Diabetic Glucose Levels Managed: Expert Guide
Introduction to Diabetic Glucose Management
For individuals living with diabetes, managing glucose levels is a critical component of maintaining overall health and preventing complications. Diabetes, a chronic condition characterized by the body’s inability to properly regulate blood sugar levels, affects millions of people worldwide. Effective glucose management is key to preventing long-term damage to organs such as the heart, kidneys, and nerves. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the nuances of diabetic glucose management, exploring the latest research, expert recommendations, and practical strategies for achieving optimal blood sugar control.
Understanding Glucose Levels
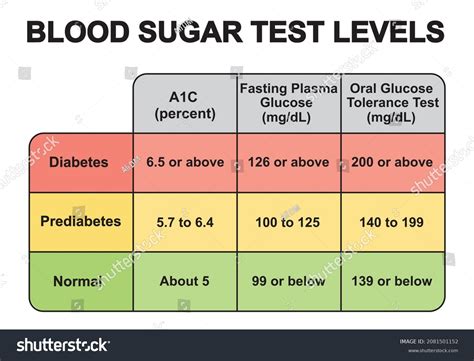
Before diving into management strategies, it’s essential to understand what glucose levels are and how they impact the body. Glucose, a simple sugar, is the primary source of energy for cells. In individuals with diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces (Type 2 diabetes), leading to elevated blood glucose levels. The American Diabetes Association recommends the following glucose level targets for individuals with diabetes:
- Fasting glucose: Less than 130 mg/dL
- Postprandial glucose (1-2 hours after meals): Less than 180 mg/dL
Lifestyle Interventions for Glucose Management
Lifestyle modifications are the cornerstone of diabetic glucose management. These interventions not only help in achieving target glucose levels but also contribute to overall health and well-being.
Dietary Changes
A Diabetes-friendly diet focuses on whole, unprocessed foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Portion control and meal timing are also crucial. Individuals with diabetes should aim to:
- Eat regular, balanced meals to maintain stable glucose levels
- Choose foods with a low glycemic index, which cause a slower and smaller rise in blood glucose
- Monitor carbohydrate intake, as carbs have the greatest impact on blood glucose levels
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, helping the body to more effectively use insulin. It’s recommended to:
- Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week
- Incorporate strength-training activities at least twice a week to build muscle, which helps with glucose uptake
Stress Management and Sleep
Chronic stress and poor sleep quality can negatively affect glucose control. Practicing stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help. Additionally, aiming for 7-8 hours of sleep per night is essential for glucose regulation and overall health.
Monitoring and Medications
In addition to lifestyle changes, monitoring glucose levels and, when necessary, using medications are vital components of diabetes management.
Blood Glucose Monitoring
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels helps individuals understand how different factors (such as food, exercise, and stress) affect their glucose levels. This information can be used to make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.
Medications and Insulin Therapy
For many individuals with diabetes, medication or insulin therapy is necessary to achieve target glucose levels. There are various types of diabetes medications, each working in a different way to lower blood glucose. Insulin therapy, which involves injecting insulin into the body, may be prescribed for individuals with Type 1 diabetes and some with Type 2 diabetes.
Advanced Strategies for Glucose Control
Beyond the basics, several advanced strategies can help individuals achieve tighter glucose control, including:
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems: These devices provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day, offering insights into glucose trends and patterns.
- Insulin Pumps and Automated Insulin Delivery Systems: These technologies can provide more precise insulin dosing and are especially useful for individuals requiring multiple daily injections.
- Smart glucometers and Mobile Apps: Digital tools can facilitate glucose tracking, provide reminders, and offer personalized advice based on glucose data.
Complications and Prevention
Effective glucose management is crucial for preventing the complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision problems. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers, along with ongoing education and support, are critical for managing diabetes and reducing the risk of these complications.
Future Trends in Diabetic Care
The landscape of diabetic care is evolving, with ongoing research into new medications, technologies, and therapeutic approaches. Emerging trends include:
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatment plans to the individual’s genetic profile, medical history, and lifestyle.
- Artificial Intelligence in Diabetes Management: Using AI to analyze glucose data, predict blood glucose levels, and provide personalized recommendations.
- Stem Cell Therapies and Regenerative Medicine: Exploring the potential of these fields to repair or replace damaged pancreatic cells.
Conclusion
Diabetic glucose management is a multifaceted and dynamic process that requires a combination of lifestyle modifications, monitoring, and, when necessary, medication or insulin therapy. By understanding the latest research, expert recommendations, and practical strategies, individuals with diabetes can achieve optimal glucose control, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their overall quality of life. As research and technology continue to advance, there is optimism for even more effective and personalized approaches to managing diabetes in the future.
What are the primary goals of diabetic glucose management?
+The primary goals are to achieve and maintain target blood glucose levels, prevent complications, and improve the quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
How often should blood glucose be monitored?
+The frequency of monitoring depends on the type of diabetes, treatment plan, and individual needs. Generally, individuals with diabetes should monitor their blood glucose at least 4 times a day, including before meals and at bedtime.
What role does physical activity play in glucose management?
+Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, helping the body to more effectively use insulin and lower blood glucose levels. Regular exercise also contributes to overall health and well-being.
How can individuals with diabetes manage stress and improve glucose control?
+Practicing stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress. Additionally, getting adequate sleep and engaging in regular physical activity are crucial for glucose regulation and overall health.
What are the benefits of using continuous glucose monitoring systems?
+Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems provide real-time glucose readings, offering insights into glucose trends and patterns. This information can be used to make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication, leading to tighter glucose control and reduced risk of complications.