Diabetes Control: Master Your Blood Sugar Levels
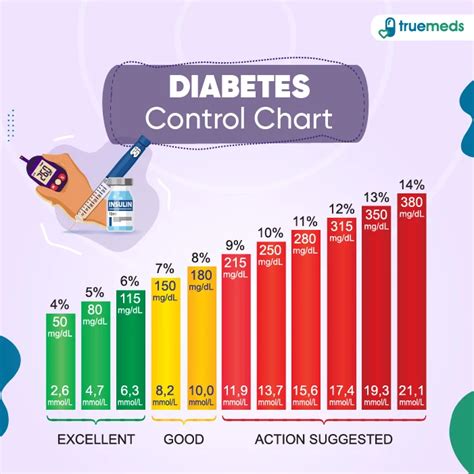
Living with diabetes requires a deep understanding of how to manage and control blood sugar levels. It’s a condition that affects millions worldwide, and while it can be challenging, the right approach to diabetes control can make a significant difference in the quality of life for those affected. Diabetes, in simple terms, is a condition where the body either attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas (Type 1 diabetes) or becomes resistant to insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar (Type 2 diabetes). The key to managing diabetes is to keep blood sugar levels within a target range, which helps prevent complications and ensures the body gets the energy it needs.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose levels, indicate the amount of glucose present in the blood. Glucose is a type of sugar that serves as the primary source of energy for the body’s cells. Normally, after eating, the body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. In response, the pancreas releases insulin, facilitating the entry of glucose into cells, thus lowering blood sugar levels. In individuals with diabetes, this process is disrupted, leading to elevated blood glucose levels.
The Importance of Diabetes Control
Controlling diabetes is crucial for preventing complications associated with high blood sugar levels. These complications can include heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, and even vision problems. Effective diabetes management not only improves the quality of life but also reduces the risk of these long-term complications. It involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, including diet, exercise, and, if necessary, medication.
Lifestyle Modifications for Diabetes Control
Dietary Changes: Eating a balanced diet is foundational in managing diabetes. This typically involves minimizing the intake of sugars and refined carbohydrates, which can cause blood sugar spikes, and focusing on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. The goal is to choose foods that are rich in nutrients but have a minimal impact on blood glucose levels.
Physical Activity: Regular physical activity is another critical component of diabetes management. Exercise not only helps lower blood sugar levels by making the body more sensitive to insulin but also contributes to weight management, improves cardiovascular health, and enhances overall well-being. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling are excellent options for those living with diabetes.
Weight Management: For individuals with Type 2 diabetes, achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is vital. Excess body fat, particularly around the abdomen, can increase insulin resistance, making it harder to control blood sugar levels. A combination of diet and exercise is often the most effective way to manage weight.
Stress Management: High levels of stress can affect blood sugar levels and worsen diabetes symptoms. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress levels and contribute to better diabetes control.
Medication and Monitoring
For many individuals with diabetes, lifestyle modifications alone may not be sufficient to control blood sugar levels. In these cases, medication may be necessary. There are several types of diabetes medications, each working in different ways to lower blood glucose levels. Insulin therapy is also a common treatment approach, especially for those with Type 1 diabetes and some with Type 2 diabetes.
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential to understand how different factors (such as food, exercise, and medication) affect blood sugar. This can be done using a glucose meter, which provides immediate feedback, allowing for timely adjustments to the management plan.
Technology and Diabetes Management
Advancements in technology have significantly impacted diabetes management, offering tools that make monitoring and controlling blood sugar levels more accessible and efficient. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems, for example, provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day and night, offering valuable insights into glucose trends and patterns.Additionally, insulin pumps and smart insulin pens can simplify insulin delivery, reducing the burden of multiple daily injections.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Living with diabetes can be emotionally challenging, with feelings of frustration, anxiety, and burnout being common. It’s essential for individuals with diabetes to have a support network, whether it’s family, friends, or support groups. Mental health professionals can also provide valuable guidance and coping strategies to deal with the emotional aspects of diabetes management.
Conclusion
Diabetes control is a multifaceted challenge that requires a comprehensive approach, including lifestyle modifications, medication (when necessary), regular monitoring, and emotional support. By understanding the intricacies of blood sugar management and leveraging the latest technologies and treatment options, individuals with diabetes can lead active, healthy lives. The journey to mastering blood sugar levels is unique to each individual, and with the right mindset, resources, and support, it is entirely possible to achieve excellent diabetes control and reduce the risk of complications.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar levels?
+Symptoms of high blood sugar levels can include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, cuts or wounds that are slow to heal, and tingling or numbness in the hands and feet. If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and treatment.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on the type of diabetes, the treatment plan, and the individual’s lifestyle. Generally, individuals with Type 1 diabetes and those with Type 2 diabetes who are on insulin may need to check their blood sugar levels several times a day. It’s essential to follow the advice of a healthcare provider regarding the timing and frequency of blood glucose monitoring.
Can diabetes be reversed?
+While Type 1 diabetes cannot be reversed, Type 2 diabetes can sometimes be managed to the point where medication is no longer needed, through significant weight loss, a healthy diet, and regular physical activity. However, it’s important to note that even if blood sugar levels return to normal, a person who has had Type 2 diabetes is still at risk for developing the condition again and should continue to be monitored by a healthcare provider.



