Current Covid Variant
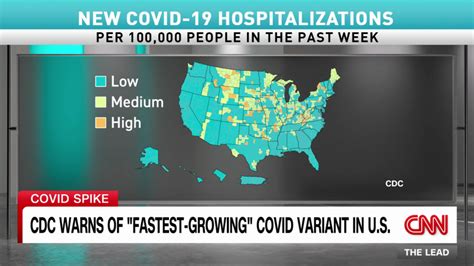
The COVID-19 pandemic has been a constantly evolving global health crisis, with new variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus emerging and spreading rapidly around the world. As of the latest reports, the current dominant COVID variant is the Omicron variant, specifically the subvariant XBB.1.5. This subvariant has been detected in numerous countries and has raised concerns due to its high transmissibility and ability to evade certain aspects of the immune system.
Understanding the Omicron Variant and Its Subvariants
The Omicron variant was first identified in November 2021, and since then, it has undergone several mutations, leading to the emergence of various subvariants. Among these, XBB.1.5 has been noted for its rapid spread and potential to cause significant illness. The World Health Organization (WHO) and other global health authorities have been closely monitoring the situation, providing updates on the spread, severity, and impact of this subvariant.
Key Characteristics of the XBB.1.5 Subvariant
- High Transmissibility: XBB.1.5 is noted for its high transmissibility, which is a significant factor in its rapid spread across different regions.
- Immune Evasion: This subvariant has shown an ability to evade parts of the immune system, particularly in individuals who have had previous infections or vaccinations. This could lead to reinfections and potentially reduce the effectiveness of current vaccines, although they are still expected to offer protection against severe disease.
- Severity and Symptoms: Reports suggest that while XBB.1.5 can cause severe illness, especially in vulnerable populations such as the elderly and those with underlying health conditions, the overall severity and symptoms are similar to those of other Omicron subvariants. Common symptoms include fever, cough, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
Global Response and Recommendations
In response to the emergence and spread of XBB.1.5, global health authorities have reiterated the importance of vaccination, including booster shots, as a primary measure to protect against severe illness and hospitalization. Other recommendations include:
- Masking: Wearing masks in crowded areas or in situations where social distancing is not possible.
- Social Distancing: Maintaining physical distance from others to reduce the chance of transmission.
- Hygiene Practices: Regular hand washing and use of hand sanitizers.
- Testing and Isolation: Getting tested if symptoms appear and isolating if positive to prevent spread.
Future Outlook and Concerns
The future trajectory of the COVID-19 pandemic, including the dominance and evolution of variants like XBB.1.5, is uncertain. Continuous monitoring by health authorities, ongoing research into vaccine effectiveness and potential updates, and the adaptation of public health strategies will be crucial in managing the pandemic’s impact.
Practical Guidance for the Public
Given the evolving nature of the pandemic, it’s essential for individuals to stay informed through reliable sources such as the WHO, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and local health departments. Following public health guidelines, maintaining vigilance, and adapting behaviors as necessary are key components of personal and community protection.
###FAQ Section
What is the current dominant COVID-19 variant?
+The current dominant COVID-19 variant is the Omicron variant, specifically the XBB.1.5 subvariant, known for its high transmissibility and potential to cause significant illness.
How can I protect myself against the XBB.1.5 subvariant?
+Protection measures include staying up to date with COVID-19 vaccines, wearing masks in crowded areas, practicing social distancing, following good hygiene practices, and getting tested if symptoms appear.
What are the symptoms of the XBB.1.5 subvariant infection?
+Symptoms of XBB.1.5 infection are similar to those of other COVID-19 variants and include fever, cough, fatigue, and shortness of breath. Severity can vary, with vulnerable populations at higher risk of severe illness.
As the world continues to navigate the COVID-19 pandemic, staying informed, adhering to public health guidelines, and supporting ongoing research and development of medical countermeasures are crucial steps in mitigating the impact of emerging variants like XBB.1.5. The adaptability of global responses to the evolving pandemic landscape will play a significant role in protecting public health and moving toward a post-pandemic future.