Copd Inhalers: Manage Symptoms Effectively
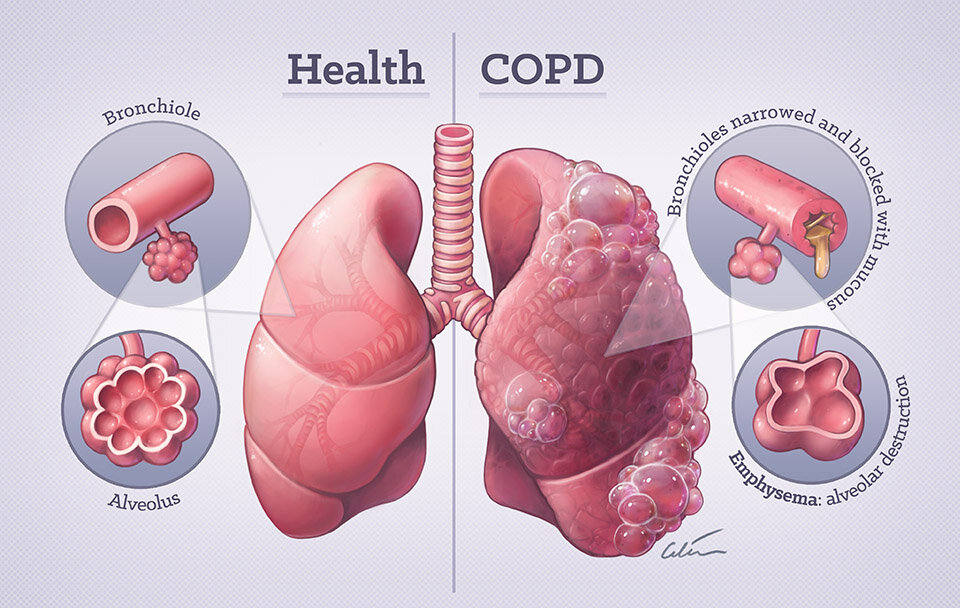
Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) can be a challenging and demanding experience, as the condition progressively impairs lung function, making everyday activities increasingly difficult. One of the most critical components of managing COPD is the use of inhalers, which deliver medication directly to the lungs, helping to alleviate symptoms such as shortness of breath, wheezing, and coughing. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of COPD inhalers, exploring their types, uses, benefits, and how to effectively incorporate them into your management plan.
Understanding COPD and Inhaler Therapy
COPD is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs, significantly impacting a person’s quality of life. Symptoms can vary but often include breathing difficulty, cough, mucus (sputum) production, and wheezing. It’s crucial to understand that while COPD has no cure, symptoms can be managed, and the progression of the disease can be slowed with appropriate treatment, including inhaler therapy.
Inhalers are the cornerstone of COPD management, providing quick relief from symptoms or long-term control of the disease. There are several types of inhalers, each with its specific use:
- Short-acting bronchodilators (SABAs): These provide quick relief from sudden symptoms. They work by relaxing the muscles around the airways, making it easier to breathe.
- Long-acting bronchodilators (LABAs): Used for ongoing control and prevention of symptoms, these keep the airway muscles relaxed over a longer period.
- Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS): These help reduce airway inflammation, an essential component of COPD, especially in more severe cases.
- Combination inhalers: Some inhalers combine different types of medications, such as a bronchodilator and an inhaled corticosteroid, offering multiple benefits in a single device.
Choosing the Right Inhaler
The choice of inhaler depends on several factors, including the severity of your COPD, the presence of other health conditions, your ability to use the device correctly, and your personal preferences. It’s essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate inhaler for your needs.
For some, a Metered-Dose Inhaler (MDI) might be the best choice, offering a precise dose of medication with each use. Others might prefer a Dry Powder Inhaler (DPI), which does not require coordination with breathing in the same way an MDI does. Soft Mist Inhalers and Nebulizers are other options, each with its advantages, especially for those who struggle with traditional inhaler devices.
Effective Use of Inhalers
To get the most out of your inhaler, proper technique is crucial. Incorrect use can lead to reduced medication effectiveness and increased side effects. Here are some general tips for effective inhaler use:
- Read the Instructions: Understand how your specific inhaler works and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Practice: Use your inhaler in front of a mirror or with a healthcare provider to ensure you’re using it correctly.
- Breathe Out: Before using your inhaler, breathe out fully to empty your lungs as much as possible.
- Inhale Slowly: Inhale the medication slowly and deeply, usually over 3-5 seconds, depending on the device.
- Hold Your Breath: Hold your breath for 10 seconds or as long as comfortably possible to allow the medication to settle in your lungs.
Managing Side Effects
While inhalers are designed to manage COPD symptoms, they can sometimes cause side effects. Common side effects include a cough, dry mouth, and throat irritation. Inhaled corticosteroids may cause oral thrush (a fungal infection in the mouth), which can be prevented by rinsing your mouth with water after each use.
Lifestyle Changes to Complement Inhaler Therapy
In addition to using inhalers as prescribed, several lifestyle changes can help manage COPD symptoms:
- Quit Smoking: The most critical step for anyone with COPD who smokes. Smoking cessation can significantly slow the progression of the disease.
- Exercise Regularly: Gentle exercises like walking or yoga can improve lung function and overall health.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support lung health.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps thin out mucus, making it easier to cough up.
Conclusion
Managing COPD effectively requires a multifaceted approach, with inhaler therapy being a vital component. By understanding the different types of inhalers, choosing the right one for your needs, using it correctly, and making complementary lifestyle changes, you can significantly improve your quality of life and slow the progression of the disease. Always consult with your healthcare provider to tailor your treatment plan to your unique situation, ensuring you receive the best possible care for your COPD.
FAQ Section
What are the most common types of COPD inhalers?
+The most common types include Short-acting bronchodilators (SABAs), Long-acting bronchodilators (LABAs), Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS), and Combination inhalers, each serving a different purpose in managing COPD symptoms.
How do I choose the right inhaler for my COPD?
+Choosing the right inhaler involves considering the severity of your COPD, other health conditions, your ability to use the device, and personal preferences. It’s crucial to work closely with your healthcare provider to make this decision.
What are some common side effects of COPD inhalers?
+Common side effects can include a cough, dry mouth, throat irritation, and for inhaled corticosteroids, oral thrush. Rinsing your mouth after use and staying hydrated can help mitigate these effects.
Can lifestyle changes help manage COPD symptoms?
+Yes, quitting smoking, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy diet, and staying hydrated can all contribute to managing COPD symptoms and improving overall lung health.



