Covid19 Symptoms 2024: Know The Signs

As we navigate the ever-evolving landscape of the Covid-19 pandemic, it’s essential to stay informed about the signs and symptoms that may indicate an infection. The year 2024 brings new challenges and insights into the virus, and understanding the most up-to-date information is crucial for protecting yourself and those around you.
Introduction to Covid-19 Symptoms
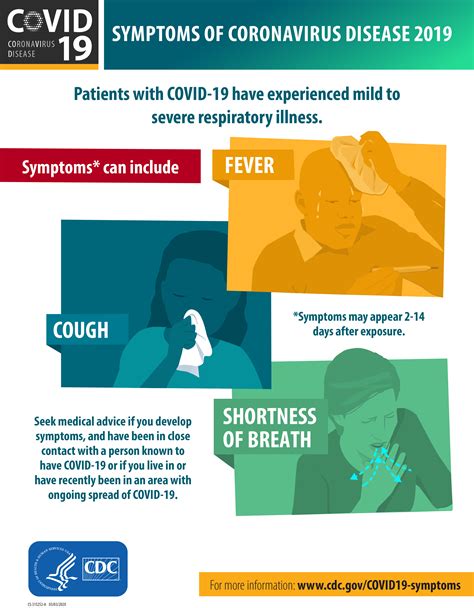
Covid-19, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, presents with a wide range of symptoms, from mild to severe. The variability in symptoms can sometimes make it difficult to diagnose based on clinical presentation alone. However, being aware of the common and less common symptoms can help in early detection and management.
Common Symptoms of Covid-19

- Fever: One of the earliest symptoms, fever can range from a low-grade temperature to a high fever, often accompanied by chills.
- Cough: A dry cough is common, though some individuals may experience a productive cough with mucus.
- Fatigue: Feeling extremely tired or weak is a prevalent symptom, often impacting daily activities.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling winded even when doing simple tasks can be a sign of Covid-19, particularly in more severe cases.
- Muscle and Body Aches: Pain in the muscles, back, and other parts of the body is common, similar to what is experienced with the flu.
- Headache: Headaches can range from mild to severe and are often described as feeling like a migraine.
- Sore Throat: Though less common than in other viral infections, a sore throat can still be a symptom of Covid-19.
- Runny Nose: Or stuffy nose, which may lead to sneezing or a feeling of having a cold.
- Diarrhea: Some people may experience gastrointestinal symptoms, including diarrhea.
- Nausea or Vomiting: These symptoms can occur, especially in severe cases or among certain populations.
Monitoring Your Symptoms
- Keep a symptom journal to track how you're feeling each day.
- Use a thermometer to monitor your temperature regularly.
- Pay attention to any changes in your breathing or energy levels.
- Stay hydrated and seek rest when needed.
Less Common Symptoms of Covid-19
- Loss of Appetite: A decrease in appetite can occur due to the feeling of being unwell.
- Confusion: In older adults or those with severe infections, confusion or disorientation may be observed.
- Skin Rashes: Some individuals have reported skin rashes as a symptom of Covid-19.
- Eye Problems: Conjunctivitis (pink eye) has been linked to Covid-19 in some cases.
Severe Symptoms Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
While many cases of Covid-19 are mild, some individuals may develop severe symptoms that require immediate medical attention. These include:
- Difficulty Breathing: Severe shortness of breath or being unable to breathe.
- Persistent Chest Pain or Pressure: This could be a sign of a serious heart condition.
- Severe Headache: Especially if accompanied by confusion or disorientation.
- Inability to Stay Awake: Feeling extremely tired or lethargic.
- Pale, Blue-Discolored, or Cold Skin: Signs of poor circulation.
- Sudden Confusion or Disorientation: Especially in older adults or those with a severe infection.
Covid-19 Symptoms in Specific Populations
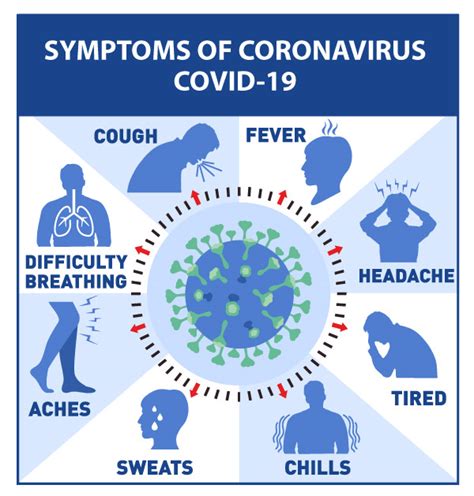
- Children: While children can contract Covid-19, they often exhibit milder symptoms. However, they can still spread the virus to others, including those at higher risk.
- Older Adults: This population may experience more severe symptoms and have a higher risk of complications.
- Pregnant Women: The risk of severe illness from Covid-19 is higher in pregnant women, making it crucial for them to take preventative measures seriously.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing Covid-19 typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) test or antigen tests. Treatment depends on the severity of symptoms and may include supportive care (e.g., rest, hydration, over-the-counter medications for symptom relief), antiviral medications for those at high risk of severe disease, and, in severe cases, hospital care, including oxygen therapy and mechanical ventilation.
Understanding Covid-19 Testing
Benefits of Early Testing
- Early detection can lead to earlier treatment and better outcomes.
- Reduces the risk of spreading the virus to others.
Challenges with Testing
- False negatives can occur, especially early in the infection.
- Access to testing may be limited in some areas.
Prevention and Vaccination
Preventing the spread of Covid-19 involves a multi-faceted approach, including:
- Vaccination: Getting vaccinated is one of the most effective ways to prevent severe illness and reduce the risk of transmission. Staying up-to-date with the latest vaccine recommendations is essential.
- Mask-Wearing: Wearing masks in crowded areas or when around vulnerable populations can significantly reduce transmission.
- Social Distancing: Maintaining physical distance from others, especially in indoor settings, can help prevent the spread.
- Hand Hygiene: Regularly washing hands with soap and water or using hand sanitizer when soap and water are not available is crucial.
- Improved Ventilation: Ensuring good ventilation in public and private spaces can reduce the concentration of viral particles in the air.
How long after exposure to Covid-19 do symptoms typically appear?
+Symptoms of Covid-19 can appear anywhere from 2 to 14 days after exposure, with the average being around 5 to 6 days.
Can you contract Covid-19 more than once?
+Yes, it is possible to contract Covid-19 more than once. Immunity from previous infections is not guaranteed to prevent future infections, especially with the emergence of new variants.
What should I do if I suspect I have Covid-19?
+If you suspect you have Covid-19, isolate yourself from others, consult a healthcare professional for testing and advice, and follow local health guidelines.
In conclusion, recognizing the signs and symptoms of Covid-19 is a critical step in managing the pandemic. By understanding the range of symptoms, from common to severe, and taking proactive measures to prevent transmission, we can work together to reduce the impact of Covid-19 on our communities. Staying informed, adapting to new information, and supporting global health initiatives are essential for navigating this evolving health landscape.


