Current Strain Of Covid

The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, has been a global health concern since its emergence in late 2019. Over time, the virus has undergone mutations, resulting in various strains with different characteristics. Understanding the current strain of COVID-19 is crucial for developing effective public health strategies, vaccines, and treatments.
Origins and Evolution of SARS-CoV-2
SARS-CoV-2 is a member of the coronavirus family, which includes viruses that cause the common cold, as well as more severe diseases like Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS). The virus is believed to have originated from an animal source, with bats being the likely natural reservoir. The first reported cases of COVID-19 occurred in Wuhan, China, in December 2019, and since then, the virus has spread rapidly around the world.
Current Strains of COVID-19
As of the latest reports, the current dominant strains of COVID-19 worldwide include variants such as Omicron and its subvariants. These variants have shown increased transmissibility compared to earlier strains and have led to significant waves of infection globally. The Omicron variant, in particular, has been notable for its rapid spread and its ability to infect individuals who have previously been vaccinated or infected with earlier strains of the virus.
Characteristics of Current Strains
Transmissibility: The current strains, especially Omicron and its subvariants, are highly transmissible. This means they can spread more easily from person to person, contributing to a higher number of cases and outbreaks.
Vaccine Efficacy: While vaccines have been highly effective against severe illness and hospitalization due to COVID-19, the current strains have shown some ability to evade immune protection, particularly against mild infections. This has led to an increased focus on booster shots to enhance and prolong vaccine efficacy.
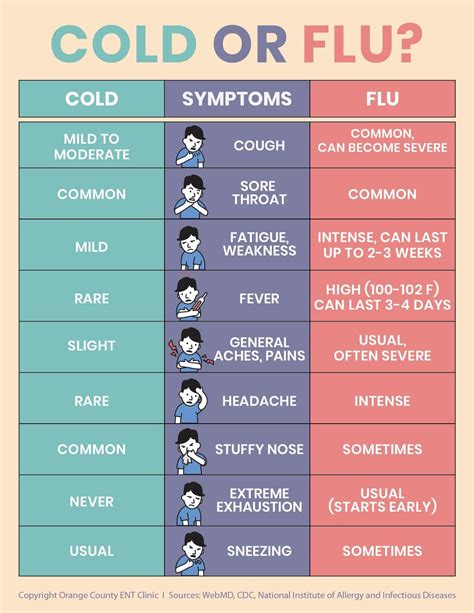
Symptoms and Severity: The symptoms of COVID-19 caused by current strains can vary widely among individuals. Common symptoms include fever, cough, fatigue, and shortness of breath. However, many individuals, especially those who are vaccinated, may experience mild or no symptoms at all. The severity of the disease can also vary, with some individuals developing severe pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and other complications.
Treatment and Management: Treatment for COVID-19 focuses on managing symptoms and supporting the body’s immune response. For severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary, where patients can receive oxygen therapy, antiviral medications, and other supportive care. Vaccination remains the most effective strategy for preventing severe illness and reducing the risk of transmission.
Public Health Response
The public health response to the current strain of COVID-19 includes a combination of vaccination campaigns, masking policies, social distancing measures, and travel restrictions. Efforts are also being made to monitor the virus’s evolution, identify new variants early, and adapt public health strategies accordingly.
Future Outlook
The future outlook for COVID-19 is complex and uncertain. As the virus continues to evolve, there is a potential for new variants to emerge that could challenge current public health measures. Continuous monitoring, research, and adaptation of strategies will be crucial in managing the pandemic. Additionally, global coordination and cooperation are essential for sharing information, distributing vaccines, and implementing effective control measures.
Conclusion
The current strain of COVID-19 presents ongoing challenges for global health. Understanding its characteristics, such as transmissibility, vaccine efficacy, and symptom severity, is vital for developing and implementing effective public health strategies. Continued research, surveillance, and adaptation will be key to managing the pandemic and reducing its impact on communities worldwide.
What are the current dominant strains of COVID-19?
+The current dominant strains of COVID-19 include variants such as Omicron and its subvariants. These variants have shown increased transmissibility and have led to significant waves of infection globally.
How effective are vaccines against the current strains of COVID-19?
+While vaccines have been highly effective against severe illness and hospitalization due to COVID-19, the current strains have shown some ability to evade immune protection, particularly against mild infections. Booster shots are recommended to enhance and prolong vaccine efficacy.
What are the common symptoms of COVID-19 caused by the current strains?
+Common symptoms include fever, cough, fatigue, and shortness of breath. However, many individuals, especially those who are vaccinated, may experience mild or no symptoms at all.
In conclusion, the current strain of COVID-19 requires a comprehensive and adaptive public health response. By understanding the virus’s characteristics, monitoring its evolution, and implementing effective strategies, we can work towards reducing its impact and managing the pandemic effectively.