Chlamydia Discharge Symptoms Guide
Understanding the symptoms of chlamydia, especially those related to discharge, is crucial for early detection, treatment, and preventing the spread of this sexually transmitted infection (STI). Chlamydia, caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis, is one of the most common STIs worldwide, affecting both men and women. It can lead to severe health issues if left untreated, including infertility and increased risk of contracting other STIs like HIV.
Introduction to Chlamydia and Discharge
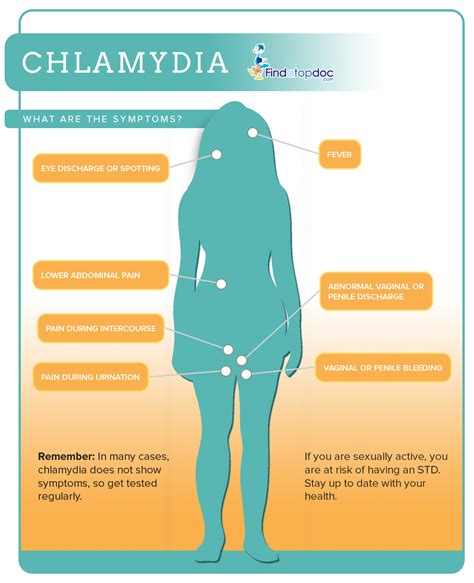
Chlamydia often presents with mild or no symptoms at all, especially in women, which can make it difficult to detect without proper testing. However, one of the noticeable symptoms in individuals who do experience them is abnormal discharge. This discharge can vary in appearance, smell, and consistency, often causing discomfort and raising concerns about one’s health.
Women’s Symptoms
In women, chlamydia can cause cervical discharge, which may appear as:
- Abnormal color: The discharge may be yellow or greenish, distinguishing it from the normal clear or white discharge.
- Increased volume: An increase in the amount of discharge is common, which can be uncomfortable and noticeable.
- Unpleasant odor: A strong, fishy smell, especially after sexual intercourse, can be indicative of an infection.
- Texture: The discharge can be thick or thin, and its appearance may change throughout the menstrual cycle.
Besides discharge, women may experience other symptoms such as:
- Painful urination
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Abdominal pain
- Bleeding between menstrual periods or heavier menstrual bleeding
Men’s Symptoms
Men with chlamydia may experience symptoms such as:
- Penile discharge: This can appear as a watery or milky fluid, primarily noticed in the morning.
- Painful urination: Burning sensation while urinating is a common symptom.
- Pain and swelling: Redness and swelling of the penis, particularly at the tip, can occur.
- Testicular pain: Pain or tenderness in the testicles.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection and treatment of chlamydia are vital to prevent complications. Untreated chlamydia can lead to:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) in women: This can cause permanent damage to the reproductive organs, leading to infertility and increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Epididymitis in men: Inflammation of the tube at the back of the testicle that stores and carries sperm, which can lead to infertility if not treated promptly.
- Increased risk of HIV transmission: Chlamydia can increase the risk of contracting or spreading HIV.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of chlamydia involves a physical examination and laboratory tests, typically a urine test or a swab test from the affected area. Treatment usually involves a course of antibiotics, which should be taken exactly as directed to ensure the infection is fully cleared. It’s also essential for sexual partners to be tested and treated if necessary, to prevent reinfection.
Prevention
Prevention plays a significant role in controlling the spread of chlamydia. Key preventive measures include:
- Safe sex practices: Using condoms correctly and consistently during sexual intercourse.
- Regular STI testing: Especially for individuals with multiple sexual partners or those in non-monogamous relationships.
- Monogamy: Being in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested and is known to be uninfected.
- Avoiding shared sex toys: Or ensuring they are properly cleaned and disinfected between uses.
Conclusion
Chlamydia discharge symptoms are just one aspect of this complex STI. Recognizing these symptoms and understanding the broader context of chlamydia infection is crucial for prompt action and prevention of long-term health consequences. By fostering a culture of open discussion about sexual health, encouraging regular testing, and practicing safe sex, we can work towards reducing the incidence of chlamydia and other STIs.
What are the common symptoms of chlamydia in men and women?
+Common symptoms include abnormal discharge, painful urination, and in women, abdominal pain and irregular menstrual bleeding. Men may experience penile discharge and testicular pain.
How is chlamydia diagnosed and treated?
+Diagnosis involves a physical examination and laboratory tests such as urine or swab tests. Treatment typically involves a course of antibiotics, which should be taken as directed. Sexual partners should also be tested and treated if necessary.
What are the potential complications of untreated chlamydia?
+Untreated chlamydia can lead to complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women, epididymitis in men, and increased risk of HIV transmission. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent these complications.
By understanding and addressing chlamydia, we not only protect our individual health but also contribute to the overall well-being of our communities. The journey towards a healthier, more informed society begins with education and open dialogue about sexual health and the importance of STI prevention and treatment.