Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy: Improve Your Quality Life
Living with diabetes can be challenging, but when complications such as diabetic autonomic neuropathy (DAN) arise, it can significantly impact one’s quality of life. DAN is a type of nerve damage that affects the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary functions of the body, such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and bowel movements. In this article, we will delve into the world of diabetic autonomic neuropathy, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, as well as provide guidance on how to improve your quality of life while living with this condition.
Understanding Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy
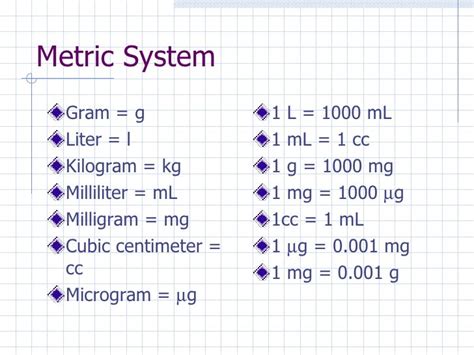
DAN is a common complication of diabetes, affecting approximately 20% of people with the condition. It occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the nerves that control the autonomic functions of the body. This damage can lead to a range of symptoms, including:
- Orthostatic hypotension: a sudden drop in blood pressure when standing up, which can cause dizziness, lightheadedness, and fainting
- Gastroparesis: delayed stomach emptying, which can cause nausea, vomiting, bloating, and abdominal pain
- Diarrhea or constipation: changes in bowel movements, which can be caused by nerve damage to the digestive system
- Urinary retention or incontinence: problems with bladder control, which can lead to urinary tract infections and other complications
- Erectile dysfunction: difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection, which can be caused by nerve damage to the genital area
- Sudomotor dysfunction: abnormal sweating, which can lead to heat intolerance and other complications
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact causes of DAN are not fully understood, several factors contribute to its development. These include:
- High blood sugar levels: prolonged exposure to high blood sugar levels can damage the nerves and lead to DAN
- Duration of diabetes: the longer you have diabetes, the higher your risk of developing DAN
- Poor blood sugar control: fluctuations in blood sugar levels can worsen nerve damage
- Age: older adults are more likely to develop DAN
- Other health conditions: certain health conditions, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and obesity, can increase the risk of developing DAN
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing DAN can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions. A comprehensive diagnosis includes:
- Medical history: a review of your medical history to identify any underlying conditions that may be contributing to your symptoms
- Physical examination: a physical examination to assess your overall health and identify any signs of nerve damage
- Blood tests: blood tests to check your blood sugar levels and other health markers
- Autonomic function tests: specialized tests to assess the function of your autonomic nervous system
Treatment for DAN typically focuses on managing the symptoms and preventing further nerve damage. This may include:
- Medications: medications to manage symptoms such as orthostatic hypotension, gastroparesis, and diarrhea or constipation
- Lifestyle changes: lifestyle changes such as eating small, frequent meals, avoiding heavy exertion, and staying hydrated to manage symptoms
- Alternative therapies: alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage, and cognitive behavioral therapy to manage pain and improve quality of life
Improving Your Quality of Life
While living with DAN can be challenging, there are several steps you can take to improve your quality of life. These include:
- Maintaining good blood sugar control: keeping your blood sugar levels within a healthy range can help prevent further nerve damage
- Exercising regularly: regular exercise can help improve circulation, reduce stress, and improve overall health
- Eating a healthy diet: eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources can help manage symptoms and improve overall health
- Staying hydrated: drinking plenty of water and other fluids can help manage symptoms such as orthostatic hypotension and gastroparesis
- Getting enough sleep: getting enough sleep and practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help manage stress and improve overall health
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the early signs of diabetic autonomic neuropathy?
+The early signs of DAN can be subtle and may include orthostatic hypotension, gastroparesis, and changes in bowel movements. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to speak with your healthcare provider.
Can diabetic autonomic neuropathy be reversed?
+While DAN cannot be reversed, there are steps you can take to manage the symptoms and prevent further nerve damage. Maintaining good blood sugar control, exercising regularly, and eating a healthy diet can help improve your quality of life and reduce the risk of complications.
What are the best treatment options for diabetic autonomic neuropathy?
+Treatment for DAN typically focuses on managing the symptoms and preventing further nerve damage. This may include medications, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies. Your healthcare provider can help you develop a personalized treatment plan that meets your unique needs and improves your quality of life.
Conclusion
Diabetic autonomic neuropathy is a common complication of diabetes that can significantly impact one’s quality of life. While there is no cure for DAN, there are steps you can take to manage the symptoms and prevent further nerve damage. By maintaining good blood sugar control, exercising regularly, eating a healthy diet, and staying hydrated, you can improve your quality of life and reduce the risk of complications. If you are experiencing symptoms of DAN, it is essential to speak with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets your unique needs. With the right treatment and support, you can manage your symptoms and improve your overall health and well-being.