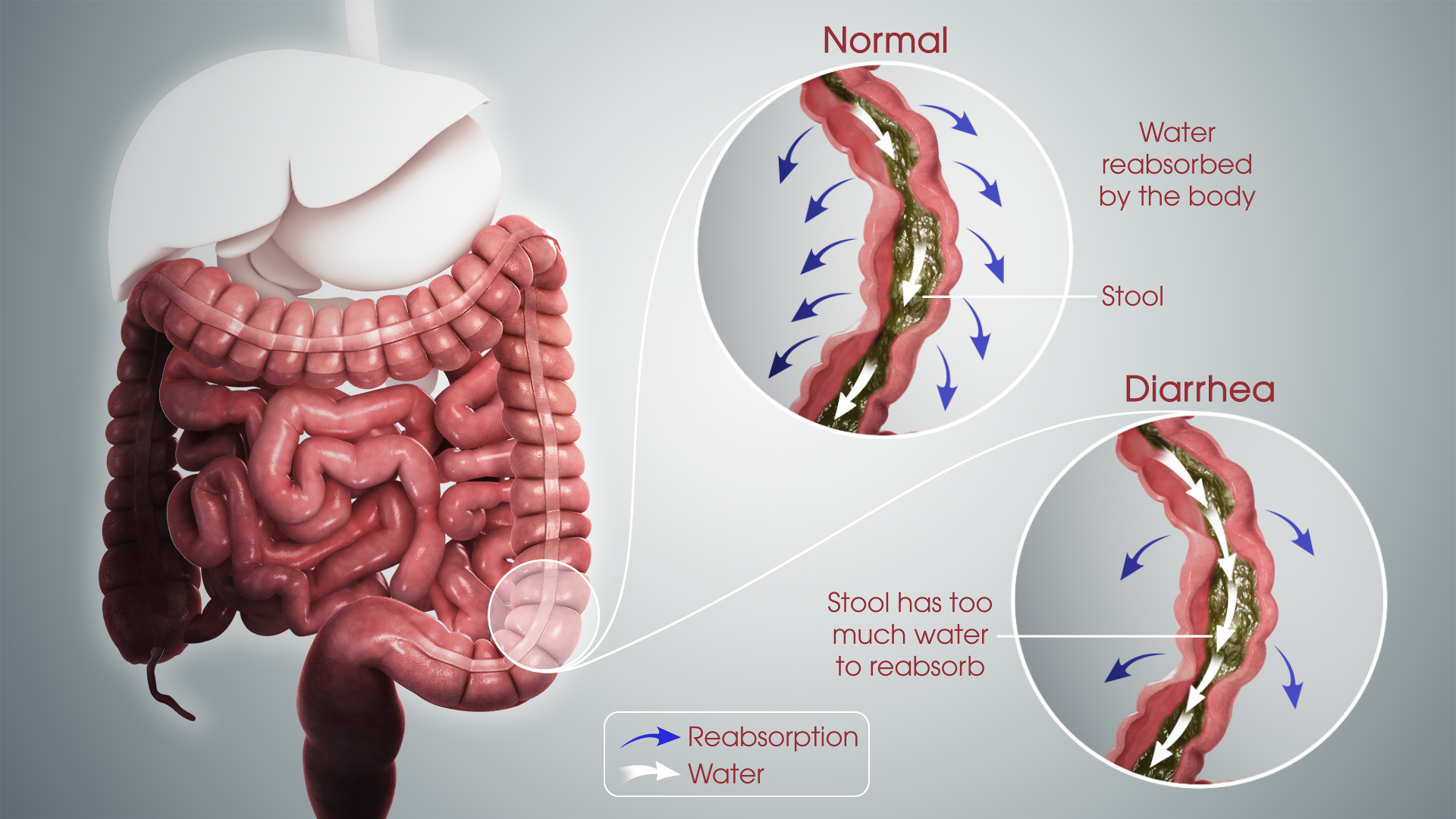
- Diarrhea serves as a mechanism to flush out pathogens from the digestive system. While it’s an effective defense, it can lead to dehydration if the lost fluids and electrolytes are not replenished.
- Vomiting is another expulsion mechanism that can help rid the body of toxins or pathogens. However, like diarrhea, it can cause dehydration and electrolyte disturbances if not properly managed.
Managing Symptoms
While the symptoms might be distressing, there are steps to take to manage them and support the body’s recovery:
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids is crucial, especially if experiencing diarrhea and vomiting. Electrolyte-rich beverages like sports drinks or oral rehydration solutions can help replace lost salts.
- Rest: Giving the body time to recover is vital. Resting can help the immune system focus on fighting off the infection.
- Diet: When feeling up to eating, opting for bland foods (like the BRAT diet: bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast) can be easier on the stomach. Avoiding spicy, fatty, or heavy foods until recovery is recommended.
- Over-the-counter Medications: For certain symptoms, such as fever or headache, over-the-counter medications can provide relief. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any medication, especially if considering anti-diarrheal medications, as they may not be appropriate for all types of infections.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many cases of chills, diarrhea, and vomiting are self-limiting and resolve with supportive care, there are situations where medical attention is necessary:
- Severe Dehydration: Signs include excessive thirst, dark urine, decreased urine output, and dizziness.
- High Fever: Especially in infants, young children, or elderly individuals, as it can be a sign of a more serious infection.
- Blood in Stool or Vomit: Indicates internal bleeding or severe inflammation.
- Severe Abdominal Pain: Could be a sign of appendicitis or another condition requiring immediate medical intervention.
Conclusion
Chills, diarrhea, and vomiting are the body’s ways of responding to infections or irritants. Understanding these symptoms and taking appropriate care can help manage them and support recovery. However, recognizing when symptoms escalate beyond normal ranges is crucial for knowing when to seek medical help. With proper management and, when necessary, medical intervention, individuals can recover from these distressing symptoms and regain their health.



