Coronavirus Covid 19
The coronavirus Covid-19 pandemic has been a globe-spanning health crisis, affecting nearly every aspect of modern life. Since its emergence in late 2019, Covid-19 has spread to every region of the world, infecting millions and causing widespread illness, death, and economic disruption. The pandemic has also sparked an unprecedented global response, with governments, healthcare systems, and individuals working together to slow the spread of the virus and develop effective treatments and vaccines.
One of the most significant challenges posed by Covid-19 is its high degree of transmissibility. The virus can be spread through respiratory droplets, contact with contaminated surfaces, and even through the air in certain environments. This has made it difficult to contain outbreaks, especially in areas with high population densities and limited access to healthcare resources. Furthermore, the virus has a relatively long incubation period, during which time individuals may be infectious but not yet showing symptoms, making it hard to track and isolate cases.
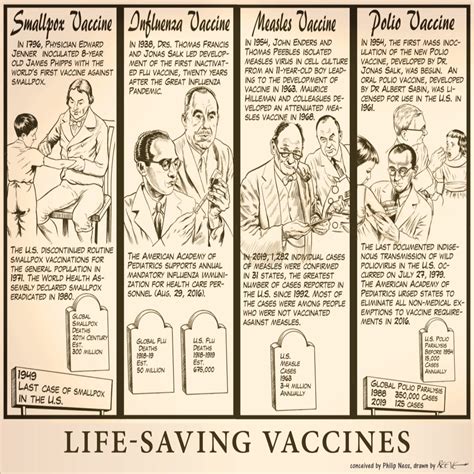
The rapid development and distribution of Covid-19 vaccines have been crucial in the fight against the pandemic. Vaccines have been shown to significantly reduce the risk of severe illness, hospitalization, and death from Covid-19, and have played a key role in slowing the spread of the virus.
Despite these challenges, there have been many successes in the response to Covid-19. The rapid development and distribution of vaccines, for example, has been a major breakthrough. Vaccines have been shown to significantly reduce the risk of severe illness, hospitalization, and death from Covid-19, and have played a key role in slowing the spread of the virus. Additionally, improvements in diagnostic testing, contact tracing, and other public health measures have helped to identify and contain outbreaks more effectively.
However, the pandemic has also highlighted significant inequities and weaknesses in global healthcare systems. In many countries, especially those with limited resources, access to testing, treatment, and vaccines has been uneven, with marginalized communities often facing the greatest challenges. This has underscored the need for more equitable and resilient healthcare systems, capable of responding effectively to emergent threats like Covid-19.
Evolving Understanding of Covid-19

Our understanding of Covid-19 has evolved significantly over the course of the pandemic. Initially, the virus was thought to primarily affect older adults and those with underlying health conditions. However, as the pandemic has progressed, it has become clear that Covid-19 can cause severe illness in people of all ages, and that certain groups, such as healthcare workers and those living in congregate settings, are at increased risk.
Understanding the Transmission of Covid-19
- Respiratory Droplets: The virus can be spread through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks.
- Contact with Contaminated Surfaces: Touching surfaces or objects that have the virus on them and then touching one's mouth, nose, or eyes can also spread the virus.
- Airborne Transmission: In certain environments, such as poorly ventilated spaces, the virus can remain suspended in the air for periods of time, potentially leading to airborne transmission.
The pandemic has also accelerated innovations in digital health, remote work, and public health communication. Telemedicine, for example, has become a critical tool for delivering healthcare services while minimizing the risk of in-person transmission. Similarly, advances in data analytics and artificial intelligence have improved our ability to track the spread of the virus and predict future outbreaks.
Future Directions and Preparedness
As the world moves forward from the Covid-19 pandemic, there is a growing recognition of the need for enhanced global preparedness and cooperation in the face of future health crises. This includes investments in healthcare infrastructure, improvements in international coordination and data sharing, and the development of novel diagnostic, therapeutic, and preventive technologies.
Benefits and Challenges of Global Health Initiatives
Benefits:
- Improved Global Coordination: Enhancing the ability of countries to work together in response to health threats.
- Increased Funding: Securing more resources for healthcare infrastructure and research into new technologies and treatments.
- Enhanced Preparedness: Building capacity to respond more effectively to future pandemics.
Challenges:
- Economic Burden: The significant cost of implementing and maintaining these initiatives.
- Equity and Access: Ensuring that all countries, regardless of their economic status, have fair access to resources and technologies.
- Global Cooperation: Overcoming political and logistical hurdles to achieve unified action.
Moreover, there is a growing emphasis on the importance of addressing the social determinants of health—factors such as poverty, housing, education, and environmental quality—that have been exposed and exacerbated by the pandemic. By tackling these underlying issues, societies can build more resilient populations better equipped to withstand future health crises.
What are the most effective ways to prevent the spread of Covid-19?
+Effective prevention measures include vaccination, wearing masks, practicing social distancing, frequent handwashing, and improving ventilation in indoor spaces.
How has Covid-19 impacted global economies?
+The pandemic has had a profound impact on global economies, leading to widespread job losses, supply chain disruptions, and a significant decrease in economic output. However, it has also accelerated digital transformation and innovation in various sectors.
What role do vaccines play in controlling the pandemic?
+Vaccines are a crucial tool in controlling the pandemic by reducing the risk of severe illness, hospitalization, and death, thereby also reducing the spread of the virus. Wide vaccination coverage is essential for achieving herd immunity and returning to pre-pandemic life.
In conclusion, the Covid-19 pandemic has presented unprecedented challenges to global health, economies, and societies. However, it has also ignited a wave of innovation, cooperation, and resilience. As we move forward, it will be critical to apply the lessons learned from this pandemic to build stronger, more equitable, and more resilient health systems capable of addressing the complex health challenges of the 21st century.