Crud: Simplify Data Management
In the realm of data management, CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations are the backbone of any application that interacts with data storage systems. These basic operations enable developers to manage data effectively, ensuring that information is handled consistently and reliably across various platforms. Understanding CRUD is essential for any developer aiming to build robust, data-driven applications.
Introduction to CRUD
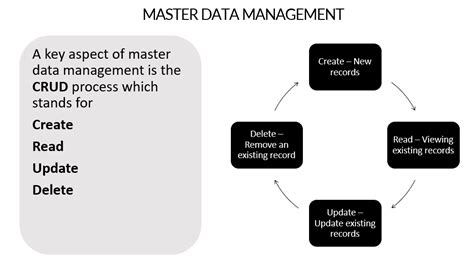
CRUD operations form the foundation of data manipulation. Each letter in the acronym represents a fundamental action that can be performed on data:
- Create: This operation involves adding new data to the storage system. It’s the process of inserting a new record or entry into the database.
- Read: This operation is about retrieving or accessing existing data from the storage. It involves selecting or querying data to display or use in the application.
- Update: As the name suggests, this operation modifies existing data. It involves changing or editing the data that already resides in the database.
- Delete: This operation removes data from the storage system. It’s about deleting records or entries that are no longer needed or are redundant.
Benefits of CRUD Operations
The CRUD framework offers several benefits that make it a preferred approach for data management:
- Simplification: CRUD simplifies data management by breaking down complex operations into four basic actions. This simplification makes it easier for developers to design, implement, and maintain data-driven applications.
- Standardization: CRUD provides a standardized way of interacting with data. This standardization facilitates collaboration among developers and ensures that data is managed consistently across different parts of an application.
- Flexibility: The CRUD operations can be applied to various types of data storage systems, including relational databases, NoSQL databases, and even file systems. This flexibility makes CRUD a versatile framework for data management.
- Scalability: Applications built around CRUD operations can scale more easily. As the volume of data grows, the basic operations of creating, reading, updating, and deleting can be optimized and scaled without altering the fundamental approach to data management.
CRUD in Real-World Applications
CRUD operations are omnipresent in real-world applications. For instance, consider a simple blog:
- Create: When a user writes and publishes a new post, the application performs a create operation by inserting the post’s content into the database.
- Read: When a visitor opens the blog to read posts, the application performs a read operation by retrieving the relevant posts from the database and displaying them.
- Update: If the blog owner decides to edit a post, the application performs an update operation by modifying the existing post in the database.
- Delete: If a post is no longer relevant and the owner decides to remove it, the application performs a delete operation by removing the post from the database.
Implementing CRUD Operations
Implementing CRUD operations involves understanding the specific requirements of the application and the capabilities of the chosen data storage system. Here are some general steps to consider:
- Design the Database: Before implementing CRUD, designing the database schema is crucial. This step involves defining the structure of the data, including the relationships between different entities.
- Choose the Right Tools: Select appropriate tools and frameworks that support CRUD operations. Many programming languages and frameworks provide built-in support or libraries for CRUD operations.
- Implement Each Operation: Write code for each CRUD operation. This involves creating functions or methods that can create, read, update, and delete data in the database.
- Test Thoroughly: Testing each CRUD operation is essential to ensure that data is managed correctly and consistently. This includes testing for errors, edge cases, and security vulnerabilities.
Security Considerations
While implementing CRUD operations, security is a critical consideration. Unauthorized access to data can lead to breaches, making it essential to implement proper security measures:
- Authentication: Ensure that only authenticated users can perform CRUD operations.
- Authorization: Implement role-based access control to restrict which users can perform which CRUD operations.
- Input Validation: Always validate user input to prevent SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.
- Encryption: Consider encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest.
Conclusion
CRUD operations are fundamental to data management, offering a simple yet effective framework for creating, reading, updating, and deleting data. Understanding and mastering CRUD is essential for developing robust, scalable, and secure data-driven applications. By following best practices and considering security and scalability from the outset, developers can build applications that manage data effectively and efficiently.
What does CRUD stand for in data management?
+CRUD stands for Create, Read, Update, Delete, which are the four basic operations in data management.
Why are CRUD operations important in application development?
+CRUD operations are important because they provide a standardized way to interact with data, simplifying data management and ensuring consistency and reliability across the application.
How can CRUD operations be secured?
+CRUD operations can be secured through authentication, authorization, input validation, and data encryption to prevent unauthorized access and protect against common web attacks.