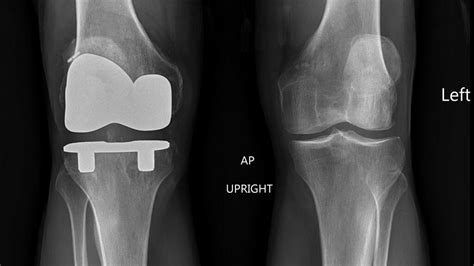
Complete Knee Replacement

Knee replacement, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure designed to resurface a knee damaged by arthritis. Most people who undergo knee replacement surgery experience significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life. During the procedure, the surgeon removes the damaged joint surfaces and replaces them with artificial components made of metal and plastic.
Understanding the Anatomy of the Knee
The knee is a complex joint that consists of three bones: the femur (thigh bone), the tibia (shin bone), and the patella (kneecap). The joint is stabilized by ligaments and surrounded by muscles, which provide movement and strength. The knee joint is divided into three compartments: the medial compartment (the inside part of the knee), the lateral compartment (the outside part of the knee), and the patellofemoral compartment (the front part of the knee, between the kneecap and the femur).
Causes of Knee Damage
Knee damage can be caused by various factors, including:
- Osteoarthritis: a degenerative joint disease that wears away the cartilage, causing bone-on-bone contact and pain.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and damage to the joint.
- Trauma: a severe injury, such as a fracture or ligament sprain, that can cause damage to the knee joint.
- Avascular Necrosis: a condition that occurs when there is a lack of blood supply to the bone, causing the bone to die.
Symptoms of Knee Damage
The symptoms of knee damage can vary depending on the underlying cause, but common symptoms include:
- Pain: aching or sharp pain in the knee, especially with weight-bearing activities.
- Stiffness: difficulty moving the knee or stiffness in the morning.
- Swelling: inflammation and swelling around the knee.
- Instability: a feeling of instability or giving way of the knee.
Types of Knee Replacement Surgery
There are several types of knee replacement surgery, including:
- Total Knee Replacement: a procedure where the entire knee joint is replaced with artificial components.
- Partial Knee Replacement: a procedure where only one compartment of the knee joint is replaced.
- Unicompartmental Knee Replacement: a procedure where only one compartment of the knee joint is replaced, usually the medial or lateral compartment.
- Patellofemoral Replacement: a procedure where only the patellofemoral joint is replaced.
The Knee Replacement Procedure
The knee replacement procedure typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation: the patient is given anesthesia and prepared for surgery.
- Incision: the surgeon makes an incision in the knee to access the joint.
- Removal of damaged tissue: the surgeon removes the damaged cartilage and bone.
- Implantation of artificial components: the surgeon implants the artificial components, which are made of metal and plastic.
- Closure: the incision is closed, and the patient is taken to the recovery room.
Recovery from Knee Replacement Surgery
The recovery from knee replacement surgery can take several months. The patient will need to follow a rehabilitation program, which includes:
- Physical therapy: exercises to improve range of motion, strength, and flexibility.
- Pain management: medications to manage pain and discomfort.
- Follow-up appointments: regular appointments with the surgeon to monitor progress and remove sutures.
Risks and Complications
As with any surgery, there are risks and complications associated with knee replacement surgery, including:
- Infection: a risk of infection, which can be treated with antibiotics.
- Blood clots: a risk of blood clots, which can be treated with medication.
- Nerve damage: a risk of nerve damage, which can cause numbness or weakness.
- Prosthetic failure: a risk of prosthetic failure, which can require revision surgery.
Conclusion
Knee replacement surgery can be a highly effective treatment for knee damage caused by arthritis or other conditions. While there are risks and complications associated with the procedure, the benefits can be significant, including improved mobility, reduced pain, and improved quality of life. It’s essential to consult with an orthopedic surgeon to determine the best course of treatment for your specific condition.
What are the benefits of knee replacement surgery?
+The benefits of knee replacement surgery include improved mobility, reduced pain, and improved quality of life. Most people who undergo knee replacement surgery experience significant improvement in their symptoms and are able to return to their normal activities.
What are the risks and complications associated with knee replacement surgery?
+The risks and complications associated with knee replacement surgery include infection, blood clots, nerve damage, and prosthetic failure. However, these risks can be minimized by following the surgeon's instructions and attending follow-up appointments.
How long does it take to recover from knee replacement surgery?
+The recovery from knee replacement surgery can take several months. Most people are able to return to their normal activities within 3-6 months, but it may take up to a year to fully recover.
What is the difference between total knee replacement and partial knee replacement?
+Total knee replacement involves replacing the entire knee joint with artificial components, while partial knee replacement involves replacing only one compartment of the knee joint. The choice between total and partial knee replacement depends on the extent of the damage and the individual's overall health.
Can I return to sports and activities after knee replacement surgery?
+Yes, most people are able to return to their sports and activities after knee replacement surgery. However, it's essential to follow the surgeon's instructions and attend physical therapy sessions to ensure a safe and successful recovery.
Knee replacement surgery is a highly effective treatment for knee damage caused by arthritis or other conditions. While there are risks and complications associated with the procedure, the benefits can be significant, including improved mobility, reduced pain, and improved quality of life. It's essential to consult with an orthopedic surgeon to determine the best course of treatment for your specific condition.
Step-by-Step Guide to Knee Replacement Surgery
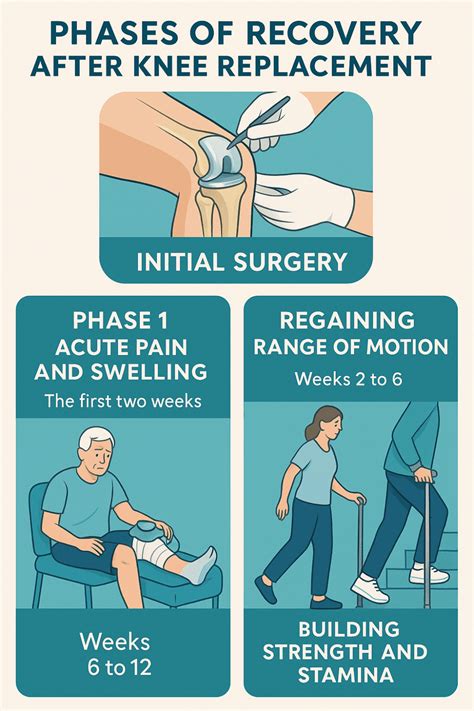
- Preparation: the patient is given anesthesia and prepared for surgery.
- Incision: the surgeon makes an incision in the knee to access the joint.
- Removal of damaged tissue: the surgeon removes the damaged cartilage and bone.
- Implantation of artificial components: the surgeon implants the artificial components, which are made of metal and plastic.
- Closure: the incision is closed, and the patient is taken to the recovery room.
Pros and Cons of Knee Replacement Surgery
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Improved mobility | Risk of infection |
| Reduced pain | Risk of blood clots |
| Improved quality of life | Risk of nerve damage |
| Ability to return to normal activities | Risk of prosthetic failure |